Back
Poster Session B
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (1004–1034) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
1009: Efficacy and Improvement in Patient-Reported Outcomes at Weeks 16 and 52 in Ixekizumab Treated Biological Naïve Patients with Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis Achieving Clinically Important Pain at Night Reduction at Week 16: Results from COAST-V Trial
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time

Sofia Ramiro, MD, PhD
Leiden University Medical Center
Bunde, Netherlands
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Sofia Ramiro1, Cédric Lukas2, Michael Nissen3, Yves Schymura4, Khai Jing Ng4, Andrew Bradley4, Gabriel Doridot4, Soyi Liu-Leage5, Antoni Chan6 and James Cheng-Chung WEI7, 1Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 2University Hospital Centre Montpellier, University of Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 3Hopitaux Universitaires de Genève, Geneva, Switzerland, 4Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN, 5Eli Lilly, Neuilly sur Seine, France, 6Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust, Reading, United Kingdom, 7Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a monoclonal antibody that selectively targets interleukin IL-17A, has shown efficacy in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA). Spinal pain, in particular spinal pain at night (SP-N), is a major contributor to the patient burden of r-axSpA. Here we assess SP-N improvement in patients up to week (W) 52 and determine the association of SP-N improvement in patients treated with IXE with other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) at W16 and with reaching ASDAS LDA at W52.
Methods: The Phase III COAST-V (NCT02696785) trial investigated the efficacy of IXE in 341 patients with r-axSpA and were biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (bDMARD)-naïve. Patients were randomised to IXE every 2W (IXEQ2W), IXE every 4W (IXEQ4W), adalimumab (ADA) or placebo (PBO) up to W16. Only approved dose IXEQ4W data are presented here. SP-N was measured at each visit using a numeric rating scale (NRS) (0-10). A clinically relevant improvement in SP-N was defined as >2 point improvement from baseline. Differences in baseline variables between those achieving versus not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N were tested using Fisher's exact test (binary variables) and analysis of variance (ANOVA; continuous variables). Associations of SP-N improvement with PROs (BASFI, Fatigue Severity NRS, Jenkins Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire (JSEQ), SF-36 PCS) at W16, and ASDAS LDA at W52 were tested using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA; continuous variables) and logistic regression (binary variables). Missing values were imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI), and modified baseline observation carried forward.
Results: A greater proportion of patients achieved >2 improvement in SP-N with IXE treatment compared to PBO at W16 (63.0% vs. 32.2%, p < 0.001) and improvement was sustained up to W52 (Figure 1). Of the 81 patients originally randomised to IXE, those achieving >2 improvement in SP-N (63%) at W16 were younger, more frequently positive for HLA-B27 and had higher disease activity at baseline compared to those that did not achieve >2 improvement (Table 1). Achieving >2 improvement in SP-N was associated with improvement in PROs including BASFI, Fatigue Severity, JSEQ and SF-36 PCS at W16 and with achieving ASDAS< 2.1 at W52 compared to those not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N (Table 1).
Conclusion: IXE improved SP-N for patients with r-axSpA not previously treated with bDMARDs. Improvements in SP-N were associated with improvements in disease activity, function, fatigue and quality of life.
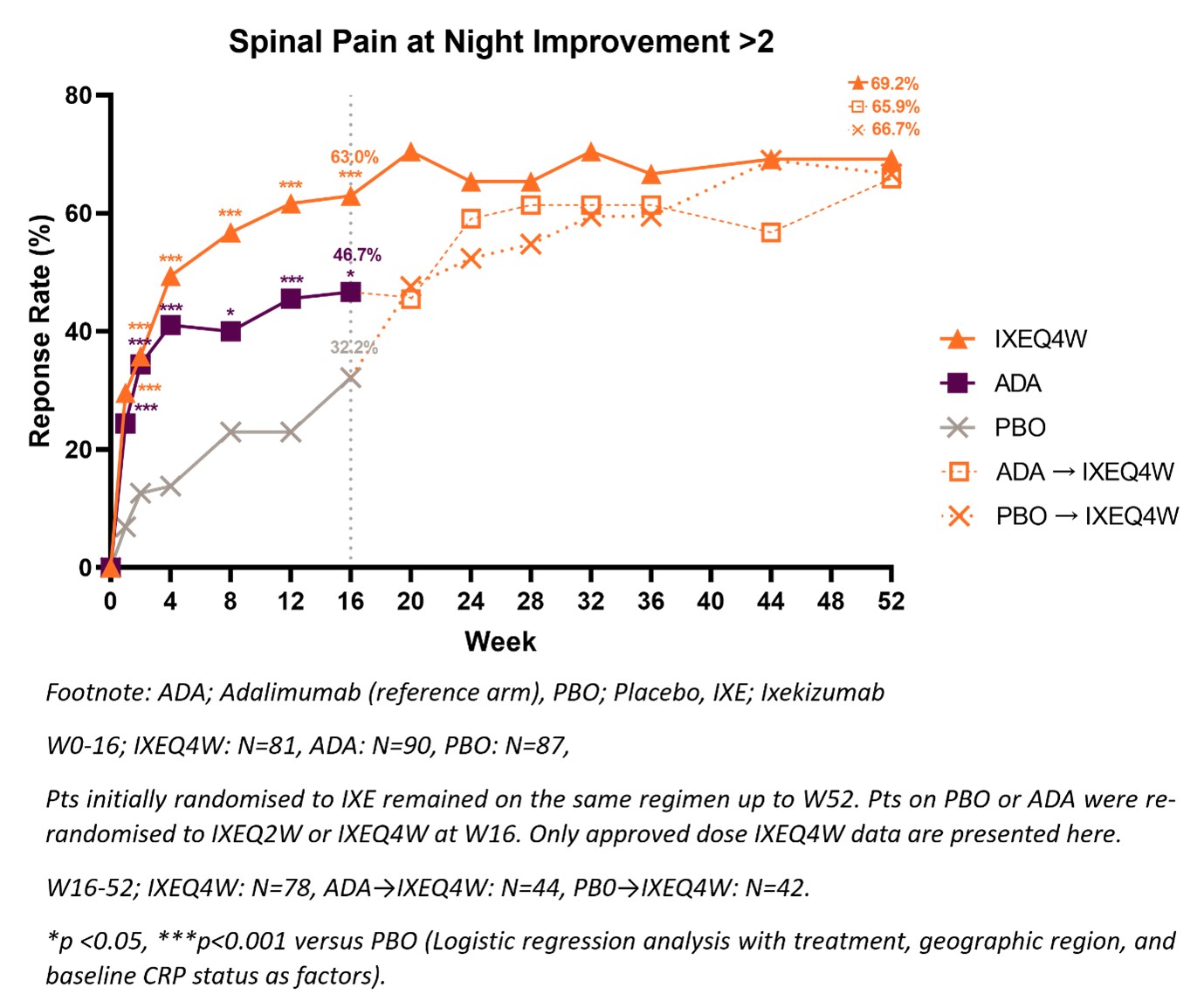 Figure 1: Patients achieving meaningful spinal pain at night improvement through W52.
Figure 1: Patients achieving meaningful spinal pain at night improvement through W52.
<img src=https://www.abstractscorecard.com/uploads/Tasks/upload/17574/QHOPTGBB-1278443-2-ANY.jpg width=440 height=526.568047337278 border=0 style=border-style: none;>
Disclosures: S. Ramiro, AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Sanofi; C. Lukas, None; M. Nissen, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Amgen, Novartis, Janssen; Y. Schymura, Eli Lilly and Company; K. Ng, Eli Lilly; A. Bradley, Eli Lilly and Company; G. Doridot, Eli Lilly and Company; S. Liu-Leage, Eli Lilly and Company; A. Chan, AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis, UCB Pharma; J. WEI, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi-Aventis, TSH Taiwan, UCB, JHL Taiwan.
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a monoclonal antibody that selectively targets interleukin IL-17A, has shown efficacy in patients with radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA). Spinal pain, in particular spinal pain at night (SP-N), is a major contributor to the patient burden of r-axSpA. Here we assess SP-N improvement in patients up to week (W) 52 and determine the association of SP-N improvement in patients treated with IXE with other patient-reported outcomes (PROs) at W16 and with reaching ASDAS LDA at W52.
Methods: The Phase III COAST-V (NCT02696785) trial investigated the efficacy of IXE in 341 patients with r-axSpA and were biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (bDMARD)-naïve. Patients were randomised to IXE every 2W (IXEQ2W), IXE every 4W (IXEQ4W), adalimumab (ADA) or placebo (PBO) up to W16. Only approved dose IXEQ4W data are presented here. SP-N was measured at each visit using a numeric rating scale (NRS) (0-10). A clinically relevant improvement in SP-N was defined as >2 point improvement from baseline. Differences in baseline variables between those achieving versus not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N were tested using Fisher's exact test (binary variables) and analysis of variance (ANOVA; continuous variables). Associations of SP-N improvement with PROs (BASFI, Fatigue Severity NRS, Jenkins Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire (JSEQ), SF-36 PCS) at W16, and ASDAS LDA at W52 were tested using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA; continuous variables) and logistic regression (binary variables). Missing values were imputed using non-responder imputation (NRI), and modified baseline observation carried forward.
Results: A greater proportion of patients achieved >2 improvement in SP-N with IXE treatment compared to PBO at W16 (63.0% vs. 32.2%, p < 0.001) and improvement was sustained up to W52 (Figure 1). Of the 81 patients originally randomised to IXE, those achieving >2 improvement in SP-N (63%) at W16 were younger, more frequently positive for HLA-B27 and had higher disease activity at baseline compared to those that did not achieve >2 improvement (Table 1). Achieving >2 improvement in SP-N was associated with improvement in PROs including BASFI, Fatigue Severity, JSEQ and SF-36 PCS at W16 and with achieving ASDAS< 2.1 at W52 compared to those not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N (Table 1).
Conclusion: IXE improved SP-N for patients with r-axSpA not previously treated with bDMARDs. Improvements in SP-N were associated with improvements in disease activity, function, fatigue and quality of life.
 Figure 1: Patients achieving meaningful spinal pain at night improvement through W52.
Figure 1: Patients achieving meaningful spinal pain at night improvement through W52.<img src=https://www.abstractscorecard.com/uploads/Tasks/upload/17574/QHOPTGBB-1278443-2-ANY.jpg width=440 height=526.568047337278 border=0 style=border-style: none;>
Table 1: Baseline demographics, clinical characteristics, and PROs of IXE treated patients achieving vs. not achieving >2 improvement in SP-N at W16.
Disclosures: S. Ramiro, AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Sanofi; C. Lukas, None; M. Nissen, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Amgen, Novartis, Janssen; Y. Schymura, Eli Lilly and Company; K. Ng, Eli Lilly; A. Bradley, Eli Lilly and Company; G. Doridot, Eli Lilly and Company; S. Liu-Leage, Eli Lilly and Company; A. Chan, AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis, UCB Pharma; J. WEI, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi-Aventis, TSH Taiwan, UCB, JHL Taiwan.

