Back
Poster Session D
Myopathic rheumatic diseases (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis)
Session: (1856–1887) Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II
1875: Assessment of Antibody Levels to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Receiving Treatment with Intravenous Immunoglobulin
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

Sangmee Bae, MD, MS
UCLA
Los Angeles, CA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Sangmee Bae1, emmanuelle Faure-Kumar1, Jennifer Wang2, Ani Shahbazian2, linh Truong2, Howard Yang2, Maureen McMahon1, John FitzGerald1 and Christina Charles-Schoeman3, 1University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, 2UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 3Division of Rheumatology, University of California, Los Angeles, Santa Monica, CA
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have been reported in pooled donor plasma and intravenous immunoglobulin products (IVIG) since May 2020 (C Romero 2021 PMID 33606999). It is not known whether regular administration of IVIG increases circulating anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies (COVID ab). The current work evaluates COVID ab titers in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) who receive regular treatments with IVIG (IVIG group) compared to a matched control IIM population not receiving IVIG (non-IVIG group).
Methods: Stored plasma samples drawn between March 2021 and February 2022 from a single center longitudinal IIM cohort were analyzed from 25 patients receiving regular IVIG treatment and 20 patients not receiving IVIG with a similar age, sex, and ethnicity distribution. All patients selected had at least 1 COVID mRNA vaccine prior to the blood draw. Pre-vaccination stored samples were also analyzed for 20 and 10 patients in the IVIG and non-IVIG groups respectively (23/30 samples collected pre-pandemic). Antibody testing was performed using a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (AN Gray et al. 2021. PMID 34748607). Univariate and multivariate linear regression analyses were used to evaluate predictors of COVID ab titers. COVID ab titers were log transformed in linear models.
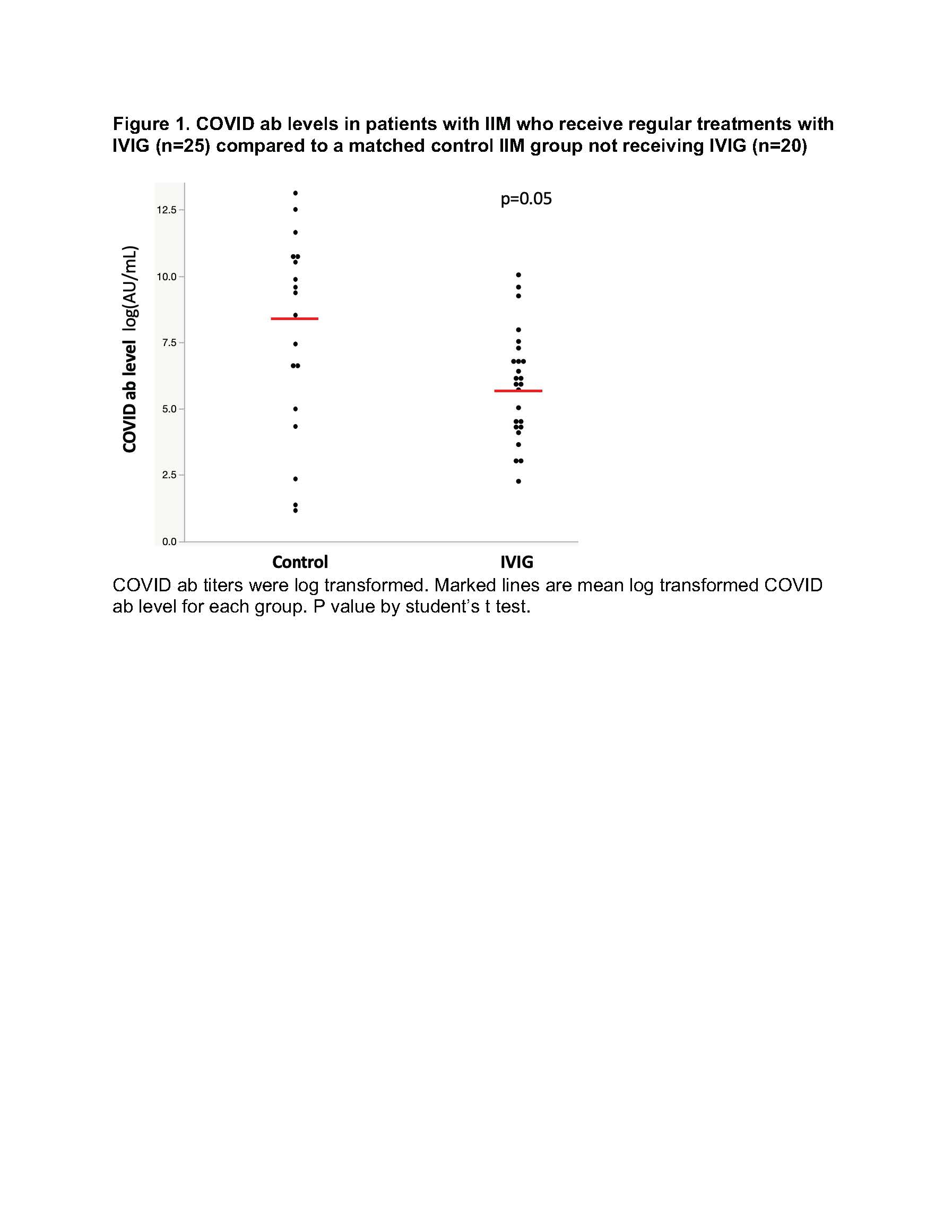
Results: Patients in the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were overall similar in clinical characteristics with the exception of more patients in the IVIG group receiving mycophenolate and less receiving hydroxychloroquine. No significant differences in COVID ab levels were noted between IVIG and non-IVIG groups with a trend for lower COVID ab levels in the IVIG group (Figure 1). In univariate regression analysis of all post vaccination patient samples (IVIG and non-IVIG groups) higher number of vaccine doses was significantly associated with higher COVID ab levels (regression coefficient [95% CI], 2.84[1.10-4.57] log AU/mL, p=0.002). Time duration between last vaccine to specimen collection was not associated with COVID ab levels (regression coefficient [95% CI], 0.003 [-0.01-0.01] log AU/mL, p=0.63). In a multivariate linear regression model evaluating predictors of COVID ab levels, use of IVIG was not a predictor of COVID ab titer after adjusting for other medication differences in bivariate analysis including mycophenolate and hydroxychloroquine.
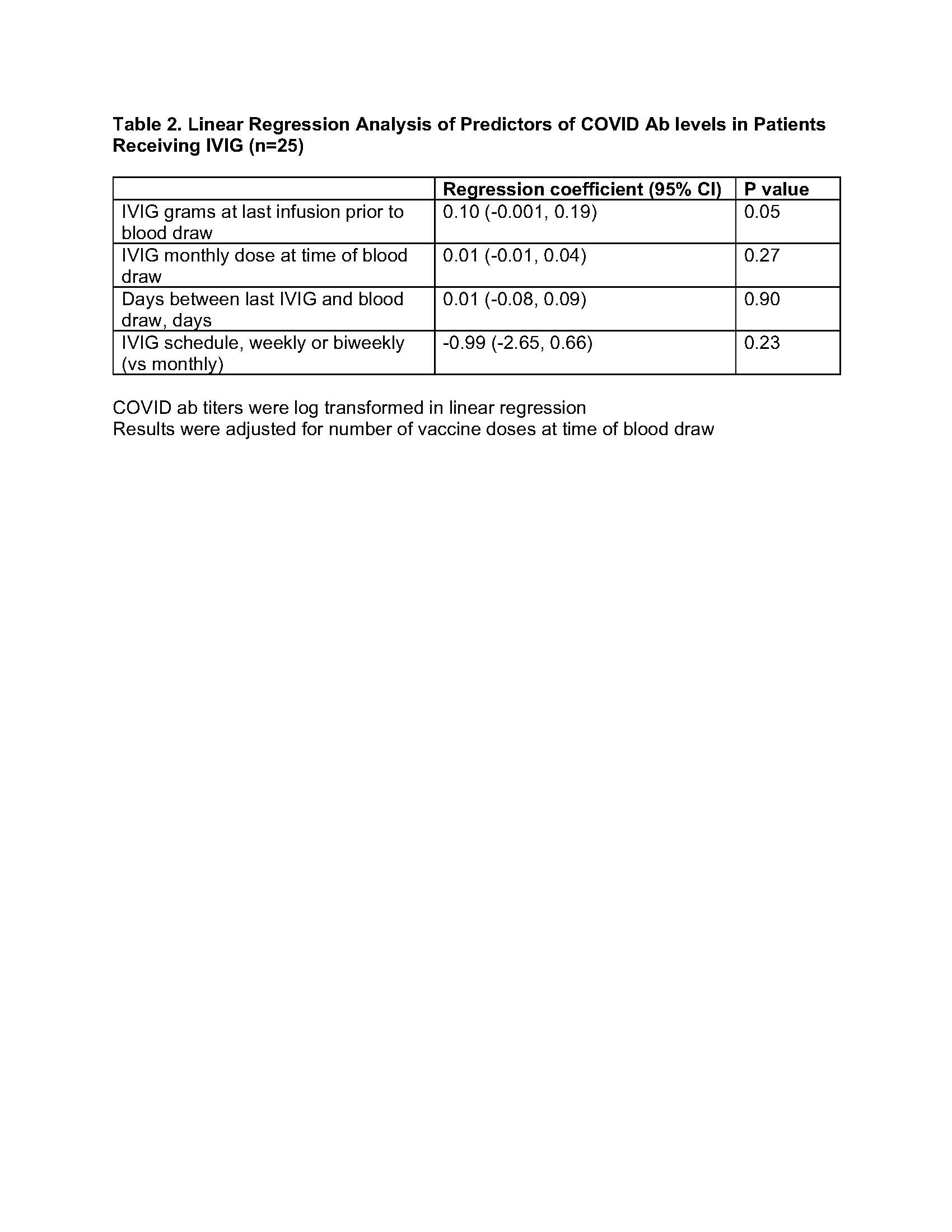
Antibody levels were negative in all pre-vaccination samples including the 7 samples collected after the pandemic onset (March 2020) which included 4 patients receiving IVIG. In multivariate analysis evaluating predictors of COVID ab levels in only IVIG group, COVID ab levels were not associated with time duration between last IVIG and specimen collection, dose of IVIG at last infusion, total monthly dose of IVIG, or schedule of IVIG treatments (weekly or bi-weekly vs monthly) (Table 2).
Conclusion: No significant differences in COVID ab titers were observed between IIM patients receiving regular treatments with IVIG compared to a matched IIM cohort not receiving IVIG.
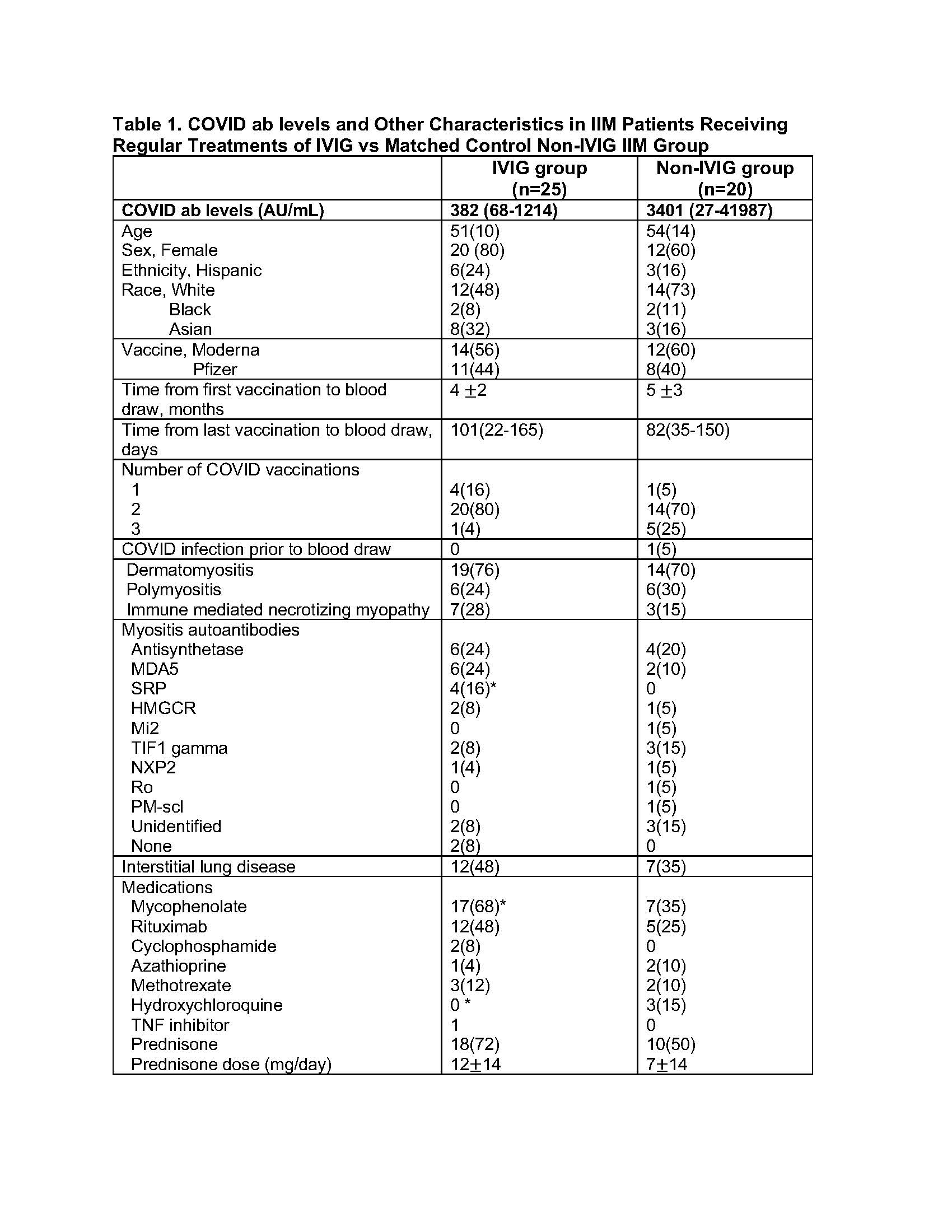 Values are reported as mean SD or n(%) or median (IQR).
Values are reported as mean SD or n(%) or median (IQR).
*p < 0.05 by student’s t-test for normally distributed data (values reported as mean SD), Wilcoxon test for skewed data (values reported as median(IQR)) or chi-square test for count data.
Antibody testing was performed using a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay to detect IgG antibodies against the RBD domain of the Spike protein per the manufacturer’s instructions and previously published protocols (AN Gray et al. 2021. PMID 34748607). Positive anti-Spike IgG titers were defined as equal to or more than 50 arbitrary units per milliliter (AU/mL). Negative titers were < 50 AU/mL.
Disclosures: S. Bae, None; e. Faure-Kumar, None; J. Wang, None; A. Shahbazian, None; l. Truong, None; H. Yang, None; M. McMahon, None; J. FitzGerald, None; C. Charles-Schoeman, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Pfizer, Regeneron-Sanofi, Gilead.
Background/Purpose: Antibodies to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have been reported in pooled donor plasma and intravenous immunoglobulin products (IVIG) since May 2020 (C Romero 2021 PMID 33606999). It is not known whether regular administration of IVIG increases circulating anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies (COVID ab). The current work evaluates COVID ab titers in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) who receive regular treatments with IVIG (IVIG group) compared to a matched control IIM population not receiving IVIG (non-IVIG group).
Methods: Stored plasma samples drawn between March 2021 and February 2022 from a single center longitudinal IIM cohort were analyzed from 25 patients receiving regular IVIG treatment and 20 patients not receiving IVIG with a similar age, sex, and ethnicity distribution. All patients selected had at least 1 COVID mRNA vaccine prior to the blood draw. Pre-vaccination stored samples were also analyzed for 20 and 10 patients in the IVIG and non-IVIG groups respectively (23/30 samples collected pre-pandemic). Antibody testing was performed using a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (AN Gray et al. 2021. PMID 34748607). Univariate and multivariate linear regression analyses were used to evaluate predictors of COVID ab titers. COVID ab titers were log transformed in linear models.
Results: Patients in the IVIG and non-IVIG groups were overall similar in clinical characteristics with the exception of more patients in the IVIG group receiving mycophenolate and less receiving hydroxychloroquine. No significant differences in COVID ab levels were noted between IVIG and non-IVIG groups with a trend for lower COVID ab levels in the IVIG group (Figure 1). In univariate regression analysis of all post vaccination patient samples (IVIG and non-IVIG groups) higher number of vaccine doses was significantly associated with higher COVID ab levels (regression coefficient [95% CI], 2.84[1.10-4.57] log AU/mL, p=0.002). Time duration between last vaccine to specimen collection was not associated with COVID ab levels (regression coefficient [95% CI], 0.003 [-0.01-0.01] log AU/mL, p=0.63). In a multivariate linear regression model evaluating predictors of COVID ab levels, use of IVIG was not a predictor of COVID ab titer after adjusting for other medication differences in bivariate analysis including mycophenolate and hydroxychloroquine.
Antibody levels were negative in all pre-vaccination samples including the 7 samples collected after the pandemic onset (March 2020) which included 4 patients receiving IVIG. In multivariate analysis evaluating predictors of COVID ab levels in only IVIG group, COVID ab levels were not associated with time duration between last IVIG and specimen collection, dose of IVIG at last infusion, total monthly dose of IVIG, or schedule of IVIG treatments (weekly or bi-weekly vs monthly) (Table 2).
Conclusion: No significant differences in COVID ab titers were observed between IIM patients receiving regular treatments with IVIG compared to a matched IIM cohort not receiving IVIG.
 Values are reported as mean SD or n(%) or median (IQR).
Values are reported as mean SD or n(%) or median (IQR). *p < 0.05 by student’s t-test for normally distributed data (values reported as mean SD), Wilcoxon test for skewed data (values reported as median(IQR)) or chi-square test for count data.
Antibody testing was performed using a chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay to detect IgG antibodies against the RBD domain of the Spike protein per the manufacturer’s instructions and previously published protocols (AN Gray et al. 2021. PMID 34748607). Positive anti-Spike IgG titers were defined as equal to or more than 50 arbitrary units per milliliter (AU/mL). Negative titers were < 50 AU/mL.


Disclosures: S. Bae, None; e. Faure-Kumar, None; J. Wang, None; A. Shahbazian, None; l. Truong, None; H. Yang, None; M. McMahon, None; J. FitzGerald, None; C. Charles-Schoeman, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Pfizer, Regeneron-Sanofi, Gilead.

