Back
Poster Session B
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0913–0938) RA – Treatment Poster II
0920: Retention Rate and Safety of Biologic or Targeted Synthetic Disease Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease: Results from the KOBIO Registry
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- JK
Ji-Won Kim, MD
Ajou university school of medicine
Suwon, South Korea
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Ji-Won Kim1, Sun-Kyung Lee2, Ju-Yang Jung1, Chang-Hee Suh3, Kichul Shin4 and Hyoun-Ah Kim1, 1Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2Hanyang university, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 3Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Republic of Korea, 4Seoul Metropolitan Government- Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Background/Purpose: The aim was to evaluate long-term drug retention and safety of biologic (bDMARDs) or targeted synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs) and to identify risk factors of drug withdrawal in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) associated with interstitial lung disease (ILD) enrolled in the Korean College of Rheumatology BIOlogics (KOBIO) registry.
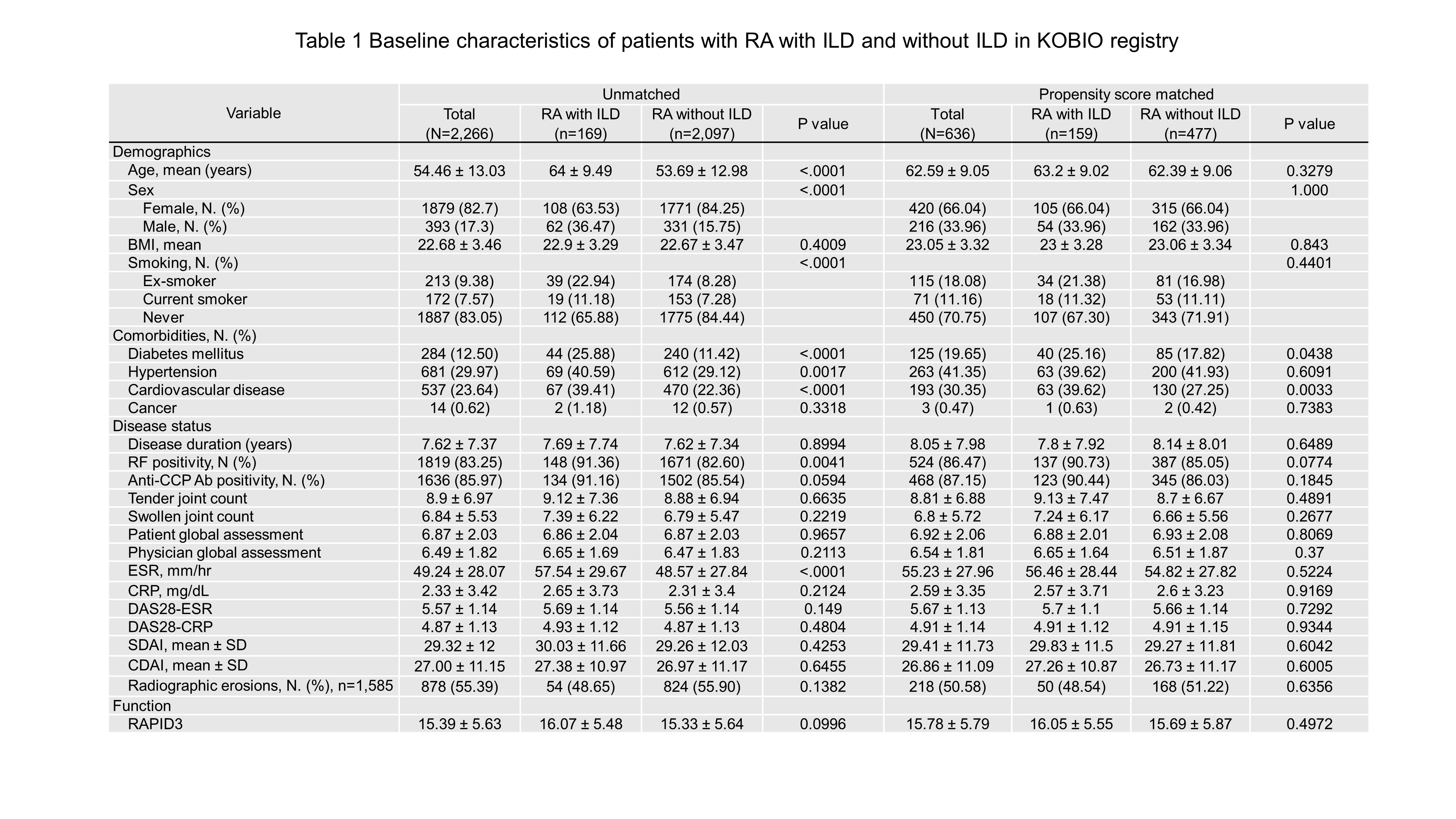
Methods: Patients included adults with RA (n=2,266) who received bDMARDs or tsDMARDs between 2012 and 2021, and 1:3 matching was performed using propensity score-matching (PSM) between RA with and without ILD. The Kaplan-Meier method was conducted to analyze drug survival and factors associated with drug withdrawal were studied using a logistic regression model.
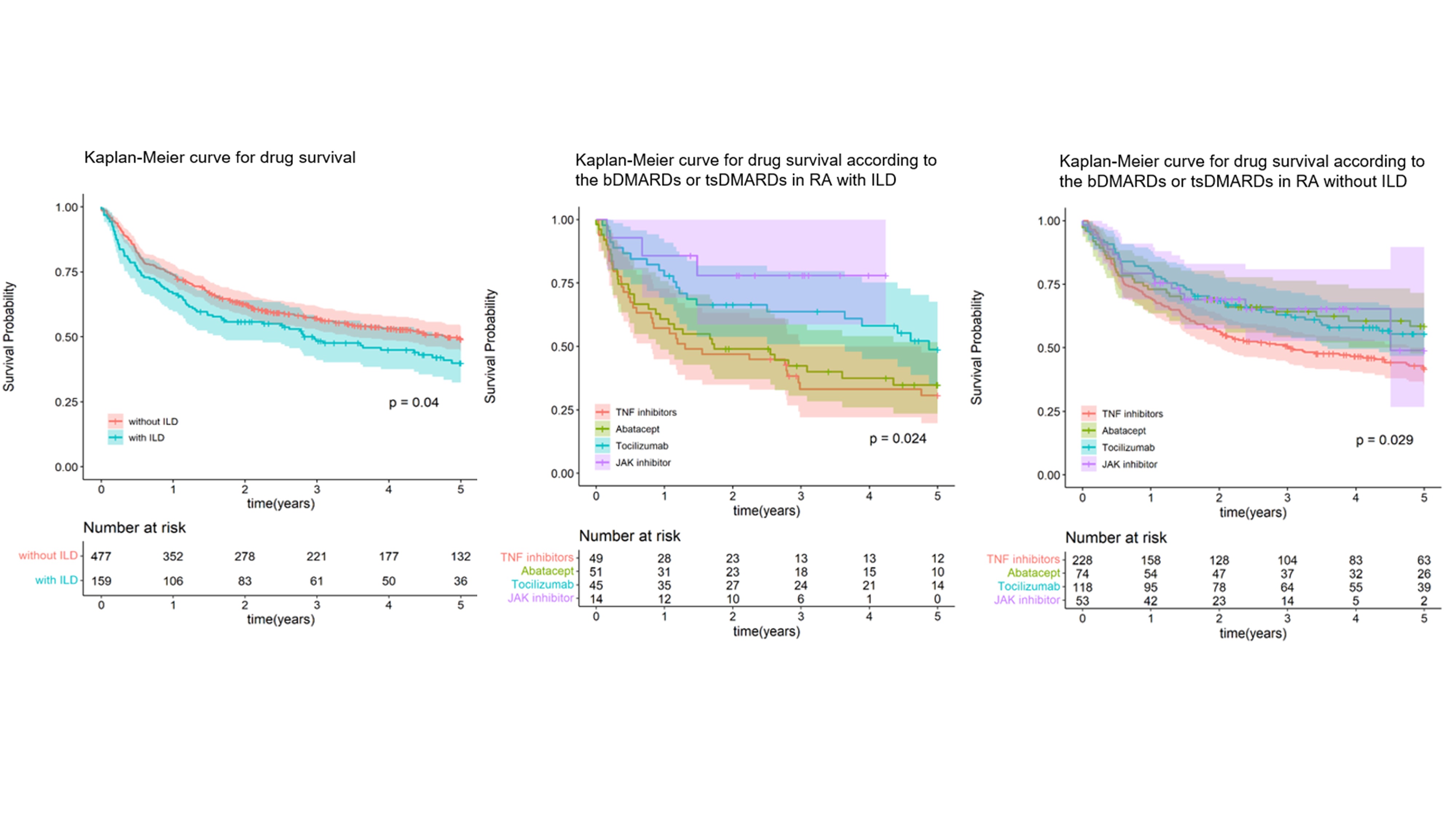
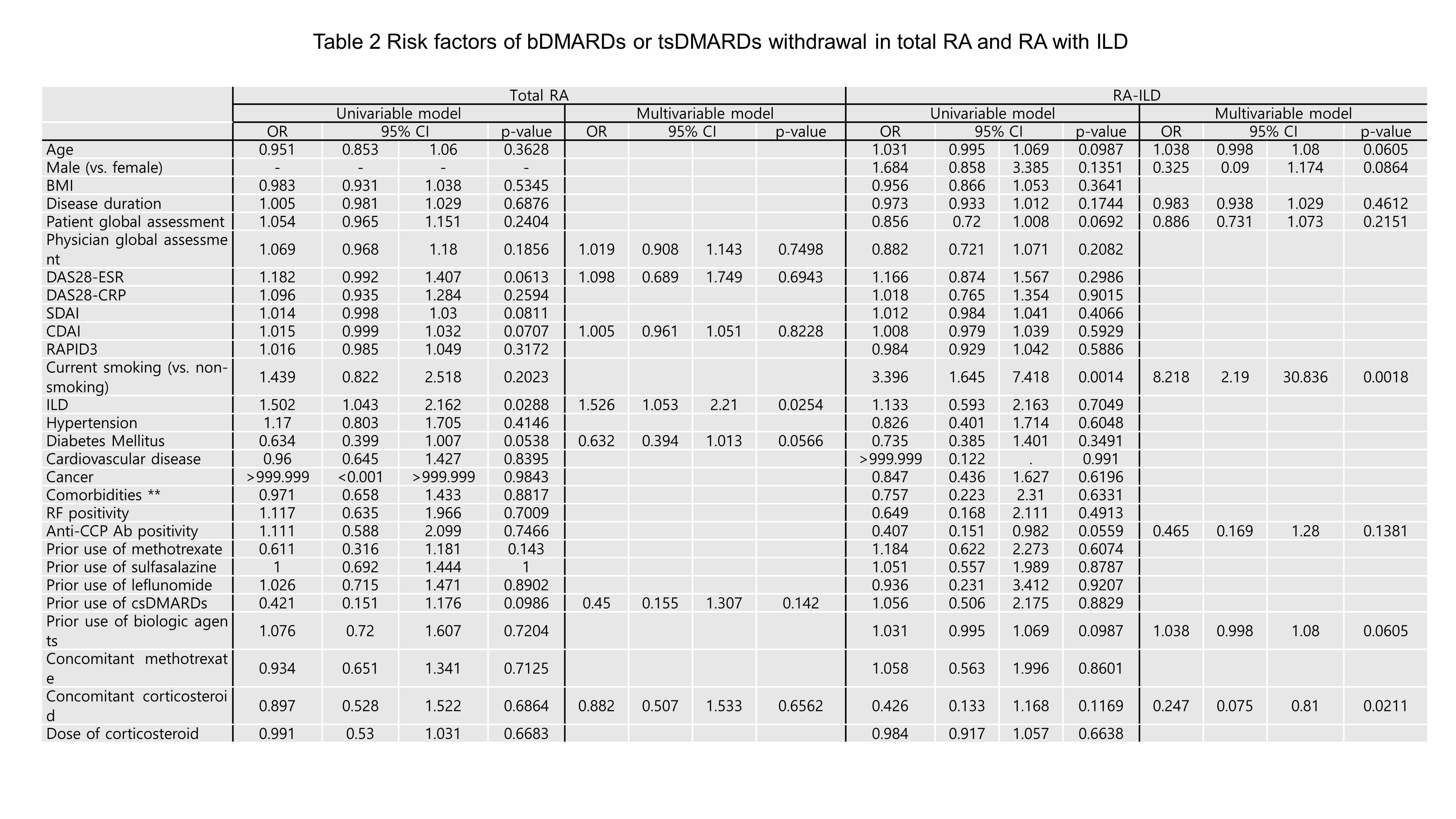
Results: PSM was effective in matching 159 RA with ILD and 477 RA without ILD. Five-year retention rates were 44.0% for RA with ILD and 52.4% for RA without ILD (p=0.04). Both groups showed significant differences depending on the agents, and in RA-ILD, JAK inhibitor was the highest retention rate. Overall, 58.5% (RA-ILD) and 48.4% (RA-no ILD) of patients discontinued or switched bDMARDs or tsDMARDs, and the main causes of drug withdrawal were adverse events (45.2% in RA-ILD and 30.3% in RA-no ILD, p< 0.001), followed by inefficacy (35.5% in RA-ILD and 41.1% in RA-no ILD, p=0.819). In logistic regression analysis, smoking is a risk factor for withdrawal [odds ratio (OR) 8.2, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.2-30.8], and concomitant steroid use has a protective effect on withdrawal (OR 0.2, CI 0.1-0.8).
Conclusion: RA patients with ILD had a lower drug retention rate of bDMARDs or tsDMARDs than those without ILD, and there was a difference according to the agents. The factors affecting drug withdrawal were smoking and concomitant steroid use.
Disclosures: J. Kim, None; S. Lee, None; J. Jung, None; C. Suh, None; K. Shin, None; H. Kim, None.
Background/Purpose: The aim was to evaluate long-term drug retention and safety of biologic (bDMARDs) or targeted synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (tsDMARDs) and to identify risk factors of drug withdrawal in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) associated with interstitial lung disease (ILD) enrolled in the Korean College of Rheumatology BIOlogics (KOBIO) registry.
Methods: Patients included adults with RA (n=2,266) who received bDMARDs or tsDMARDs between 2012 and 2021, and 1:3 matching was performed using propensity score-matching (PSM) between RA with and without ILD. The Kaplan-Meier method was conducted to analyze drug survival and factors associated with drug withdrawal were studied using a logistic regression model.
Results: PSM was effective in matching 159 RA with ILD and 477 RA without ILD. Five-year retention rates were 44.0% for RA with ILD and 52.4% for RA without ILD (p=0.04). Both groups showed significant differences depending on the agents, and in RA-ILD, JAK inhibitor was the highest retention rate. Overall, 58.5% (RA-ILD) and 48.4% (RA-no ILD) of patients discontinued or switched bDMARDs or tsDMARDs, and the main causes of drug withdrawal were adverse events (45.2% in RA-ILD and 30.3% in RA-no ILD, p< 0.001), followed by inefficacy (35.5% in RA-ILD and 41.1% in RA-no ILD, p=0.819). In logistic regression analysis, smoking is a risk factor for withdrawal [odds ratio (OR) 8.2, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.2-30.8], and concomitant steroid use has a protective effect on withdrawal (OR 0.2, CI 0.1-0.8).
Conclusion: RA patients with ILD had a lower drug retention rate of bDMARDs or tsDMARDs than those without ILD, and there was a difference according to the agents. The factors affecting drug withdrawal were smoking and concomitant steroid use.



Disclosures: J. Kim, None; S. Lee, None; J. Jung, None; C. Suh, None; K. Shin, None; H. Kim, None.

