Back
Poster Session D
Sjögren's syndrome
Session: (2017–2051) Sjögren's Syndrome – Basic and Clinical Science Poster
2044: Abnormalities of Extracellular Matrix Modeling Gene Expression in Salivary Gland Epithelial Cells of Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

Elodie Riviere, MD, PhD
INSERM U1184, Université Paris Saclay
Le Kremlin Bicêtre, France
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Elodie Riviere1, Juliette Pascaud1, Franck Letourneur2, Gaetane Nocturne3 and Xavier Mariette4, 1Université Paris-Saclay, INSERM U1184, Le Kremlin Bicêtre, France, 2Genomic, Hôpital Cochin, Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Paris, France, 3APHP, Le Kremlin Bicêtre, France, 4Paris-Saclay University, Rueil Malmaison, Ile-de-France, France
Background/Purpose: Salivary gland epithelial cells (SGECs) are not only the target of autoimmunity in primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS). SGECs may interact with lymphocytes and therefore participate to the over activation of the immune system (1). Moreover, SGECs may undergo TGFb mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition during pSS (2).
We aimed to determine whether SGECs from pSS present intrinsic abnormalities that may be involved in pSS pathogenesis, especially concerning their potential role in salivary gland microenvironment modifications.
Methods: Minor salivary gland (MSG) biopsies were obtained from patients referred for suspicion of pSS to the Rheumatology Department of Bicêtre hospital, AP-HP, Université Paris-Saclay, a tertiary reference center for systemic auto-immune diseases. pSS was defined according to the 2016 ACR/EULAR criteria. RNAseq analysis of primary SGECs (5 controls and 5 pSS) was performed after 2-3 weeks of culture (Illumina). Statistical analyses on the read counts were performed with the DESeq2 package. Absolute FC value >1.5 and p-value< 0.05 was applied to identify up and down-regulated genes. Confirmation RT-qPCR were then performed on additional SGECs samples (n = 15 controls and 13 pSS).
Results: RNAseq analysis of SGECs from pSS compared to controls identified 251 upregulated and 260 downregulated genes. Functional enrichment pathway analysis highlighted an over-representation of the Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteases signaling pathway (Table1). Among the most upregulated genes, using string DB software, we identified hubs corresponding to genes involved in extracellular matrix formation, such as collagen genes and ADAMTS genes (Figure 1). RT-qPCR allowed to confirm the upregulation of COL3A1 in SGECs from pSS compared to controls (Figure 2A). Interestingly, among the other upregulated genes in RNAseq, MMP24 was significantly higher in SGECs from pSS with a focus score (FS) >1 on MSG biopsy than pSS with a FS < 1 (Figure 2B). We hypothesized that SGECs may undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during pSS. We looked at EMT transcription factors, and observed a trend for an up regulation of SNAI1 (coding for SNAIL) and ZEB2, and for a down regulation of SLUG in SGECs from pSS with FS >1 compared to pSS with a FS< 1 (Figure 2B). Interestingly, there was an inverse correlation between SLUG expression and the focus score in SG, and we also observed a correlation between ZEB2 expression and the focus score (Figure 2C)
Conclusion: We found an increased expression of Matrix Metalloproteases signaling pathway and a trend for increased expression of several genes involved in EMT between pSS and controls. Thus, besides a role in immune cells activation, we found another possible pathogenic role of SGECs in pSS through the induction of SG fibrosis development. The correlation between genes involved in EMT expression and lymphocytic infiltrates in the SG suggests that the crosstalk between SGECs and lymphoid cells could be bi-directional from SGECs to immune cells, but also from immune cells to SGECs.
References:
1. Rivière E, et al., Ann Rheum Dis. 2020
2. Sisto M, et al. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 2020
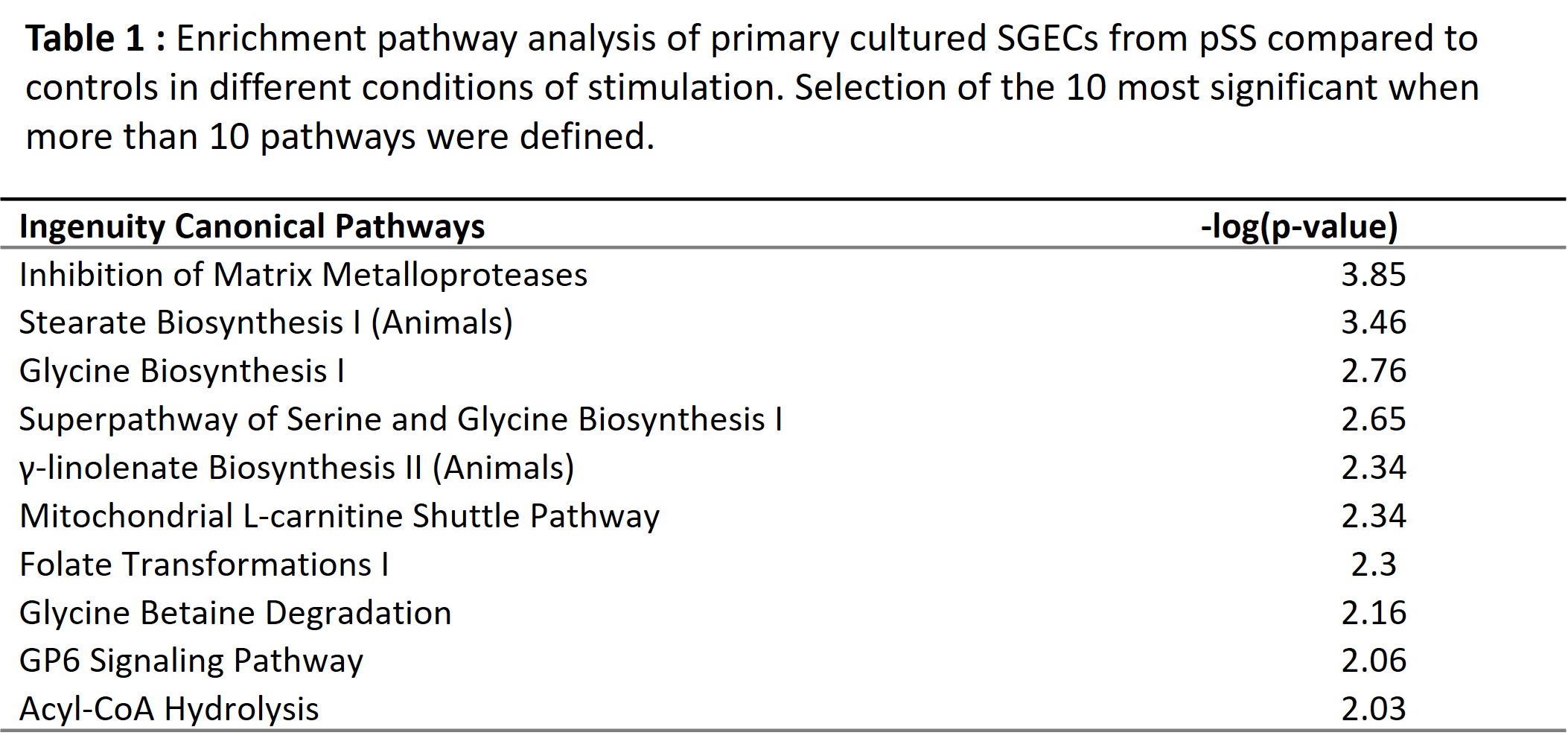 Table 1
Table 1
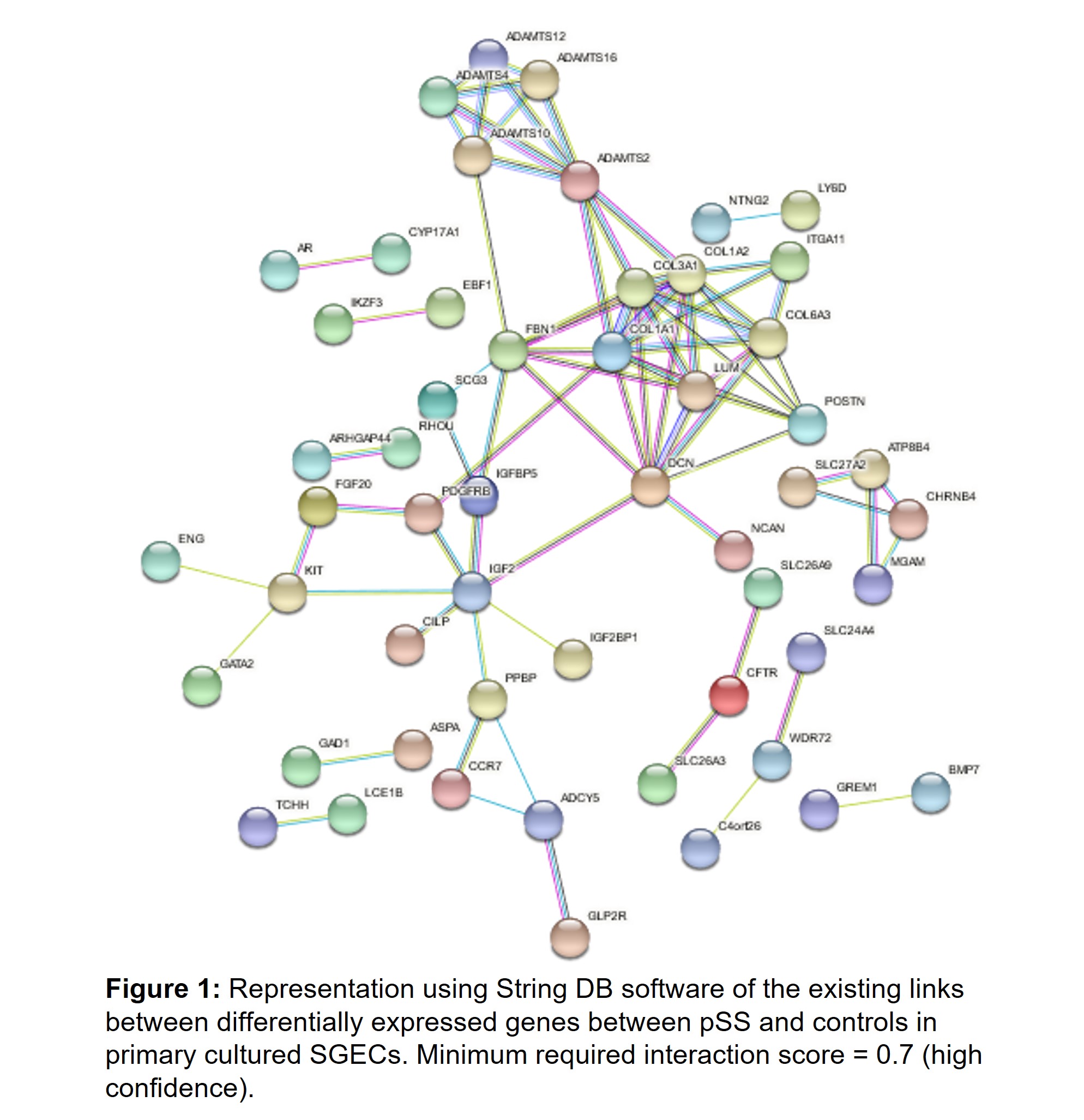 Figure 1
Figure 1
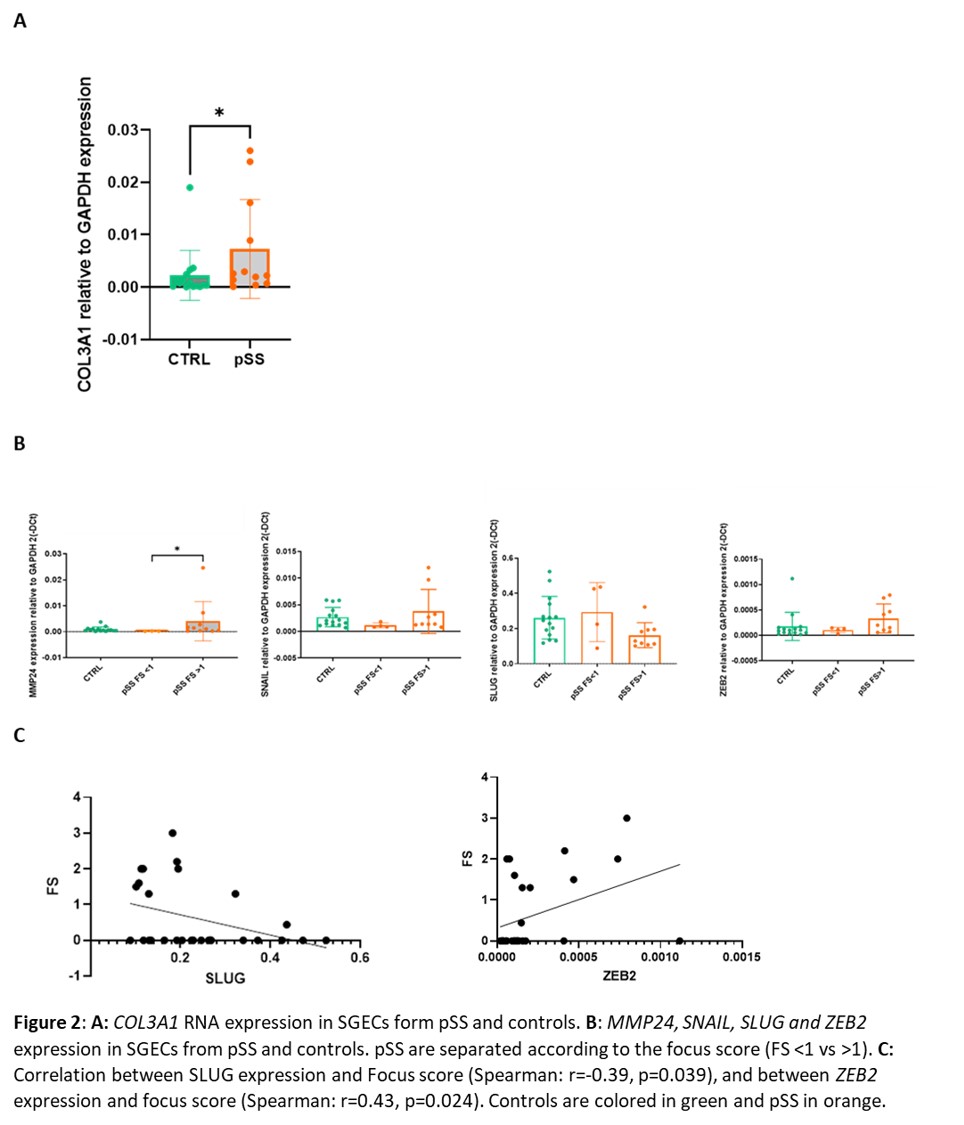 Figure 2
Figure 2
Disclosures: E. Riviere, None; J. Pascaud, None; F. Letourneur, None; G. Nocturne, Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Amgen; X. Mariette, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer.
Background/Purpose: Salivary gland epithelial cells (SGECs) are not only the target of autoimmunity in primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS). SGECs may interact with lymphocytes and therefore participate to the over activation of the immune system (1). Moreover, SGECs may undergo TGFb mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition during pSS (2).
We aimed to determine whether SGECs from pSS present intrinsic abnormalities that may be involved in pSS pathogenesis, especially concerning their potential role in salivary gland microenvironment modifications.
Methods: Minor salivary gland (MSG) biopsies were obtained from patients referred for suspicion of pSS to the Rheumatology Department of Bicêtre hospital, AP-HP, Université Paris-Saclay, a tertiary reference center for systemic auto-immune diseases. pSS was defined according to the 2016 ACR/EULAR criteria. RNAseq analysis of primary SGECs (5 controls and 5 pSS) was performed after 2-3 weeks of culture (Illumina). Statistical analyses on the read counts were performed with the DESeq2 package. Absolute FC value >1.5 and p-value< 0.05 was applied to identify up and down-regulated genes. Confirmation RT-qPCR were then performed on additional SGECs samples (n = 15 controls and 13 pSS).
Results: RNAseq analysis of SGECs from pSS compared to controls identified 251 upregulated and 260 downregulated genes. Functional enrichment pathway analysis highlighted an over-representation of the Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteases signaling pathway (Table1). Among the most upregulated genes, using string DB software, we identified hubs corresponding to genes involved in extracellular matrix formation, such as collagen genes and ADAMTS genes (Figure 1). RT-qPCR allowed to confirm the upregulation of COL3A1 in SGECs from pSS compared to controls (Figure 2A). Interestingly, among the other upregulated genes in RNAseq, MMP24 was significantly higher in SGECs from pSS with a focus score (FS) >1 on MSG biopsy than pSS with a FS < 1 (Figure 2B). We hypothesized that SGECs may undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during pSS. We looked at EMT transcription factors, and observed a trend for an up regulation of SNAI1 (coding for SNAIL) and ZEB2, and for a down regulation of SLUG in SGECs from pSS with FS >1 compared to pSS with a FS< 1 (Figure 2B). Interestingly, there was an inverse correlation between SLUG expression and the focus score in SG, and we also observed a correlation between ZEB2 expression and the focus score (Figure 2C)
Conclusion: We found an increased expression of Matrix Metalloproteases signaling pathway and a trend for increased expression of several genes involved in EMT between pSS and controls. Thus, besides a role in immune cells activation, we found another possible pathogenic role of SGECs in pSS through the induction of SG fibrosis development. The correlation between genes involved in EMT expression and lymphocytic infiltrates in the SG suggests that the crosstalk between SGECs and lymphoid cells could be bi-directional from SGECs to immune cells, but also from immune cells to SGECs.
References:
1. Rivière E, et al., Ann Rheum Dis. 2020
2. Sisto M, et al. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 2020
 Table 1
Table 1 Figure 1
Figure 1 Figure 2
Figure 2Disclosures: E. Riviere, None; J. Pascaud, None; F. Letourneur, None; G. Nocturne, Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Amgen; X. Mariette, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer.

