Back
Poster Session B
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0589–0628) RA – Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster
0602: Cellworks Biosimulation Model (CBM) for Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Accurately Captures Patient’s Disease Activity at the Molecular Level Using Their Omics Data and Can Bring Personalization to Treatment Selection in RA
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- HG
Himanshu Grover, MSc
Cellworks Group, Inc.
South San Francisco, CA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Himanshu Grover1, Ansu Kumar1, Anushua Chakraborty1, Susheel George Chandy1, Vivek Patil1, Swati Khandelwal1, Vishwas Joseph1, Deepak Anil Lala1, Prashant Ramachandran Nair1, Karthik Sundara Raju1, Kunal Ghosh Roy1, Shahabuddin Usmani1, Aftab Alam1, Swaminathan Rajagopalan1, Yatin Mundkur1 and Andrew Concoff2, 1Cellworks Group Inc., South San Francisco, CA, 2United Rheumatology, Hauppauge, NY
Background/Purpose: Patients with RA demonstrate varied individual responses to the many treatment options available. In the absence of accurate, precision prediction of medication response, current treatment approaches are based upon trial and error according to formulary-driven ordering of available medications. Accordingly, patients often cycle through multiple medications before finding one that works for them, if at all. Cellworks Biosimulation Model (CBM) captures the complex multi-cell signaling with associated disease phenotypes at the molecular level for each patient using their omics data. CBM can accurately predict a patient's disease activity and can further be used to select their optimal treatment regimen.
Methods: We developed a predictive ODE based mathematical model of 8 cell systems representing cross-talks and interactions among 25,000 molecules, validated using over 4600 published experimental studies and human clinical drug data for RA. Personalized disease models are created by overlaying processed cell type sorted RNA-Seq data for 29 patients from AMP Phase I study. A disease activity score is created using 7 pathobiological phenotypes constituted of over 150 markers from CBM and compared to reported clinical disease measures for each patient. The signaling network responsible for disease phenotypes is dissected by exhaustive knockdown(KD) and overexpression(OE) experiments performed in the model.
Results: CBM Disease Activity Score is well correlated with CDAI, DAS28, SJC and TJC reported from the study (Fig.1). From CBM, reported SJC are found to correlate more with markers associated with invasion, migration and angiogenesis while TJC show higher correlation with secretory pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. From over 5K KD/OE experiments performed in CBM, patients show marked heterogeneity in signaling as well as levels and activation of various cell types. RA-FLS are found to be playing a consistent and crucial role for the majority of patients. 7/29 patients with low dependence on RA-FLS signaling in CBM had significantly lower reported SJC than the rest of cohort. (Fig.2). KD of key signaling molecules such as IL6, TNF, IL1B shows significant reduction in disease phenotypes as expected but the results are not consistent as other molecules such as CSF2, IL23, TNFSF13B are found to be much better targets in certain patients.
Conclusion: CBM accurately captures disease activity and associated molecular signaling from patient's omics data. Higher correlation of reported SJCs with markers of invasion, migration and angiogenesis from CBM indicates role of cellular migration in expanding SJCs while higher correlation of TJCs with inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicates that secretory molecules are drivers of joint pain. Lower SJCs seen in patients with low dominance of RA-FLS in CBM indicates importance of RA-FLS in direct or indirect spreading of disease to unaffected joints. The personalized disease models from CBM show marked heterogeneity in disease signaling, highlighting need for identifying relevant molecular targets that can guide optimal therapy selection for each patient. These results require further validation in a larger patient cohort.
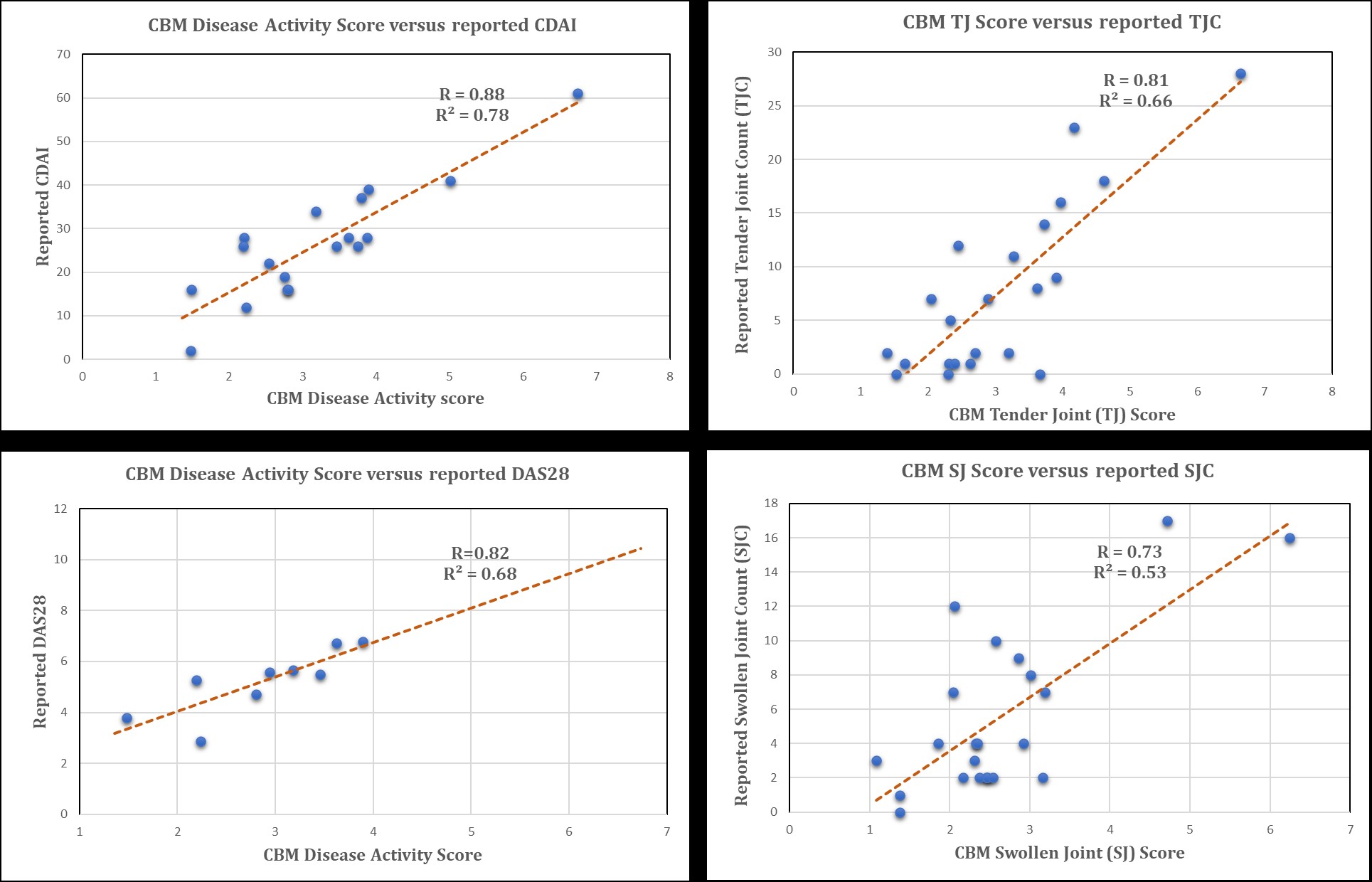 Figure 1. Correlation between CBM Disease Activity scores and Clinical Disease Measures from the AMP phase 1 study.
Figure 1. Correlation between CBM Disease Activity scores and Clinical Disease Measures from the AMP phase 1 study.
CBM correlates well with CDAI, DAS28, SJC and TJC (R=0.88, 0.82, 0.73, 0.81 respectively)
.jpg) Figure 2. Patients with High/Low dependence on RA-FLS from CBM and their reported SJCs from the AMP phase 1 study.
Figure 2. Patients with High/Low dependence on RA-FLS from CBM and their reported SJCs from the AMP phase 1 study.
Disclosures: H. Grover, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Kumar, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Chakraborty, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. George Chandy, Cellworks Group, Inc.; V. Patil, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. Khandelwal, Cellworks Group, Inc.; V. Joseph, Cellworks Group, Inc.; D. Anil Lala, Cellworks Group, Inc.; P. Ramachandran Nair, Cellworks Group, Inc.; K. Sundara Raju, Cellworks Group, Inc.; K. Ghosh Roy, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. Usmani, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Alam, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. Rajagopalan, Cellworks Group, Inc.; Y. Mundkur, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Concoff, Exagen, Pacira Biosciences.
Background/Purpose: Patients with RA demonstrate varied individual responses to the many treatment options available. In the absence of accurate, precision prediction of medication response, current treatment approaches are based upon trial and error according to formulary-driven ordering of available medications. Accordingly, patients often cycle through multiple medications before finding one that works for them, if at all. Cellworks Biosimulation Model (CBM) captures the complex multi-cell signaling with associated disease phenotypes at the molecular level for each patient using their omics data. CBM can accurately predict a patient's disease activity and can further be used to select their optimal treatment regimen.
Methods: We developed a predictive ODE based mathematical model of 8 cell systems representing cross-talks and interactions among 25,000 molecules, validated using over 4600 published experimental studies and human clinical drug data for RA. Personalized disease models are created by overlaying processed cell type sorted RNA-Seq data for 29 patients from AMP Phase I study. A disease activity score is created using 7 pathobiological phenotypes constituted of over 150 markers from CBM and compared to reported clinical disease measures for each patient. The signaling network responsible for disease phenotypes is dissected by exhaustive knockdown(KD) and overexpression(OE) experiments performed in the model.
Results: CBM Disease Activity Score is well correlated with CDAI, DAS28, SJC and TJC reported from the study (Fig.1). From CBM, reported SJC are found to correlate more with markers associated with invasion, migration and angiogenesis while TJC show higher correlation with secretory pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. From over 5K KD/OE experiments performed in CBM, patients show marked heterogeneity in signaling as well as levels and activation of various cell types. RA-FLS are found to be playing a consistent and crucial role for the majority of patients. 7/29 patients with low dependence on RA-FLS signaling in CBM had significantly lower reported SJC than the rest of cohort. (Fig.2). KD of key signaling molecules such as IL6, TNF, IL1B shows significant reduction in disease phenotypes as expected but the results are not consistent as other molecules such as CSF2, IL23, TNFSF13B are found to be much better targets in certain patients.
Conclusion: CBM accurately captures disease activity and associated molecular signaling from patient's omics data. Higher correlation of reported SJCs with markers of invasion, migration and angiogenesis from CBM indicates role of cellular migration in expanding SJCs while higher correlation of TJCs with inflammatory cytokines and chemokines indicates that secretory molecules are drivers of joint pain. Lower SJCs seen in patients with low dominance of RA-FLS in CBM indicates importance of RA-FLS in direct or indirect spreading of disease to unaffected joints. The personalized disease models from CBM show marked heterogeneity in disease signaling, highlighting need for identifying relevant molecular targets that can guide optimal therapy selection for each patient. These results require further validation in a larger patient cohort.
 Figure 1. Correlation between CBM Disease Activity scores and Clinical Disease Measures from the AMP phase 1 study.
Figure 1. Correlation between CBM Disease Activity scores and Clinical Disease Measures from the AMP phase 1 study.CBM correlates well with CDAI, DAS28, SJC and TJC (R=0.88, 0.82, 0.73, 0.81 respectively)
.jpg) Figure 2. Patients with High/Low dependence on RA-FLS from CBM and their reported SJCs from the AMP phase 1 study.
Figure 2. Patients with High/Low dependence on RA-FLS from CBM and their reported SJCs from the AMP phase 1 study.Disclosures: H. Grover, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Kumar, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Chakraborty, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. George Chandy, Cellworks Group, Inc.; V. Patil, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. Khandelwal, Cellworks Group, Inc.; V. Joseph, Cellworks Group, Inc.; D. Anil Lala, Cellworks Group, Inc.; P. Ramachandran Nair, Cellworks Group, Inc.; K. Sundara Raju, Cellworks Group, Inc.; K. Ghosh Roy, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. Usmani, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Alam, Cellworks Group, Inc.; S. Rajagopalan, Cellworks Group, Inc.; Y. Mundkur, Cellworks Group, Inc.; A. Concoff, Exagen, Pacira Biosciences.

