Back
Poster Session A
Vasculitis
Session: (0458–0497) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated and Related Disorders Poster I: Giant Cell Arteritis
0491: Markers of Neutrophil Activation in Patients with ANCA-associated Vasculitis and Large-vessel Vasculitis
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- DM
Despoina Michailidou, MD
University of Washington
Seattle, WA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Despina Michailidou1, Bhargavi Duvvuri1, Runa Kuley1, David Cuthbertson2, Peter Grayson3, Nader Khalidi4, Curry Koening5, Carol Langford6, Carol McAlear7, Larry Moreland8, Christian Pagnoux9, Philip Seo10, Ulrich Specks11, Antoine Sreih7, Kenneth J. Warrington11, Tomas Mustelin1, Paul Monach12, Peter Merkel13 and Christian Lood1, 1Division of Rheumatology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 2University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, 3National Institutes of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, 4Division of Rheumatology, Mc Master University, Ontario, Canada, Ontario, Canada, 5Division of Rheumatology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, Salt Lake City, UT, 6Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, 7Division of Rheumatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA, Philadelphia, PA, 8University of Colorado, Denver, CO, 9Division of Rheumatology, Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada, 10Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, 11Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 12VA Boston Healthcare System, Boston, MA, 13University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Background/Purpose: Neutrophils contribute to the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases. The purpose of the study was to assess two markers of neutrophil activation, calprotectin and N-formyl methionine (fMET), in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) and large-vessel vasculitis (LVV). As fMET induces via its highly expressed G-protein coupled receptor, formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) neutrophil chemotaxis, degranulation, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, we sought to determine whether fMET/FPR1-mediated signaling can drive neutrophil activation in patients with vascultis.
Methods: Levels of fMET and calprotectin were measured by ELISA in the plasma of healthy controls (n=30) and patients with AAV (granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA, n=123), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA, n=61)), and LVV (Takayasu's arteritis (TAK, n=58), giant cell arteritis (GCA, n=68)), at times of remission or flare. Disease activity was assessed by physician global assessment. In vitro neutrophil activation assays, analyzing ROS induction using flow cytometry were performed in the presence or absence of FPR1 inhibitor cyclosporine H.
Results: Levels of calprotectin and fMET were elevated in patients with vasculitis as compared to healthy individuals (Figures 1A and 2A). Levels of fMET correlated with markers of systemic inflammation: C-reactive protein (r=0.82, p< 0.0001) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (r=0.235, p< 0.0001). Calprotectin was not associated with disease activity (Figure 1B). Circulating levels of fMET were associated with neutrophil activation (p< 0.01) (Figure 3) and were able to induce de novo neutrophil activation via FPR1-mediated signaling that was abrogated by the selective FPR1 antagonist cyclosporine H (Figure 2B).
Conclusion:
Circulating fMET appears to propagate neutrophil activation in AAV and LVV. Inhibition of fMET-mediated FPR1 signaling could be a novel therapeutic intervention for systemic vasculitides.
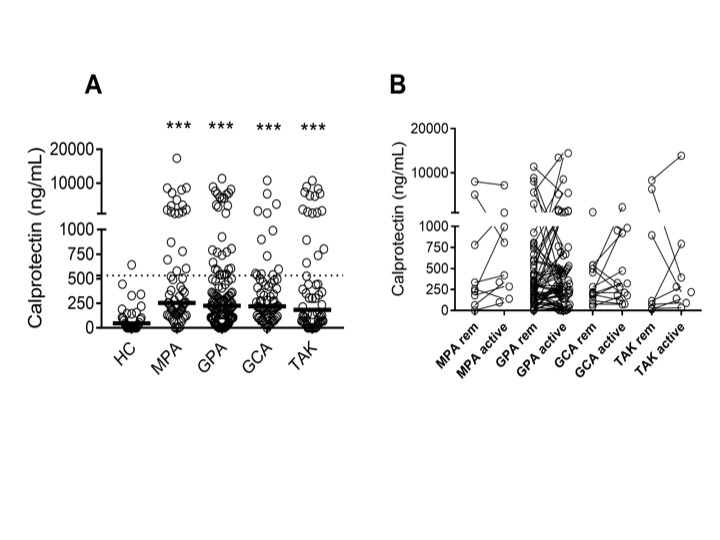 Figure 1. Levels of neutrophil activation marker calprotectin in patients with AAV and LVV. Plasma levels of (A) calprotectin were measured by ELISA in healthy controls (HC), and patients with microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), giant cell arteritis (GCA) and Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) in remission. Plasma levels of (B) calprotectin were related to disease activity in patients in remission (rem) and matching patients with active disease (active) as assessed by physician global assessment (PGA) in MPA, GPA, GCA and TAK. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test, (A), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test (B) with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Unless otherwise indicated, all analyses are compared to healthy controls. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group. The dotted line represents the 95th percentile of the HC.
Figure 1. Levels of neutrophil activation marker calprotectin in patients with AAV and LVV. Plasma levels of (A) calprotectin were measured by ELISA in healthy controls (HC), and patients with microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), giant cell arteritis (GCA) and Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) in remission. Plasma levels of (B) calprotectin were related to disease activity in patients in remission (rem) and matching patients with active disease (active) as assessed by physician global assessment (PGA) in MPA, GPA, GCA and TAK. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test, (A), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test (B) with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Unless otherwise indicated, all analyses are compared to healthy controls. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group. The dotted line represents the 95th percentile of the HC.
 Figure 2. Levels of N formyl methionine peptides (fMET) and activation of neutrophils via its receptor formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) in patients with AAV and LVV. Levels of (A) fMET were analyzed by ELISA in healthy controls (HC,) and patients with MPA, GPA, GCA, and TAK in remission. Neutrophils from a healthy donor (B) were incubated with plasma from HC or patients with vasculitis (Vasc) in presence or absence of Cyclosporine H (CsH) that is a selective FPR1 inhibitor and analyzed for reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction using flow cytometry.
Figure 2. Levels of N formyl methionine peptides (fMET) and activation of neutrophils via its receptor formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) in patients with AAV and LVV. Levels of (A) fMET were analyzed by ELISA in healthy controls (HC,) and patients with MPA, GPA, GCA, and TAK in remission. Neutrophils from a healthy donor (B) were incubated with plasma from HC or patients with vasculitis (Vasc) in presence or absence of Cyclosporine H (CsH) that is a selective FPR1 inhibitor and analyzed for reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction using flow cytometry.
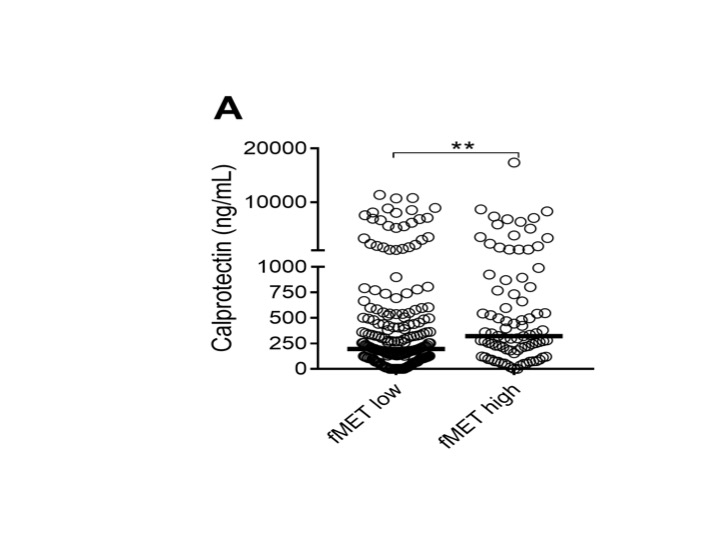 Figure 3. fMET-mediated release of calprotectin. Comparison of plasma levels of calprotectin in patients with either high or low levels of fMET, as determined by the 95th percentile of HC. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test (A), with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group.
Figure 3. fMET-mediated release of calprotectin. Comparison of plasma levels of calprotectin in patients with either high or low levels of fMET, as determined by the 95th percentile of HC. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test (A), with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group.
Disclosures: D. Michailidou, Chemocentryx, Pfizer US Pharmaceuticals Group; B. Duvvuri, None; R. Kuley, None; D. Cuthbertson, None; P. Grayson, None; N. Khalidi, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, Katsuka, Otsuka, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Sanofi; C. Koening, None; C. Langford, None; C. McAlear, None; L. Moreland, None; C. Pagnoux, otsuka, AstraZeneca, Pfizer; P. Seo, None; U. Specks, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Genentech, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, ChemoCentryx; A. Sreih, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca; K. Warrington, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Kiniksa, Chemocentryx; T. Mustelin, None; P. Monach, Chemocentryx, Kiniksa, BMS/Celgene, Gilead; P. Merkel, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boeringher-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, ChemoCentryx, Forbius, Genentech/Roche, Genzyme/Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, InflaRx, Neutrolis, Takeda, CSL Behring, Dynacure, EMDSerono, Immagene, Jannsen, Kiniksa, Magenta, Novartis, Pfizer, Q32, Regeneron, Sparrow, Eicos, Electra, Kyverna, UpToDate; C. Lood, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Redd Pharma, Horizon Diagnostic, Exagen Diagnostic.
Background/Purpose: Neutrophils contribute to the pathogenesis of many autoimmune diseases. The purpose of the study was to assess two markers of neutrophil activation, calprotectin and N-formyl methionine (fMET), in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis (AAV) and large-vessel vasculitis (LVV). As fMET induces via its highly expressed G-protein coupled receptor, formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) neutrophil chemotaxis, degranulation, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, we sought to determine whether fMET/FPR1-mediated signaling can drive neutrophil activation in patients with vascultis.
Methods: Levels of fMET and calprotectin were measured by ELISA in the plasma of healthy controls (n=30) and patients with AAV (granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA, n=123), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA, n=61)), and LVV (Takayasu's arteritis (TAK, n=58), giant cell arteritis (GCA, n=68)), at times of remission or flare. Disease activity was assessed by physician global assessment. In vitro neutrophil activation assays, analyzing ROS induction using flow cytometry were performed in the presence or absence of FPR1 inhibitor cyclosporine H.
Results: Levels of calprotectin and fMET were elevated in patients with vasculitis as compared to healthy individuals (Figures 1A and 2A). Levels of fMET correlated with markers of systemic inflammation: C-reactive protein (r=0.82, p< 0.0001) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (r=0.235, p< 0.0001). Calprotectin was not associated with disease activity (Figure 1B). Circulating levels of fMET were associated with neutrophil activation (p< 0.01) (Figure 3) and were able to induce de novo neutrophil activation via FPR1-mediated signaling that was abrogated by the selective FPR1 antagonist cyclosporine H (Figure 2B).
Conclusion:
Circulating fMET appears to propagate neutrophil activation in AAV and LVV. Inhibition of fMET-mediated FPR1 signaling could be a novel therapeutic intervention for systemic vasculitides.
 Figure 1. Levels of neutrophil activation marker calprotectin in patients with AAV and LVV. Plasma levels of (A) calprotectin were measured by ELISA in healthy controls (HC), and patients with microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), giant cell arteritis (GCA) and Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) in remission. Plasma levels of (B) calprotectin were related to disease activity in patients in remission (rem) and matching patients with active disease (active) as assessed by physician global assessment (PGA) in MPA, GPA, GCA and TAK. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test, (A), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test (B) with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Unless otherwise indicated, all analyses are compared to healthy controls. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group. The dotted line represents the 95th percentile of the HC.
Figure 1. Levels of neutrophil activation marker calprotectin in patients with AAV and LVV. Plasma levels of (A) calprotectin were measured by ELISA in healthy controls (HC), and patients with microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), giant cell arteritis (GCA) and Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) in remission. Plasma levels of (B) calprotectin were related to disease activity in patients in remission (rem) and matching patients with active disease (active) as assessed by physician global assessment (PGA) in MPA, GPA, GCA and TAK. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test, (A), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test (B) with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Unless otherwise indicated, all analyses are compared to healthy controls. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group. The dotted line represents the 95th percentile of the HC. Figure 2. Levels of N formyl methionine peptides (fMET) and activation of neutrophils via its receptor formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) in patients with AAV and LVV. Levels of (A) fMET were analyzed by ELISA in healthy controls (HC,) and patients with MPA, GPA, GCA, and TAK in remission. Neutrophils from a healthy donor (B) were incubated with plasma from HC or patients with vasculitis (Vasc) in presence or absence of Cyclosporine H (CsH) that is a selective FPR1 inhibitor and analyzed for reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction using flow cytometry.
Figure 2. Levels of N formyl methionine peptides (fMET) and activation of neutrophils via its receptor formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) in patients with AAV and LVV. Levels of (A) fMET were analyzed by ELISA in healthy controls (HC,) and patients with MPA, GPA, GCA, and TAK in remission. Neutrophils from a healthy donor (B) were incubated with plasma from HC or patients with vasculitis (Vasc) in presence or absence of Cyclosporine H (CsH) that is a selective FPR1 inhibitor and analyzed for reactive oxygen species (ROS) induction using flow cytometry. Figure 3. fMET-mediated release of calprotectin. Comparison of plasma levels of calprotectin in patients with either high or low levels of fMET, as determined by the 95th percentile of HC. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test (A), with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group.
Figure 3. fMET-mediated release of calprotectin. Comparison of plasma levels of calprotectin in patients with either high or low levels of fMET, as determined by the 95th percentile of HC. Statistical analyses were done using Mann-Whitney U test (A), with * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Each circle represents an individual sample, with the bar representing the median of the group.Disclosures: D. Michailidou, Chemocentryx, Pfizer US Pharmaceuticals Group; B. Duvvuri, None; R. Kuley, None; D. Cuthbertson, None; P. Grayson, None; N. Khalidi, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, Katsuka, Otsuka, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Sanofi; C. Koening, None; C. Langford, None; C. McAlear, None; L. Moreland, None; C. Pagnoux, otsuka, AstraZeneca, Pfizer; P. Seo, None; U. Specks, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Genentech, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, ChemoCentryx; A. Sreih, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca; K. Warrington, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Kiniksa, Chemocentryx; T. Mustelin, None; P. Monach, Chemocentryx, Kiniksa, BMS/Celgene, Gilead; P. Merkel, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boeringher-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, ChemoCentryx, Forbius, Genentech/Roche, Genzyme/Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, InflaRx, Neutrolis, Takeda, CSL Behring, Dynacure, EMDSerono, Immagene, Jannsen, Kiniksa, Magenta, Novartis, Pfizer, Q32, Regeneron, Sparrow, Eicos, Electra, Kyverna, UpToDate; C. Lood, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Redd Pharma, Horizon Diagnostic, Exagen Diagnostic.

