Back
Poster Session B
Reproductive health
Session: (0939–0969) Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders Poster
0940: Effect of an 8-week Tailored Physical Therapy Program on Sexual Function in Women with Systemic Sclerosis and Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: A Pilot Controlled Study
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- BH
Barbora Heřmánková, MS
Institute of Rheumatology, Prague, Czech Republic
Hlavní město Praha, Czech Republic
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Barbora Hermankova1, Maja Spiritovic1, Sabina Oreska2, Hana Storkanova2, Karel Pavelka3, Ladislav Šenolt4, Jiří Vencovský4, Radim Becvar2 and Michal Tomcik2, 1Institute of Rheumatology, Department of Physiotherapy, Faculty of Physical Education and Sport, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic, 2Institute of Rheumatology, Department of Rheumatology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, Prague, Czech Republic, 3Institute of Rheumatology, Department of Rheumatology, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, Praha, Czech Republic, 4Institute of Rheumatology and Department of Rheumatology, First Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic
Background/Purpose: Systemic rheumatic diseases like systemic sclerosis (SSc) and idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) may affect all aspects of life, including sexual health. However, no non-pharmacological treatment has been proposed to date. This is the pilot project aiming to investigate the effect of an 8-week physical therapy program on sexual function in women with SSc and IIM.
Methods: In total, 12 women with SSc and 4 women with IIM, who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria for SSc and the Bohan/Peter 1975 criteria for DM/PM, were enrolled in the study. Based on patient's possibilities and willingness to participate in the program, they were divided into an intervention group (IG) (6 SSc/2 IIM, mean age: 46.8±3.1 years) and a control group (CG) (6 SSc/2 IIM, mean age: 46.3±3.0 years). The IG underwent the 8-week tailored physiotherapy program, including the pelvic floor exercise and physiotherapy of musculoskeletal problems subjectively limiting the patient's sexual function (1 hour supervised physiotherapy twice weekly), whereas the control group received no specialized therapy. At weeks 0 and 8, all patients filled in questionnaires assessing sexual function: Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), Brief Index of Sexual Functioning for Women (BISF-W); sexual quality of life: Sexual Quality of Life-Female (SQoL-F); functional ability: Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ); quality of life: Medical Outcomes Short Form-36 (SF-36) and depression: Beck's Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II). At the baseline, patients in IG were assessed by a physician (medical history, mRSS, ESSG activity score, MITAX, MYOACT) and by a physiotherapist (pelvic floor function assessment–PERFECT scheme, MMT-8, Functional Index-II). Normality of data was tested, and inter-group analysis was performed with 2-way ANOVA and intra-group analysis by Friedmann's test.
Results: Compared to observed statistically significant deterioration in CG over the period of weeks 0-8, we found statistically significant improvement in both sexual function questionnaires: FSFI (p=0.043), BISF-W (p=0.040), functional status: HAQ (p=0.018), and quality of life: SF-36 Physical Somponent score (0.050). Only numerical improvement in IG compared to numerical deterioration in CG, which has not reached statistical significance, was observed in SQoL-F, BDI-II, and SF-36 Mental Component Score.
Conclusion:
Our physiotherapy program not only prevented the natural course of progressive deterioration of functional abilities, but also led to a significant improvement in sexual function and overall quality of life in women with SSc and IIM. Physical therapy might become one of the possible therapeutic treatments for sexual problems in women with SSc and IIM. This pilot study should be validated on larger cohorts, optimally in a randomized manner, which was not applicable in our case, due to the limited number of volunteers who met the criteria.
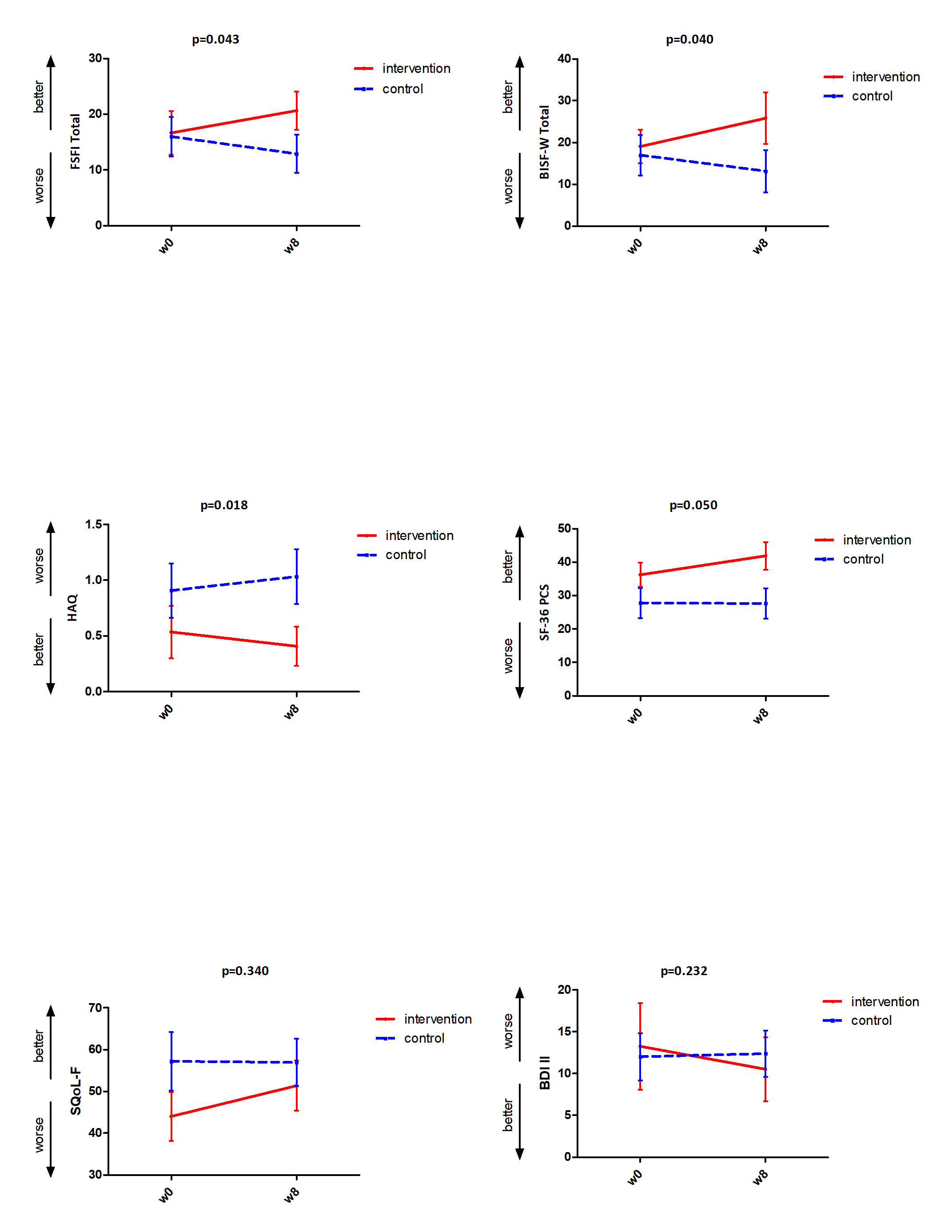 Significant and non-significant changes wchich we observed after 8 week of physical therapy program in the intervention group compared to the control group
Significant and non-significant changes wchich we observed after 8 week of physical therapy program in the intervention group compared to the control group
Disclosures: B. Hermankova, None; M. Spiritovic, None; S. Oreska, None; H. Storkanova, None; K. Pavelka, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Eli Lilly, Medac, UCB, SOBI, Biogen, Sandoz, Viatris; L. Šenolt, None; J. Vencovský, Abbvie, Biogen, Boehringer, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Kezar, Merck, Novartis, Octapharma, Pfizer, Takeda, UCB, Werfen, Argenx; R. Becvar, None; M. Tomcik, None.
Background/Purpose: Systemic rheumatic diseases like systemic sclerosis (SSc) and idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) may affect all aspects of life, including sexual health. However, no non-pharmacological treatment has been proposed to date. This is the pilot project aiming to investigate the effect of an 8-week physical therapy program on sexual function in women with SSc and IIM.
Methods: In total, 12 women with SSc and 4 women with IIM, who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria for SSc and the Bohan/Peter 1975 criteria for DM/PM, were enrolled in the study. Based on patient's possibilities and willingness to participate in the program, they were divided into an intervention group (IG) (6 SSc/2 IIM, mean age: 46.8±3.1 years) and a control group (CG) (6 SSc/2 IIM, mean age: 46.3±3.0 years). The IG underwent the 8-week tailored physiotherapy program, including the pelvic floor exercise and physiotherapy of musculoskeletal problems subjectively limiting the patient's sexual function (1 hour supervised physiotherapy twice weekly), whereas the control group received no specialized therapy. At weeks 0 and 8, all patients filled in questionnaires assessing sexual function: Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), Brief Index of Sexual Functioning for Women (BISF-W); sexual quality of life: Sexual Quality of Life-Female (SQoL-F); functional ability: Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ); quality of life: Medical Outcomes Short Form-36 (SF-36) and depression: Beck's Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II). At the baseline, patients in IG were assessed by a physician (medical history, mRSS, ESSG activity score, MITAX, MYOACT) and by a physiotherapist (pelvic floor function assessment–PERFECT scheme, MMT-8, Functional Index-II). Normality of data was tested, and inter-group analysis was performed with 2-way ANOVA and intra-group analysis by Friedmann's test.
Results: Compared to observed statistically significant deterioration in CG over the period of weeks 0-8, we found statistically significant improvement in both sexual function questionnaires: FSFI (p=0.043), BISF-W (p=0.040), functional status: HAQ (p=0.018), and quality of life: SF-36 Physical Somponent score (0.050). Only numerical improvement in IG compared to numerical deterioration in CG, which has not reached statistical significance, was observed in SQoL-F, BDI-II, and SF-36 Mental Component Score.
Conclusion:
Our physiotherapy program not only prevented the natural course of progressive deterioration of functional abilities, but also led to a significant improvement in sexual function and overall quality of life in women with SSc and IIM. Physical therapy might become one of the possible therapeutic treatments for sexual problems in women with SSc and IIM. This pilot study should be validated on larger cohorts, optimally in a randomized manner, which was not applicable in our case, due to the limited number of volunteers who met the criteria.
 Significant and non-significant changes wchich we observed after 8 week of physical therapy program in the intervention group compared to the control group
Significant and non-significant changes wchich we observed after 8 week of physical therapy program in the intervention group compared to the control groupDisclosures: B. Hermankova, None; M. Spiritovic, None; S. Oreska, None; H. Storkanova, None; K. Pavelka, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Eli Lilly, Medac, UCB, SOBI, Biogen, Sandoz, Viatris; L. Šenolt, None; J. Vencovský, Abbvie, Biogen, Boehringer, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Kezar, Merck, Novartis, Octapharma, Pfizer, Takeda, UCB, Werfen, Argenx; R. Becvar, None; M. Tomcik, None.

