Back
Poster Session A
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (0403–0431) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: AxSpA
0421: Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis by Prior bDMARD Treatment: Analysis of a Phase 3 Trial
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
.png)
Atul Deodhar, MD
Professor of Medicine, Division of Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases, School of Medicine
Oregon Health & Science University
Portland, OR, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Atul Deodhar1, Helena Marzo-Ortega2, Joseph Wu3, Cunshan Wang3, Oluwaseyi Dina4, Keith S Kanik3, Lara Fallon5 and Lianne Gensler6, 1Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA, Portland, OR, 2Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust and University of Leeds, Leeds, United Kingdom, 3Pfizer Inc, Groton, CT, 4Pfizer Inc, New York, NY, 5Pfizer Inc, Montréal, QC, Canada, 6Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Background/Purpose: Prior exposure to biologic (b)DMARD therapy of patients (pts) with AS may influence treatment response.1-3 Tofacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor for the treatment of AS. The impact of prior treatment on tofacitinib efficacy and safety in pts with AS was evaluated.
Methods: Data from a placebo (PBO)-controlled, double‑blind study of pts with active AS (NCT03502616)4 were analyzed. Pts received tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) or PBO for 16 weeks; after Week (W)16, all pts received open-label tofacitinib 5 mg BID to W48 and were analyzed by prior treatment subgroup: bDMARD‑naïve and TNF inhibitor (TNFi)‑inadequate responders (IR), including bDMARD‑experienced (non‑IR). Efficacy and pt-reported outcomes assessed to W16 (PBO controlled) and W48 (open label): Assessment in SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS)20/40 and LS mean change from baseline (Δ) in AS‑Disease Activity Score-CRP (ASDAS-CRP), high-sensitivity (hs)CRP (mg/dL), BASFI, BASMI, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), Short Form‑36 Physical Component Summary (SF-36v2 PCS), AS Quality of Life (ASQoL), total back pain, pt global assessment (PtGA), and morning stiffness. Assessment of ASAS20/40 at W16 was pre‑specified; all other analyses were post hoc. Safety assessed throughout.
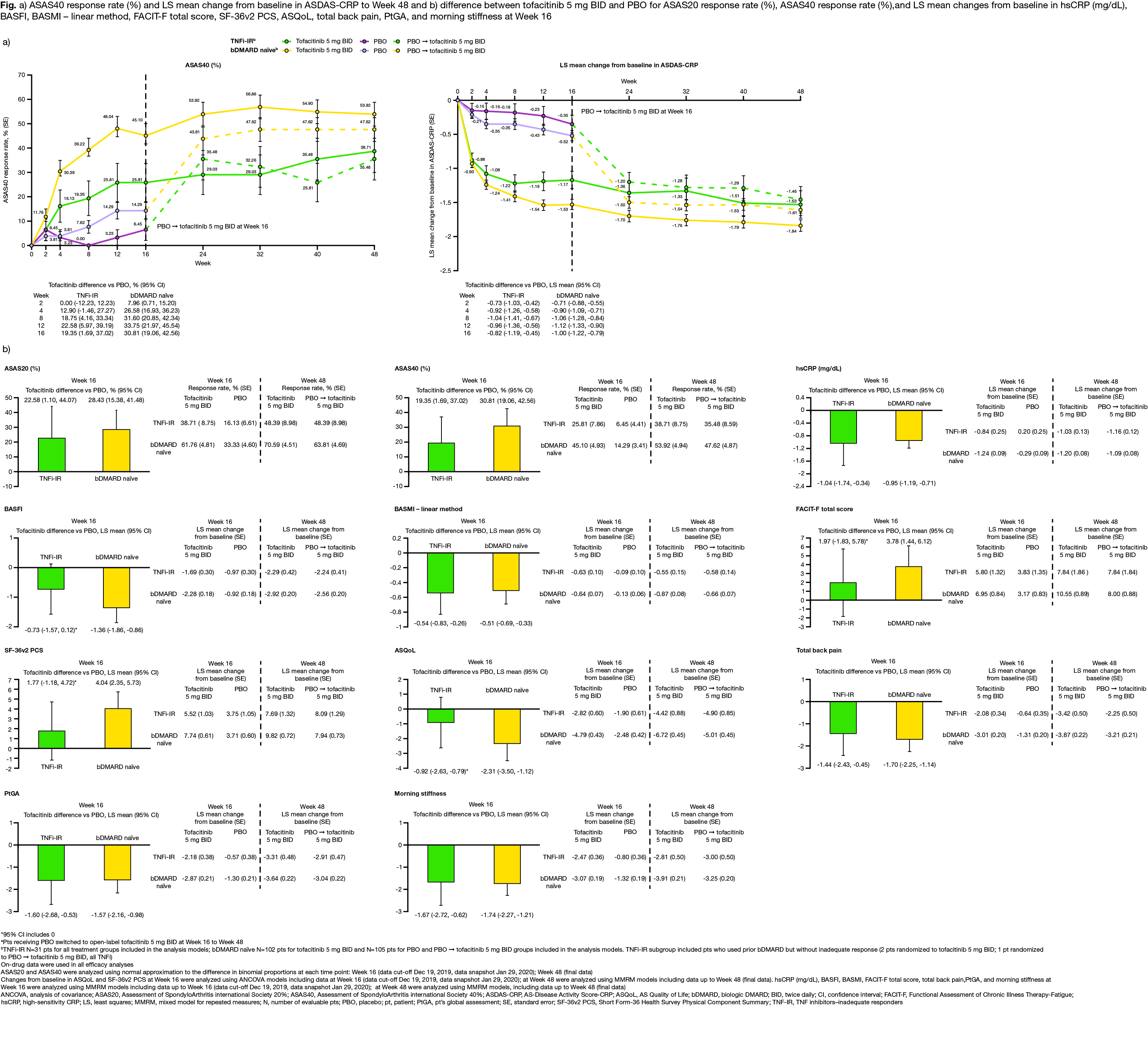
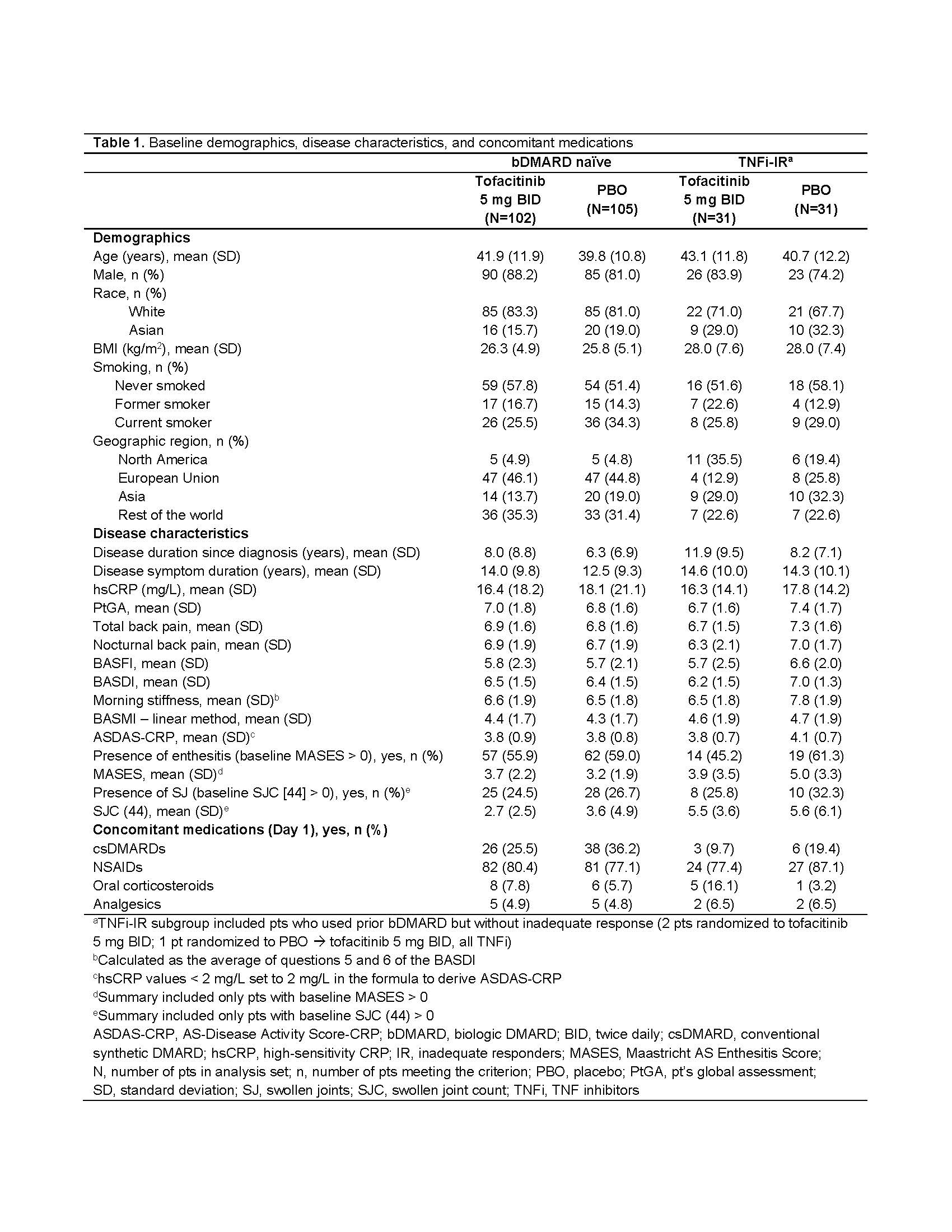
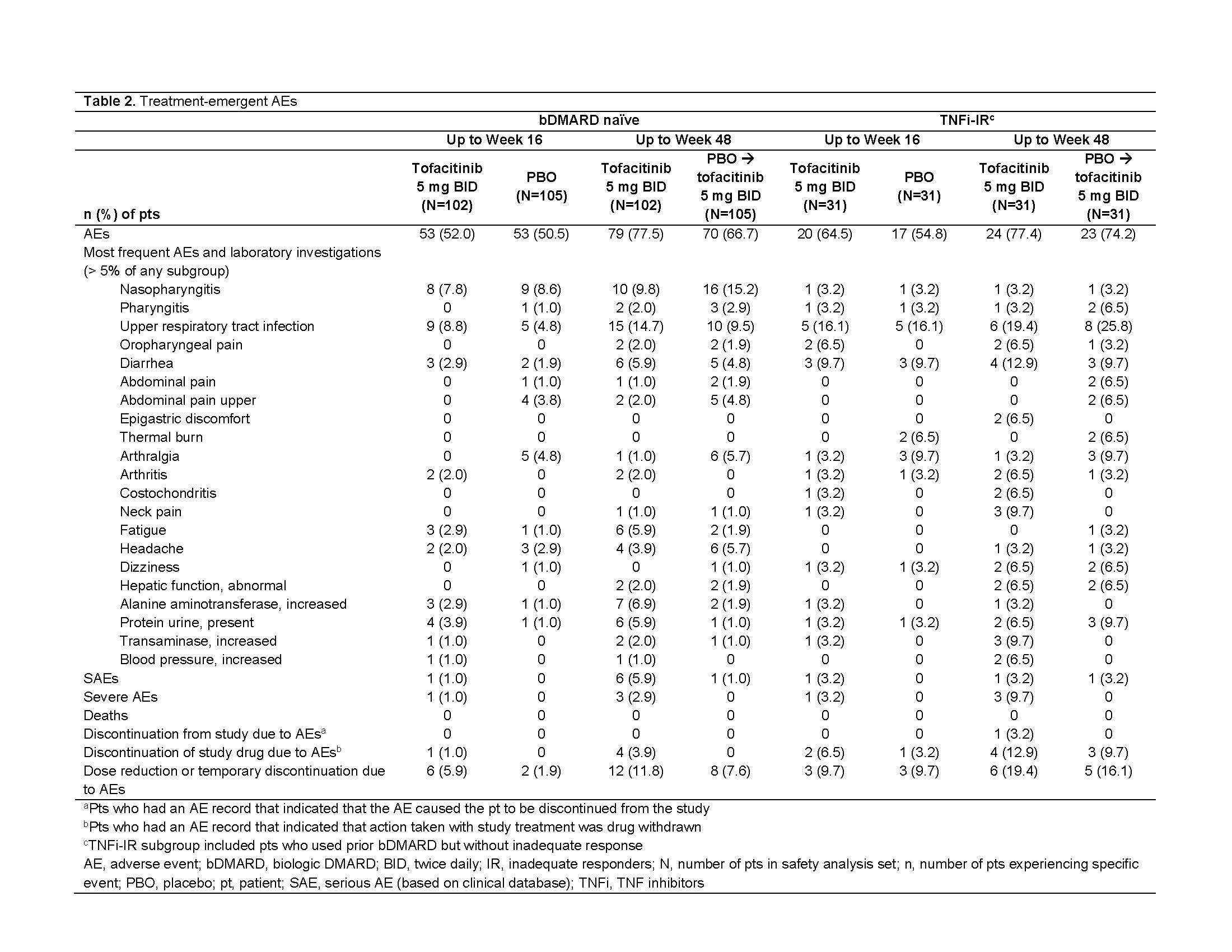
Results: This analysis included 269 randomized and treated pts: 207 (77%) bDMARD‑naïve and 62 (23%) TNFi-IR (incl. 3 bDMARD-experienced [non‑IR] pts, all TNFi). At baseline, TNFi‑IR had higher BMI, longer disease duration, and lower rates of conventional synthetic DMARD use vs bDMARD‑naïve pts; a greater % of TNFi-IR were from North America/Asia vs European Union/rest of world (Table 1). In TNFi-IR pts, baseline disease activity differed between treatment groups. At W16, for ASAS40 response and ΔASDAS-CRP, tofacitinib 5 mg BID efficacy was greater than PBO for bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR pts; efficacy was sustained up to W48 (Fig a). At W16, difference from PBO (95% CI) for tofacitinib 5 mg BID was similar for bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR pts across endpoints including ASAS20/40 response, Δ in hsCRP, BASFI, BASMI, FACIT‑F, SF‑36v2 PCS, ASQoL, total back pain, PtGA, and morning stiffness (Fig b). The % of pts with adverse events (AEs) was similar for TNFi‑IR vs bDMARD‑naïve pts for tofacitinib and PBO; no deaths were reported. The % of pts who discontinued or dose reduced/temporarily discontinued tofacitinib due to AE was numerically higher for TNFi‑IR vs bDMARD-naïve pts for tofacitinib and PBO (Table 2).
Conclusion: Tofacitinib efficacy was greater vs PBO at W16 for bDMARD‑naïve and TNFi-IR pts, with differences from PBO generally consistent between both groups and sustained up to W48. More TNFi-IR pts experienced discontinuations, dose reduction, or temporary discontinuation due to AE vs bDMARD-naïve pts. This analysis was limited by the small sample size overall and differences in sample size between subgroups.
1. Dougados et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79: 176-85
2. Deodhar et al. Arthritis Rheum 2019; 71: 599-611
3. Navarro-Compán et al. RMD Open 2017; 3: e000524
4. Deodhar et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80: 1004-13
Study sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support provided by L Rodgers, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer.
Disclosures: A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, Aurinia, Moonlake; H. Marzo-Ortega, None; J. Wu, Pfizer; C. Wang, Pfizer Inc; O. Dina, Pfizer; K. Kanik, Pfizer; L. Fallon, Pfizer Inc; L. Gensler, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Moonlake.
Background/Purpose: Prior exposure to biologic (b)DMARD therapy of patients (pts) with AS may influence treatment response.1-3 Tofacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor for the treatment of AS. The impact of prior treatment on tofacitinib efficacy and safety in pts with AS was evaluated.
Methods: Data from a placebo (PBO)-controlled, double‑blind study of pts with active AS (NCT03502616)4 were analyzed. Pts received tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) or PBO for 16 weeks; after Week (W)16, all pts received open-label tofacitinib 5 mg BID to W48 and were analyzed by prior treatment subgroup: bDMARD‑naïve and TNF inhibitor (TNFi)‑inadequate responders (IR), including bDMARD‑experienced (non‑IR). Efficacy and pt-reported outcomes assessed to W16 (PBO controlled) and W48 (open label): Assessment in SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS)20/40 and LS mean change from baseline (Δ) in AS‑Disease Activity Score-CRP (ASDAS-CRP), high-sensitivity (hs)CRP (mg/dL), BASFI, BASMI, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), Short Form‑36 Physical Component Summary (SF-36v2 PCS), AS Quality of Life (ASQoL), total back pain, pt global assessment (PtGA), and morning stiffness. Assessment of ASAS20/40 at W16 was pre‑specified; all other analyses were post hoc. Safety assessed throughout.
Results: This analysis included 269 randomized and treated pts: 207 (77%) bDMARD‑naïve and 62 (23%) TNFi-IR (incl. 3 bDMARD-experienced [non‑IR] pts, all TNFi). At baseline, TNFi‑IR had higher BMI, longer disease duration, and lower rates of conventional synthetic DMARD use vs bDMARD‑naïve pts; a greater % of TNFi-IR were from North America/Asia vs European Union/rest of world (Table 1). In TNFi-IR pts, baseline disease activity differed between treatment groups. At W16, for ASAS40 response and ΔASDAS-CRP, tofacitinib 5 mg BID efficacy was greater than PBO for bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR pts; efficacy was sustained up to W48 (Fig a). At W16, difference from PBO (95% CI) for tofacitinib 5 mg BID was similar for bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR pts across endpoints including ASAS20/40 response, Δ in hsCRP, BASFI, BASMI, FACIT‑F, SF‑36v2 PCS, ASQoL, total back pain, PtGA, and morning stiffness (Fig b). The % of pts with adverse events (AEs) was similar for TNFi‑IR vs bDMARD‑naïve pts for tofacitinib and PBO; no deaths were reported. The % of pts who discontinued or dose reduced/temporarily discontinued tofacitinib due to AE was numerically higher for TNFi‑IR vs bDMARD-naïve pts for tofacitinib and PBO (Table 2).
Conclusion: Tofacitinib efficacy was greater vs PBO at W16 for bDMARD‑naïve and TNFi-IR pts, with differences from PBO generally consistent between both groups and sustained up to W48. More TNFi-IR pts experienced discontinuations, dose reduction, or temporary discontinuation due to AE vs bDMARD-naïve pts. This analysis was limited by the small sample size overall and differences in sample size between subgroups.
1. Dougados et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020; 79: 176-85
2. Deodhar et al. Arthritis Rheum 2019; 71: 599-611
3. Navarro-Compán et al. RMD Open 2017; 3: e000524
4. Deodhar et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80: 1004-13
Study sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support provided by L Rodgers, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer.



Disclosures: A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, Aurinia, Moonlake; H. Marzo-Ortega, None; J. Wu, Pfizer; C. Wang, Pfizer Inc; O. Dina, Pfizer; K. Kanik, Pfizer; L. Fallon, Pfizer Inc; L. Gensler, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Moonlake.

