Abstract Session
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
0544: Bimekizumab Improves Signs and Symptoms, Including Inflammation, in Patients with Active Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: 24-Week Efficacy & Safety from a Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo Controlled Study
.png)
Atul Deodhar, MD
Professor of Medicine, Division of Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases, School of Medicine
Oregon Health & Science University
Portland, OR, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A. In patients (pts) with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS), BKZ has demonstrated sustained efficacy and was well tolerated up to 156 weeks (wks) in a phase 2b study, and up to 24 wks in the phase 3 study BE MOBILE 2.1,2,3 Here we present results on the efficacy and safety of BKZ vs placebo (PBO) in pts with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) up to Wk 24 in the ongoing pivotal phase 3 study, BE MOBILE 1.
Methods: BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704) comprises a 16-wk double-blind, PBO-controlled period and 36-wk maintenance period. Pts were aged ≥18 years (yrs), had BASDAI ≥4 and spinal pain ≥4 at baseline (BL), and sacroiliitis on MRI and/or elevated CRP at screening. Pts were randomized 1:1 BKZ 160 mg Q4W:PBO. From Wk 16, all pts received BKZ 160 mg Q4W. Primary and secondary efficacy endpoints were assessed at Wk 16, and up to Wk 24. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs; MedDRA v19.0) are reported among patients who received ≥1 BKZ dose by preferred term up to Wk 24.
Results: Of 254 randomized pts (BKZ: 128; PBO: 126), 244 (96.1%) completed Wk 16, 240 (94.5%) Wk 24. BL characteristics were comparable between groups: mean age 39.4 yrs, symptom duration 9.0 yrs; 45.7% pts were female, 77.6% HLA-B27+ and 10.6% TNFi-inadequate responders (IR).
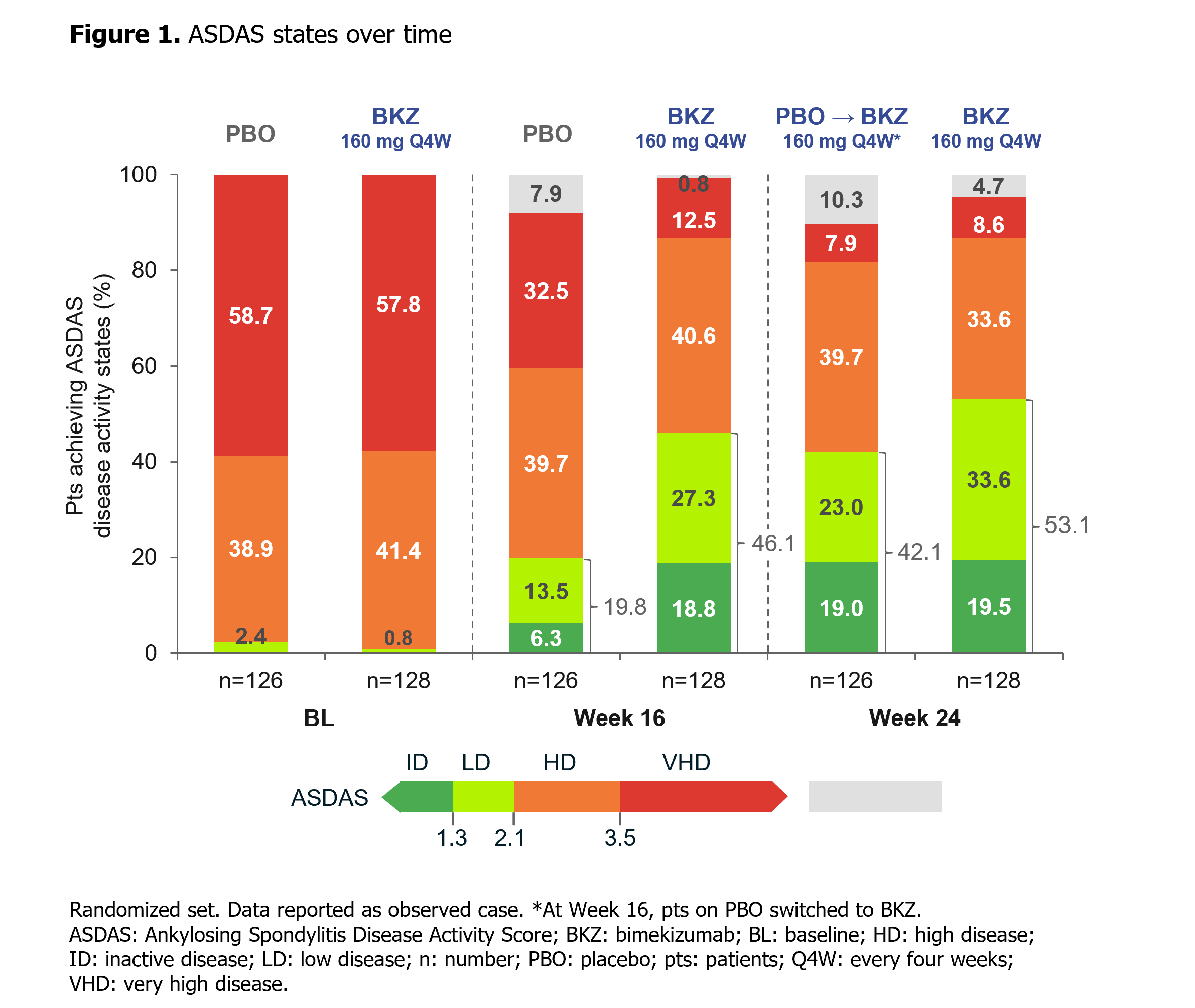
At Wk 16, the primary (ASAS40: 47.7% BKZ vs 21.4% PBO; p< 0.001) and all ranked secondary endpoints were met (Table). ASAS40 responses at Wk 16 were consistent across both TNFi-naïve (46.6% BKZ vs 22.9% PBO) and TNFi-IR (60.0% BKZ vs 11.8% PBO) populations. Responses were rapid with BKZ, including in PBO pts who switched to BKZ at Wk 16, and increased to Wk 24 (Table; Figure 1). At Wk 24, >50% of BKZ-randomized pts achieved ASDAS < 2.1 (Figure 1).
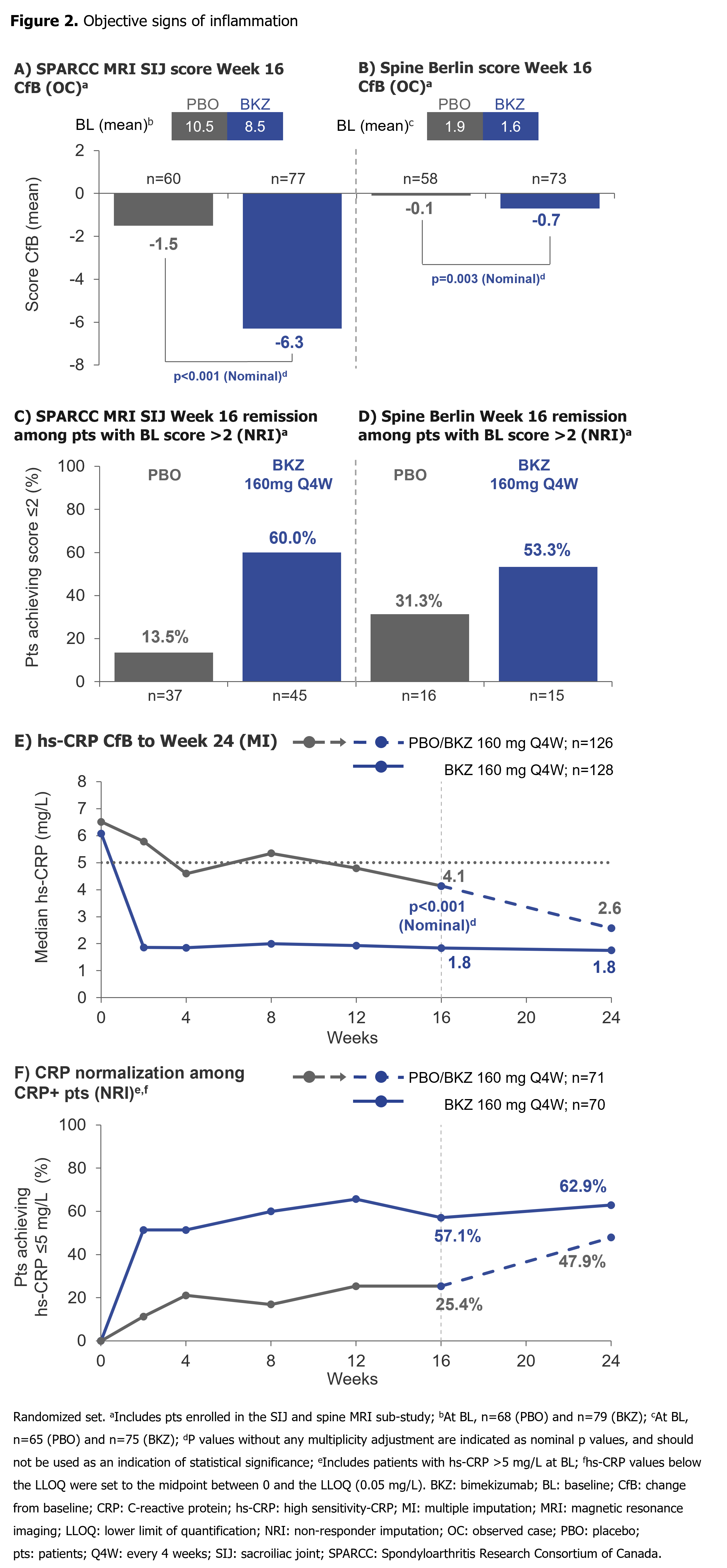
Substantial reductions from BL in SPARCC MRI SIJ inflammation and Berlin MRI Spine scores by Wk 16, and hs-CRP by Wk 2, were achieved with BKZ vs PBO (Figure 2). A higher proportion of pts with SPARCC MRI SIJ and Berlin MRI Spine scores >2 at BL achieved MRI remission (score ≤2) at Wk 16 with BKZ vs PBO. Among CRP+ pts (hs-CRP >5.0 mg/L), a greater proportion treated with BKZ vs PBO achieved normalization (hs-CRP ≤5.0 mg/L) of CRP through Wk 16. For pts who switched from PBO to BKZ at Wk 16, Wk 24 normalization rates approached those seen in BKZ-randomized pts (Figure 2).
Up to Wk 24, 124/244 (50.8%) patients had ≥1 TEAE; most frequent were upper respiratory tract infection (7.0%), nasopharyngitis (6.6%), pharyngitis (2.9%) and oral candidiasis (2.9%). All cases of oral candidiasis were non-severe and non-systemic, and none led to treatment discontinuation. Up to Wk 24, incidence of serious TEAEs was low (0.4%). No IBD, active tuberculosis, MACE or deaths were reported; incidence of uveitis was low (0.8%).
Conclusion: Dual inhibition of IL-17A and IL-17F with BKZ in pts with active nr-axSpA resulted in rapid, clinically relevant improvements in efficacy outcomes vs PBO, including suppression of inflammation. No new safety signals were observed.1,2
References: 1. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:595–604; 2. Gensler L. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021;73(suppl 10):0491. 3. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;OP0019.
.jpeg)
Disclosures: A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, Aurinia, Moonlake; D. van der Heijde, AbbVie, Bayer, BMS, Cyxone, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Imaging Rheumatology bv, Lilly; L. Gensler, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Moonlake; H. Xu, None; K. Gaffney, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, UCB Pharma, Gilead; H. Dobashi, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), Chugai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein (GSK), MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, CARE Arthritis Limited; M. Rudwaleit, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; M. Magrey, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB; D. Elewaut, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Novartis, UCB Pharma; M. Oortgiesen, UCB Pharma; C. Fleurinck, UCB Pharma; N. de Peyrecave, UCB Pharma, GlaxoSmithKlein (GSK); A. Ellis, UCB Pharma; T. Vaux, UCB Pharma; J. Shepherd-Smith, UCB Pharma; X. Baraliakos, AbbVie, Lilly, Galapagos, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi.

