Back
Poster Session A
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0241–0271) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I
0257: High Density Lipoprotein Bound miR-1246 Is Enriched in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Is Proinflammatory
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- QW
Qiong Wu, PhD
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Franklin, TN, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Qiong Wu, Quanhu Sheng, Danielle Michell, Kasey Vickers and Michelle Ormseth, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN
Background/Purpose: High density lipoprotein (HDL) is known for its anti-atherogenic cholesterol efflux and antioxidant functions. HDL has additional relevance to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) because of its high concentration within the joint and its direct interaction with cells of the immune system and vasculature. Some studies have reported that patients with RA have altered HDL function. A function of HDL which has been unstudied in RA is its ability to transport microRNAs (miRNAs) between cells to alter gene expression and thus cellular function. The purpose of this study was to determine if miRNAs in HDL are altered in RA and if these HDL-miRNAs alter inflammation.
Methods: HDL was purified from 30 patients with RA and 30 control subjects by density gradient centrifugation and fast protein liquid chromatography. Total RNA was extracted from the purified HDL and matched plasma from each patient. Small RNA (sRNA) libraries were constructed and next generation sequencing (NGS) was performed. The TIGER pipeline was used to quantify miRNAs. miRNAs were compared between RA and control subjects by DESeq2 using 5% false discovery rate and multiple comparison adjustment by Benjamini-Hochberg method. Significantly altered miRNAs and miRNAs of interest were validated by qPCR. Putative function of miRNAs of interest was assessed by transfecting miRNA mimics, scramble control or no RNA controls into PMA-treated THP-1 cells (human monocyte-derived macrophages) stimulated with/without LPS and performing RNAseq. The function of miRNA targets was assessed by siRNA knockdown. Luciferase assay was performed to confirm targets.
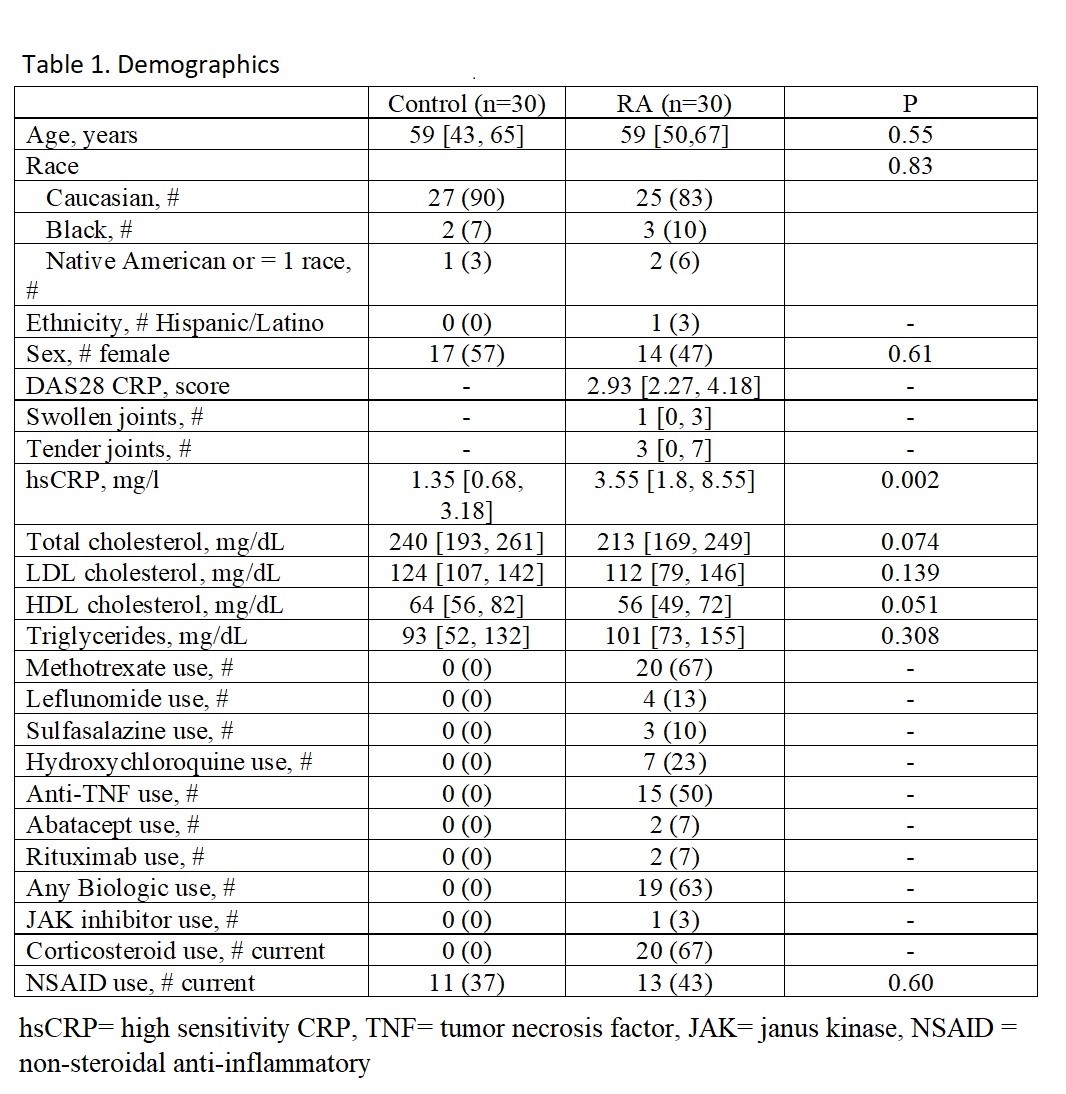
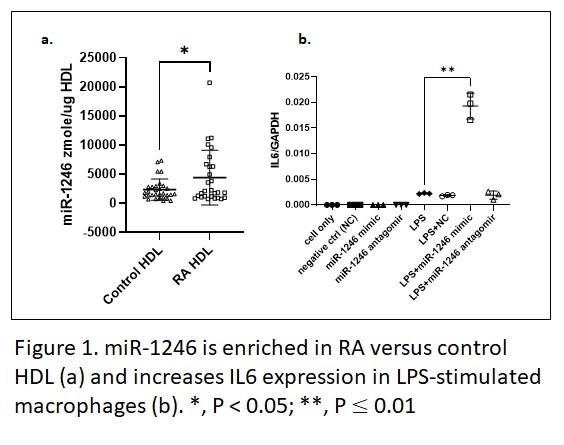
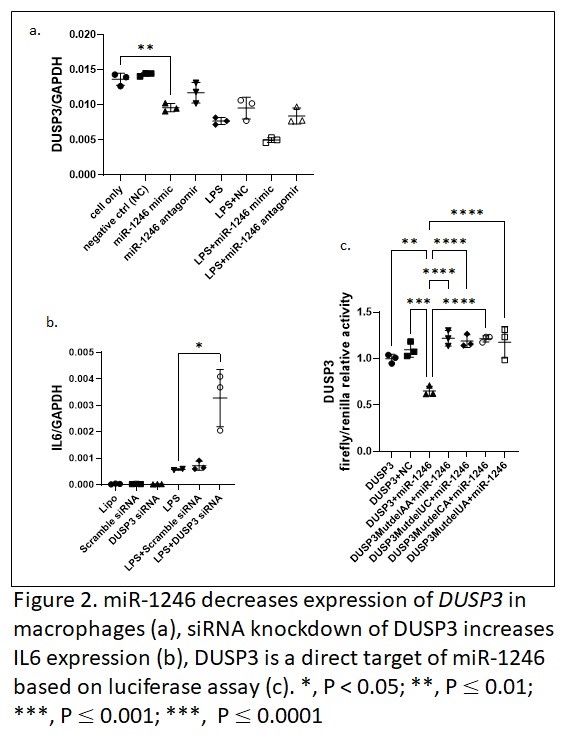
Results: Patient demographics are presented in Table 1. Based on sRNA NGS and qPCR validation, miR-1246 was the most abundant miRNA and enriched in RA HDL. miR-1246 was more concentrated in HDL versus plasma (NGS base mean = 5781 in HDL versus NGS base mean 212 in plasma), suggesting HDL is the main carrier of miR-1246 in plasma. Further, miR-1246 was 3-fold enriched based on NGS and 1.9-fold enriched based on qPCR in RA versus control HDL (Figure 1a). Transfection of miR-1246 increased IL-6 expression 8-fold (Figure 1b). Based on mRNA NGS and qPCR validation, expression of DUSP3 was reduced significantly in miR-1246 transfected group compared to control group (Figure 2a). DUSP3 siRNA knockdown enhances LPS-induced IL-6 expression (Figure 2b). Luciferase assay indicated DUSP3 is a direct target of miR-1246 (Figure 2c).
Conclusion: HDL-bound miR-1246 is increased in RA versus control subjects. miR-1246 enhances LPS-induced IL-6 expression in human monocyte derived macrophages, likely through direct targeting of DUSP3. Further work will be dedicated to examining HDL delivery of miR-1246 based on disease state and the effect of miR-1246 on the anti/pro-inflammatory function of HDL in RA.
Disclosures: Q. Wu, None; Q. Sheng, None; D. Michell, None; K. Vickers, None; M. Ormseth, None.
Background/Purpose: High density lipoprotein (HDL) is known for its anti-atherogenic cholesterol efflux and antioxidant functions. HDL has additional relevance to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) because of its high concentration within the joint and its direct interaction with cells of the immune system and vasculature. Some studies have reported that patients with RA have altered HDL function. A function of HDL which has been unstudied in RA is its ability to transport microRNAs (miRNAs) between cells to alter gene expression and thus cellular function. The purpose of this study was to determine if miRNAs in HDL are altered in RA and if these HDL-miRNAs alter inflammation.
Methods: HDL was purified from 30 patients with RA and 30 control subjects by density gradient centrifugation and fast protein liquid chromatography. Total RNA was extracted from the purified HDL and matched plasma from each patient. Small RNA (sRNA) libraries were constructed and next generation sequencing (NGS) was performed. The TIGER pipeline was used to quantify miRNAs. miRNAs were compared between RA and control subjects by DESeq2 using 5% false discovery rate and multiple comparison adjustment by Benjamini-Hochberg method. Significantly altered miRNAs and miRNAs of interest were validated by qPCR. Putative function of miRNAs of interest was assessed by transfecting miRNA mimics, scramble control or no RNA controls into PMA-treated THP-1 cells (human monocyte-derived macrophages) stimulated with/without LPS and performing RNAseq. The function of miRNA targets was assessed by siRNA knockdown. Luciferase assay was performed to confirm targets.
Results: Patient demographics are presented in Table 1. Based on sRNA NGS and qPCR validation, miR-1246 was the most abundant miRNA and enriched in RA HDL. miR-1246 was more concentrated in HDL versus plasma (NGS base mean = 5781 in HDL versus NGS base mean 212 in plasma), suggesting HDL is the main carrier of miR-1246 in plasma. Further, miR-1246 was 3-fold enriched based on NGS and 1.9-fold enriched based on qPCR in RA versus control HDL (Figure 1a). Transfection of miR-1246 increased IL-6 expression 8-fold (Figure 1b). Based on mRNA NGS and qPCR validation, expression of DUSP3 was reduced significantly in miR-1246 transfected group compared to control group (Figure 2a). DUSP3 siRNA knockdown enhances LPS-induced IL-6 expression (Figure 2b). Luciferase assay indicated DUSP3 is a direct target of miR-1246 (Figure 2c).
Conclusion: HDL-bound miR-1246 is increased in RA versus control subjects. miR-1246 enhances LPS-induced IL-6 expression in human monocyte derived macrophages, likely through direct targeting of DUSP3. Further work will be dedicated to examining HDL delivery of miR-1246 based on disease state and the effect of miR-1246 on the anti/pro-inflammatory function of HDL in RA.



Disclosures: Q. Wu, None; Q. Sheng, None; D. Michell, None; K. Vickers, None; M. Ormseth, None.

