Back
Poster Session B
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (1004–1034) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
1022: Validation of the SPARCCRETIC E-Tool for Ensuring Scoring Proficiency of MRI Lesions in Axial Spondyloarthritis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- WM
Walter P. Maksymowych, MD
University of Alberta
Edmonton, AB, Canada
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Walter P Maksymowych1, Anna Hadsbjerg2, Mikkel Østergaard3, Raphael Micheroli4, Susanne J. Pedersen5, Adrian Ciurea6, Nora Vladimirova2, Michael Nissen7, Kristyna Bubova8, Stephanie Wichuk9, Manouk de Hooge10, Ashish J Mathew11, Karlo Pintaric12, Monika gregova13, Ziga Snoj12, Marie Wetterslev14, Karel Gorican15, Joel Paschke16, Iris Eshed17 and Robert G Lambert9, 1Department of Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2Copenhagen Center for Arthritis Research, Copenhagen, Denmark, 3Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Denmark, 4University Hospital Zurich, Department of Rheumatology, Zürich, Switzerland, 5Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark, 6University Hospital Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 7Hopitaux Universitaires de Genève, Geneva, Switzerland, 8First Faculty of Medicine, Charles University,, Prague, Czech Republic, 9University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 10Ghent University Hospital, Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 11Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark, 12Radiology, University Medical Centre Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 13Institue of Rheumatology, Prague, 14Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Glostrup, Denmark, 15MSK radiology unit, Radiology section – Diagnostic department, Geneva University Hospitals, Geneva, Switzerland, 16CARE Arthritis LTD, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 17Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel
Background/Purpose: Quantification of inflammatory and structural lesions in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) on MRI scans from patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has a growing list of applications, especially for clinical trials. It is therefore essential that knowledge transfer tools are made available that can ensure understanding of scoring methodologies and enable remote training of readers across the globe so that they can reliably perform assessments. The web-based Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) real-time iterative calibration (RETIC) modules for scoring inflammatory and structural MRI lesions in axSpA have been created by SPARCC developers to enable remote training of readers to appropriately use the SPARCC MRI inflammation and structural damage instruments and to attain adequate scoring proficiency. We aimed to test the performance of these modules in enhancing scoring proficiency in comparison to SPARCC developer gold standard.
Methods: The SPARCCRETIC SIJ inflammation and structural damage modules are each comprised of 50 DICOM axSpA cases with baseline and follow up scans and an online scoring interface based on SIJ quadrants. Continuous visual real-time feedback regarding concordance/discordance of scoring per SIJ quadrant with expert readers is provided by a color-coding scheme. Reliability is assessed in real-time by intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), ICC data being provided every 10 cases, which are scored until proficiency targets for ICC are attained. Participants (n=15) from the EuroSpA Imaging project were randomized, stratified by reader expertise in scoring with SPARCC, to one of two reader training strategies (A and B) that each comprised 3 stages: A. 1. Review of original SPARCC manuscript describing scoring method. 2. Review of powerpoint summary of SPARCC method plus completion of SPARCCRETIC module. 3. Re-review of powerpoint summary. B. Same 3-step strategy as A except SPARCCRETIC module completed at stage 3. Participants scored scans from 25 axSpA cases blinded to time point after each stage of training and reliability of scoring was compared to SPARCC developer scores by ICC. Each of the 75 cases that were scored by the 15 readers had 2 time points varying from 3 months to 2 years and each batch of 25 cases had comparable scores for BME and structural lesions when scored by SPARCC developers.
Results: Very good scoring proficiency for status and change scores was evident for SPARCC BME even at stage 1 and even by non-experienced readers with similar levels of reliability irrespective of reader prior expertise with the method (Table). The beneficial impact of the SPARCCRETIC module on scoring proficiency was most consistently evident for the scoring of structural lesions and for Strategy B, where the impact was evident for all structural lesions, level of reader expertise, and status as well as change scores (Figures 1 and 2).
Conclusion: Attaining scoring proficiency for MRI structural lesions in axSpA is difficult but can be consistently improved by using the SPARCCRETIC module, even for experienced readers.
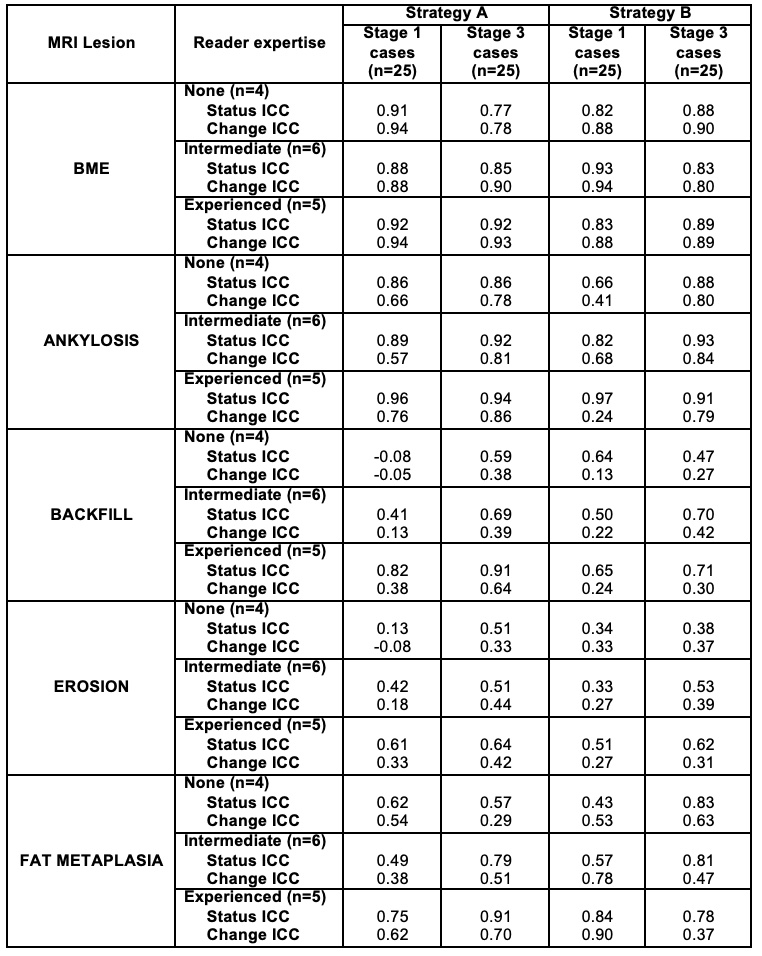 Table. Inter-rater reliability (Status/Change ICC) compared to radiologist SPARCC developer
Table. Inter-rater reliability (Status/Change ICC) compared to radiologist SPARCC developer
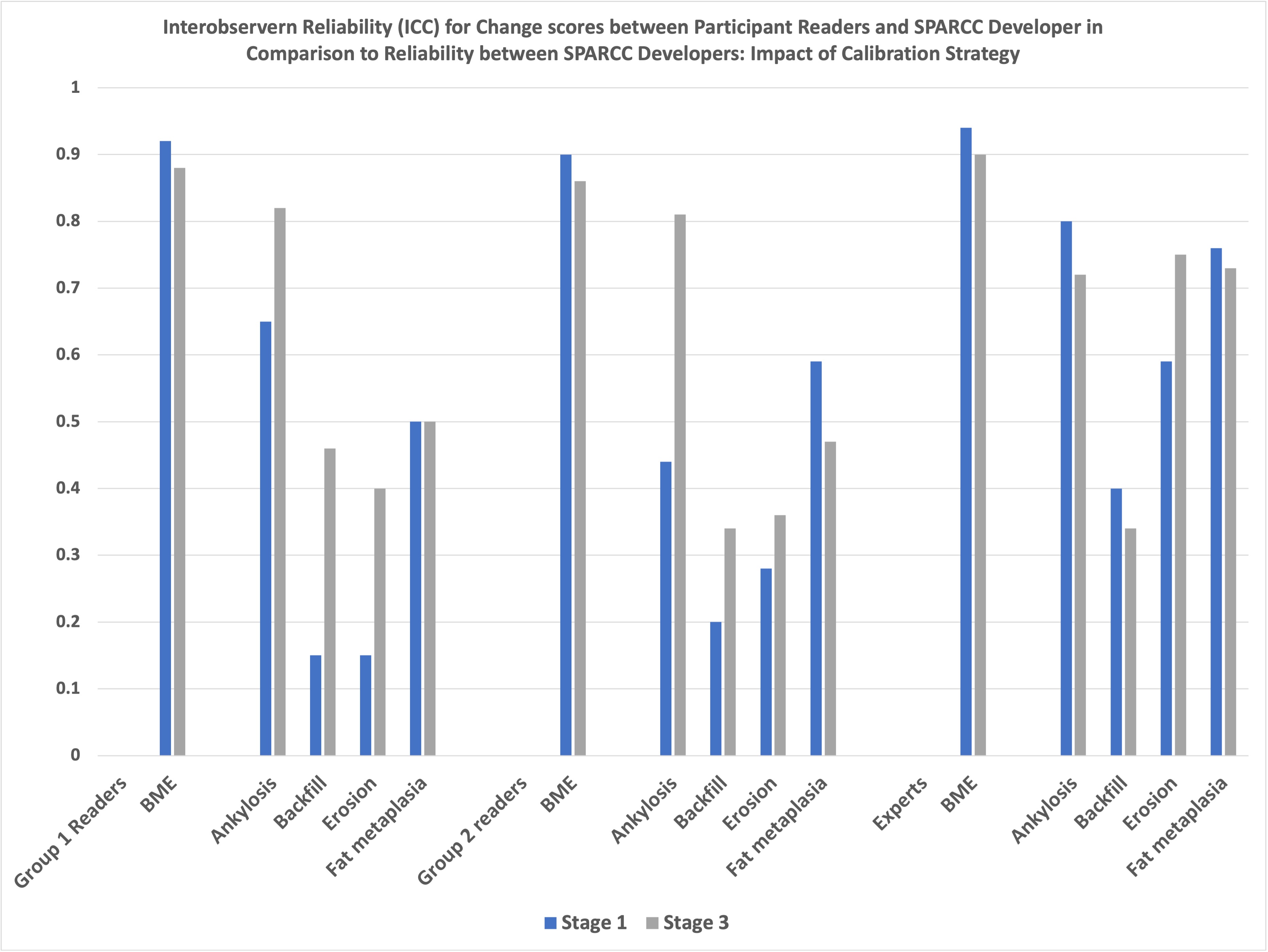 Figure 1
Figure 1
.jpg) Figure 2
Figure 2
Disclosures: W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, CARE Arthritis Limited; A. Hadsbjerg, Novartis; M. Østergaard, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB; R. Micheroli, None; S. Pedersen, Novartis, AbbVie/Abbott, UCB, Pfizer, Merck/MSD; A. Ciurea, AbbVie, Novartis, Merck/MSD; N. Vladimirova, Novartis; M. Nissen, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Amgen, Novartis, Janssen; K. Bubova, None; S. Wichuk, None; M. de Hooge, None; A. Mathew, None; K. Pintaric, None; M. gregova, None; Z. Snoj, None; M. Wetterslev, None; K. Gorican, None; J. Paschke, None; I. Eshed, None; R. Lambert, Calyx, CARE Arthritis, Image Analysis Group.
Background/Purpose: Quantification of inflammatory and structural lesions in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) on MRI scans from patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has a growing list of applications, especially for clinical trials. It is therefore essential that knowledge transfer tools are made available that can ensure understanding of scoring methodologies and enable remote training of readers across the globe so that they can reliably perform assessments. The web-based Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) real-time iterative calibration (RETIC) modules for scoring inflammatory and structural MRI lesions in axSpA have been created by SPARCC developers to enable remote training of readers to appropriately use the SPARCC MRI inflammation and structural damage instruments and to attain adequate scoring proficiency. We aimed to test the performance of these modules in enhancing scoring proficiency in comparison to SPARCC developer gold standard.
Methods: The SPARCCRETIC SIJ inflammation and structural damage modules are each comprised of 50 DICOM axSpA cases with baseline and follow up scans and an online scoring interface based on SIJ quadrants. Continuous visual real-time feedback regarding concordance/discordance of scoring per SIJ quadrant with expert readers is provided by a color-coding scheme. Reliability is assessed in real-time by intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), ICC data being provided every 10 cases, which are scored until proficiency targets for ICC are attained. Participants (n=15) from the EuroSpA Imaging project were randomized, stratified by reader expertise in scoring with SPARCC, to one of two reader training strategies (A and B) that each comprised 3 stages: A. 1. Review of original SPARCC manuscript describing scoring method. 2. Review of powerpoint summary of SPARCC method plus completion of SPARCCRETIC module. 3. Re-review of powerpoint summary. B. Same 3-step strategy as A except SPARCCRETIC module completed at stage 3. Participants scored scans from 25 axSpA cases blinded to time point after each stage of training and reliability of scoring was compared to SPARCC developer scores by ICC. Each of the 75 cases that were scored by the 15 readers had 2 time points varying from 3 months to 2 years and each batch of 25 cases had comparable scores for BME and structural lesions when scored by SPARCC developers.
Results: Very good scoring proficiency for status and change scores was evident for SPARCC BME even at stage 1 and even by non-experienced readers with similar levels of reliability irrespective of reader prior expertise with the method (Table). The beneficial impact of the SPARCCRETIC module on scoring proficiency was most consistently evident for the scoring of structural lesions and for Strategy B, where the impact was evident for all structural lesions, level of reader expertise, and status as well as change scores (Figures 1 and 2).
Conclusion: Attaining scoring proficiency for MRI structural lesions in axSpA is difficult but can be consistently improved by using the SPARCCRETIC module, even for experienced readers.
 Table. Inter-rater reliability (Status/Change ICC) compared to radiologist SPARCC developer
Table. Inter-rater reliability (Status/Change ICC) compared to radiologist SPARCC developer Figure 1
Figure 1.jpg) Figure 2
Figure 2Disclosures: W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, CARE Arthritis Limited; A. Hadsbjerg, Novartis; M. Østergaard, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB; R. Micheroli, None; S. Pedersen, Novartis, AbbVie/Abbott, UCB, Pfizer, Merck/MSD; A. Ciurea, AbbVie, Novartis, Merck/MSD; N. Vladimirova, Novartis; M. Nissen, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Amgen, Novartis, Janssen; K. Bubova, None; S. Wichuk, None; M. de Hooge, None; A. Mathew, None; K. Pintaric, None; M. gregova, None; Z. Snoj, None; M. Wetterslev, None; K. Gorican, None; J. Paschke, None; I. Eshed, None; R. Lambert, Calyx, CARE Arthritis, Image Analysis Group.

