Back
Poster Session B
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (1004–1034) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
1008: Endothelial Dysfunction in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Its Association with Clinical Disease Characteristics
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
- ML
Maria Lourdes Ladehesa Pineda, PhD
Reina Sofia Universitary Hospital
Cordoba, Spain
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
lourdes Ladehesa-Pineda1, Clementina Lopez-Medina2, Maria Angeles Puche Larrubia3, Raquel Granados4 and Eduardo Collantes5, 1Reina Sofia University Hospital/Rheumatology Department/Maimonides Institute for Biomedical Research (IMIBIC), Cordoba, Spain, 2Reina Sofia University Hospital, Rheumatology Department, Jaén, Spain, 3Reina Sofia University Hospital/Rheumatology Department/Maimonides Institute for Biomedical Research (IMIBIC), Granada, Spain, 4Reina Sofia University Hospital/Rheumatology Department/Maimonides Institute for Biomedical Research (IMIBIC), Córdoba, Spain, 5IMIBIC/University of Cordoba/Reina Sofia Hospital, Cordoba, Spain
Background/Purpose: It has been described an increased presence of cardiovascular risk factors and subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). Several studies have shown that endothelial dysfunction (ED) is a vascular abnormality frequently presented in radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) patients. We aim to evaluate the association of endothelial dysfunction and clinical characteristics, including radiographic structural damage, in patients with axSpA.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 121 axSpA patients from the CASTRO registry and 119 age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HCs). Characteristics related with disease activity, cardiovascular risk factors and presence of atherosclerotic plaques were registered, and ED was assessed using a Periflux System 5010 Laser-Doppler Flowmeter to measure the microvascular function.The association between ED and clinical characteristics was tested using Pearson correlation and an age-adjusted cluster analysis was performed to identify different phenotypes dependent on variables associated to microvascular function.
Results: Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients and HCs can be found in the table.Correlation analysis showed that Rest Flow (RF) and Area of hyperemia (AH) were significantly associated with mSASSS (total, cervical and lumbar) and BASMI. RF was associated also with years of disease and BASFI, and AH with the presence of carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Clusters based on AH, Peak flow (PF)-RF and presence of atherosclerotic plaques distinguished two groups of patients, with significant differences regarding mSASSS, number of bone bridges and syndesmophytes, SCORE index, years of disease, BASFI and BASMI.
Conclusion: Patients with axSpA display endotelial dysfunction when compared to HCs. Parameters associated to endothelial dysfunction are associated with SpA characteristics such as mSASSS, time of disease evolution, BASMI and BASFI. In axSpA patients, endothelial dysfunction is associated to the presence of carotid atherosclerotic plaques.
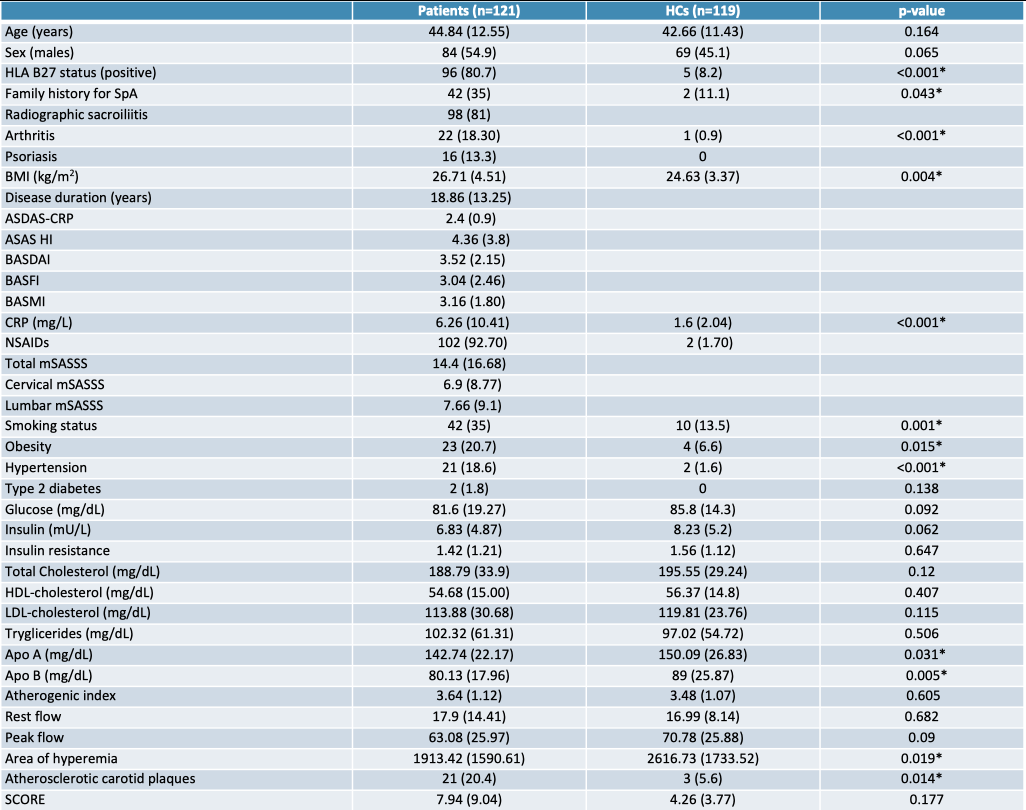 Demographic and clinical details and characteristics related to endothelial function of axial spondyloarthritis patients and healthy controls.
Demographic and clinical details and characteristics related to endothelial function of axial spondyloarthritis patients and healthy controls.
Data are shown as mean (standard deviation) or frequency (percentage). HCs: Healthy Controls; SpA: Spondyloarthritis; BMI: Body Mass Index; VAS: Visual Analogic Scale; ASDAS-CRP: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-C Reactive Protein; ASAS HI: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society Health Index; BASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BASFI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index; BASMI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index; CRP: C Reactive Protein; NSAIDs: Non Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs; mSASSS: Modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score; HDL: High density lipoprotein; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; Apo A: Apolipoprotein A; Apo B: Apolipoprotein B; cIMT: carotid intima-media thickness.
*Significant differences
Disclosures: l. Ladehesa-Pineda, None; C. Lopez-Medina, None; M. Puche Larrubia, None; R. Granados, None; E. Collantes, None.
Background/Purpose: It has been described an increased presence of cardiovascular risk factors and subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). Several studies have shown that endothelial dysfunction (ED) is a vascular abnormality frequently presented in radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) patients. We aim to evaluate the association of endothelial dysfunction and clinical characteristics, including radiographic structural damage, in patients with axSpA.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study including 121 axSpA patients from the CASTRO registry and 119 age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HCs). Characteristics related with disease activity, cardiovascular risk factors and presence of atherosclerotic plaques were registered, and ED was assessed using a Periflux System 5010 Laser-Doppler Flowmeter to measure the microvascular function.The association between ED and clinical characteristics was tested using Pearson correlation and an age-adjusted cluster analysis was performed to identify different phenotypes dependent on variables associated to microvascular function.
Results: Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients and HCs can be found in the table.Correlation analysis showed that Rest Flow (RF) and Area of hyperemia (AH) were significantly associated with mSASSS (total, cervical and lumbar) and BASMI. RF was associated also with years of disease and BASFI, and AH with the presence of carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Clusters based on AH, Peak flow (PF)-RF and presence of atherosclerotic plaques distinguished two groups of patients, with significant differences regarding mSASSS, number of bone bridges and syndesmophytes, SCORE index, years of disease, BASFI and BASMI.
Conclusion: Patients with axSpA display endotelial dysfunction when compared to HCs. Parameters associated to endothelial dysfunction are associated with SpA characteristics such as mSASSS, time of disease evolution, BASMI and BASFI. In axSpA patients, endothelial dysfunction is associated to the presence of carotid atherosclerotic plaques.
 Demographic and clinical details and characteristics related to endothelial function of axial spondyloarthritis patients and healthy controls.
Demographic and clinical details and characteristics related to endothelial function of axial spondyloarthritis patients and healthy controls.Data are shown as mean (standard deviation) or frequency (percentage). HCs: Healthy Controls; SpA: Spondyloarthritis; BMI: Body Mass Index; VAS: Visual Analogic Scale; ASDAS-CRP: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-C Reactive Protein; ASAS HI: Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society Health Index; BASDAI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BASFI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index; BASMI: Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index; CRP: C Reactive Protein; NSAIDs: Non Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs; mSASSS: Modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score; HDL: High density lipoprotein; LDL: Low density lipoprotein; Apo A: Apolipoprotein A; Apo B: Apolipoprotein B; cIMT: carotid intima-media thickness.
*Significant differences
Disclosures: l. Ladehesa-Pineda, None; C. Lopez-Medina, None; M. Puche Larrubia, None; R. Granados, None; E. Collantes, None.

