Back
Poster Session D
Epidemiology, health policy and outcomes
Session: (1750–1786) Epidemiology and Public Health Poster III
1758: Intake of Dairy Products as a Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis; A Nested Case-Control Study
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- CT
Carl Turesson
Lund University
Malmö, Sweden
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Camilla LIndegren1, Emily Sonestedt1, Emil Rydell1, Linnea Arvidsson1, Ulf Bergström1 and Carl Turesson2, 1Lund University, Malmö, Sweden, 2Rheumatology, Department of Clinical Sciences, Malmö, Lund University, Malmö, Sweden
Background/Purpose: There has been increasing interest in diet as a factor that may contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). There is limited and somewhat contradictory information on the impact of dairy products in this context. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relation between intake of various dairy products and the risk of RA in a nested case-control study.
Methods: Participants in a population-based survey conducted in 1991-1996 who were subsequently diagnosed with RA (from inclusion until December 2016) were identified through register linkage and validated in a structured review of case records. Four controls for each validated case, matched for sex, year of birth, and year of inclusion, were selected from the study cohort. The controls were alive and free of RA when the index person was diagnosed with RA. At inclusion in the survey, diet was assessed using a modified diet history method, consisting of a seven-day food record, a food questionnaire, and a structured interview. Reported intakes of dairy products were divided into groups based on quartiles, with the lowest quartile set as the reference in all analyses. Based on conditional logistical regression, including adjustments for total energy intake and for potential confounders that have been associated with diet and RA (i.e. current smoking, physical activity and alcohol intake), odds ratios (ORs) for RA were estimated, with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Potential misreporters of total energy intake were excluded. Assessed types of dairy products included regular (non-fermented) milk, fermented milk, cream, cheese, and butter.
Results: There were 305 incident cases of RA (76 % females, 67 % anti-citrullinated protein antibody and/or rheumatoid factor positive, mean age 68.9 years at onset and mean duration of 12 years from screening to RA diagnosis). The group with highest intake of regular milk ( >398 g/day) had a significantly increased risk of RA (multi-adjusted OR 1.86; 95% CI 1.08-3.22). High intake of cheese with >11% fat ( >56 g/day) was inversely associated with risk of RA (adjusted OR 0.53; 95% CI 0.31-0.92) and a trend of lower risk across quartiles of cheese intake was observed. Intake of cream, fermented milk or butter did not have a significant impact on the risk of developing RA. Associations for intakes of cheese and regular milk with the risk of RA remained significant in multivariable analysis, including both exposures (Table 1).
Conclusion: High intake of regular milk appears to increase the risk of RA, whereas high intake of cheese may reduce the risk. Potential explanations for these patterns include differential effects of dairy product depending on the extent of processing and fermentation, that may affect the gut microbiota and modulate the risk of developing RA.
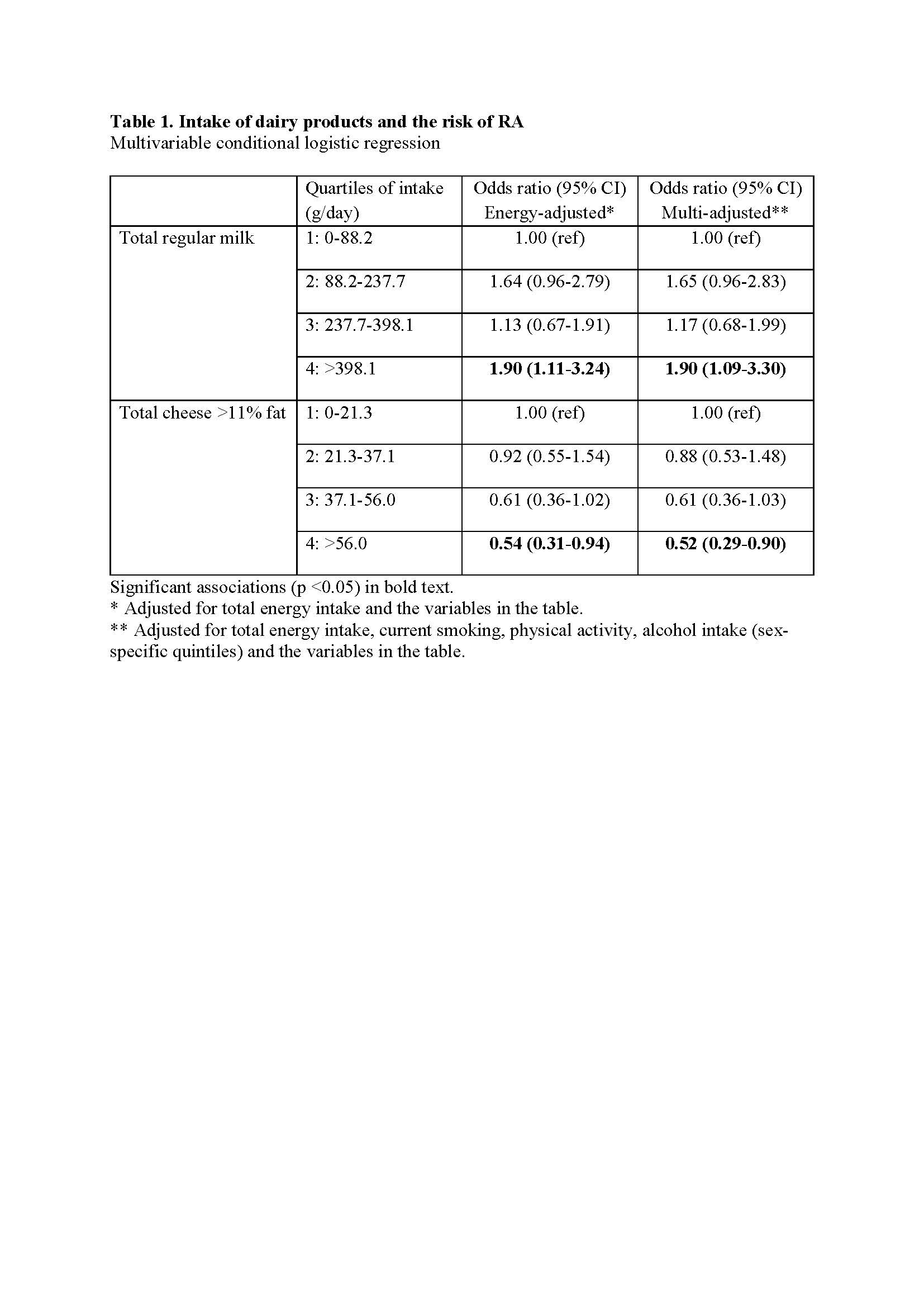 Table 1. Intake of dairy products and the risk of RA. Multivariable conditional logistic regression
Table 1. Intake of dairy products and the risk of RA. Multivariable conditional logistic regression
Disclosures: C. LIndegren, None; E. Sonestedt, None; E. Rydell, None; L. Arvidsson, None; U. Bergström, None; C. Turesson, AbbVie/Abbott, Nordic Drugs, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS).
Background/Purpose: There has been increasing interest in diet as a factor that may contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). There is limited and somewhat contradictory information on the impact of dairy products in this context. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relation between intake of various dairy products and the risk of RA in a nested case-control study.
Methods: Participants in a population-based survey conducted in 1991-1996 who were subsequently diagnosed with RA (from inclusion until December 2016) were identified through register linkage and validated in a structured review of case records. Four controls for each validated case, matched for sex, year of birth, and year of inclusion, were selected from the study cohort. The controls were alive and free of RA when the index person was diagnosed with RA. At inclusion in the survey, diet was assessed using a modified diet history method, consisting of a seven-day food record, a food questionnaire, and a structured interview. Reported intakes of dairy products were divided into groups based on quartiles, with the lowest quartile set as the reference in all analyses. Based on conditional logistical regression, including adjustments for total energy intake and for potential confounders that have been associated with diet and RA (i.e. current smoking, physical activity and alcohol intake), odds ratios (ORs) for RA were estimated, with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Potential misreporters of total energy intake were excluded. Assessed types of dairy products included regular (non-fermented) milk, fermented milk, cream, cheese, and butter.
Results: There were 305 incident cases of RA (76 % females, 67 % anti-citrullinated protein antibody and/or rheumatoid factor positive, mean age 68.9 years at onset and mean duration of 12 years from screening to RA diagnosis). The group with highest intake of regular milk ( >398 g/day) had a significantly increased risk of RA (multi-adjusted OR 1.86; 95% CI 1.08-3.22). High intake of cheese with >11% fat ( >56 g/day) was inversely associated with risk of RA (adjusted OR 0.53; 95% CI 0.31-0.92) and a trend of lower risk across quartiles of cheese intake was observed. Intake of cream, fermented milk or butter did not have a significant impact on the risk of developing RA. Associations for intakes of cheese and regular milk with the risk of RA remained significant in multivariable analysis, including both exposures (Table 1).
Conclusion: High intake of regular milk appears to increase the risk of RA, whereas high intake of cheese may reduce the risk. Potential explanations for these patterns include differential effects of dairy product depending on the extent of processing and fermentation, that may affect the gut microbiota and modulate the risk of developing RA.
 Table 1. Intake of dairy products and the risk of RA. Multivariable conditional logistic regression
Table 1. Intake of dairy products and the risk of RA. Multivariable conditional logistic regressionDisclosures: C. LIndegren, None; E. Sonestedt, None; E. Rydell, None; L. Arvidsson, None; U. Bergström, None; C. Turesson, AbbVie/Abbott, Nordic Drugs, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS).

