Back
Poster Session C
Imaging
Session: (1228–1266) Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster
1241: Towards a Simplified Fluid-sensitive MRI Protocol in Small Joints of the Hand in Early Arthritis Patients: Reliability Between mDixon and Regular FSE Fat Saturation MRI-sequences
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AB
Anna M.P. Boeren, MD
Erasmus MC
Rotterdam, Netherlands
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Anna M.P. Boeren1, Ellis Niemantsverdriet2, Marloes Verstappen3, Fenne Wouters4, Monique Reijnierse3, J.L. Bloem5 and Annette van der Helm-van Mil6, 1Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Rotterdam, 2LUMC, Leiden, Netherlands, 3Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 4Leiden University Medical Centre (LUMC), Leiden, 5Leiden University Medical Centre (LUMC), Leiden, Netherlands, 6Leiden University Medical Center, Erasmus Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
Background/Purpose: MRI of small joints is, despite its sensitivity in demonstrating inflammation, hardly used in rheumatologic clinical practice. Widespread use is hampered by invasiveness, long scan-time, and consequent high costs, associated with the recommended scan protocol, including contrast-agent enhanced and fluid sensitive-sequences. To improve the feasibility of MRI implementation in clinical practice, we introduce a modified Dixon-(mDixon)-sequence, which does not require contrast-agents and reduces total acquisition-time to 6-minutes. Because the reliability in relation to conventional MRI-sequences is unknown, we determined this.
Methods: Prior to our conventional MRI protocol, including Gd-chelate enhanced T1 sequences, a coronal and axial T2 weighted mDixon acquisition, of metacarpophalangeal-2-5 and wrist-joints were made of 29 early arthritis patients. Two readers scored osteitis, synovitis and tenosynovitis (summed as total MRI-inflammation), and erosions (all summed as total RAMRIS). Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) between readers, and comparing the two sequences, were studied. Spearman correlations were determined.
Results: Performance between readers was good/excellent. Comparing mDixon- and conventional sequences revealed good/excellent reliability: ICC for total MRI-inflammation score was 0.84 (95%CI:0.69-0.82), for erosions 0.88 (95%CI:0.69-0.95), and for the total RAMRIS score 0.87 (95%CI:0.74-0.94). The scores of total MRI-inflammation, erosions and total RAMRIS were highly correlated (ρ=0.80, ρ=0.81, ρ=0.82, respectively).
Conclusion: mDixon-MRI providing fluid sensitive and in-phase images in two planes is reliable compared to the conventional extensive MRI protocol, suggesting it is accurate to detect joint-inflammation. The good correlation suggests this can be the first step towards a patient-friendly, short and affordable MRI-protocol, which can facilitate implementation of MRI for early detection of joint inflammation in rheumatology practice.
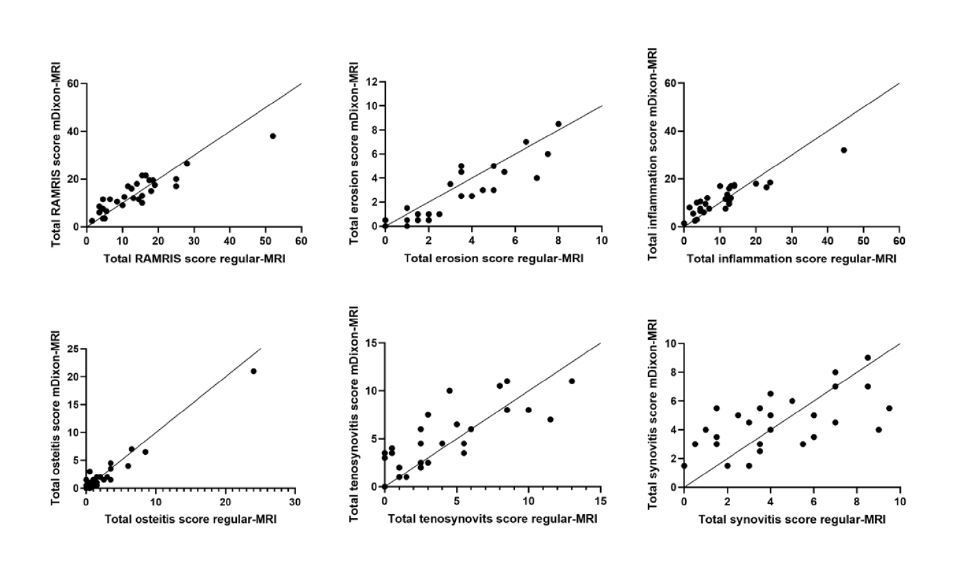 Figure 1: Correlation plots
Figure 1: Correlation plots
Legend: Spearman correlation coefficients for total RAMRIS (ρ=0.82), erosions (ρ=0.81), total inflammation score (ρ=0.80), osteitis (ρ=0.95), tenosynovitis ρ=0.64), and synovitis (ρ=0.36).
Disclosures: A. Boeren, None; E. Niemantsverdriet, None; M. Verstappen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS); F. Wouters, None; M. Reijnierse, ASAS, International Skeletal Society; J. Bloem, None; A. van der Helm-van Mil, None.
Background/Purpose: MRI of small joints is, despite its sensitivity in demonstrating inflammation, hardly used in rheumatologic clinical practice. Widespread use is hampered by invasiveness, long scan-time, and consequent high costs, associated with the recommended scan protocol, including contrast-agent enhanced and fluid sensitive-sequences. To improve the feasibility of MRI implementation in clinical practice, we introduce a modified Dixon-(mDixon)-sequence, which does not require contrast-agents and reduces total acquisition-time to 6-minutes. Because the reliability in relation to conventional MRI-sequences is unknown, we determined this.
Methods: Prior to our conventional MRI protocol, including Gd-chelate enhanced T1 sequences, a coronal and axial T2 weighted mDixon acquisition, of metacarpophalangeal-2-5 and wrist-joints were made of 29 early arthritis patients. Two readers scored osteitis, synovitis and tenosynovitis (summed as total MRI-inflammation), and erosions (all summed as total RAMRIS). Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) between readers, and comparing the two sequences, were studied. Spearman correlations were determined.
Results: Performance between readers was good/excellent. Comparing mDixon- and conventional sequences revealed good/excellent reliability: ICC for total MRI-inflammation score was 0.84 (95%CI:0.69-0.82), for erosions 0.88 (95%CI:0.69-0.95), and for the total RAMRIS score 0.87 (95%CI:0.74-0.94). The scores of total MRI-inflammation, erosions and total RAMRIS were highly correlated (ρ=0.80, ρ=0.81, ρ=0.82, respectively).
Conclusion: mDixon-MRI providing fluid sensitive and in-phase images in two planes is reliable compared to the conventional extensive MRI protocol, suggesting it is accurate to detect joint-inflammation. The good correlation suggests this can be the first step towards a patient-friendly, short and affordable MRI-protocol, which can facilitate implementation of MRI for early detection of joint inflammation in rheumatology practice.
 Figure 1: Correlation plots
Figure 1: Correlation plotsLegend: Spearman correlation coefficients for total RAMRIS (ρ=0.82), erosions (ρ=0.81), total inflammation score (ρ=0.80), osteitis (ρ=0.95), tenosynovitis ρ=0.64), and synovitis (ρ=0.36).
Disclosures: A. Boeren, None; E. Niemantsverdriet, None; M. Verstappen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS); F. Wouters, None; M. Reijnierse, ASAS, International Skeletal Society; J. Bloem, None; A. van der Helm-van Mil, None.

