Back
Poster Session A
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0045–0055) RA – Animal Models Poster
0053: Natural Microbial Exposure Increases Susceptibility of C57BL/6 Mice to Collagen-induced Arthritis
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

Sahar Lotfi-Emran, MD, PhD
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, MN, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Sahar Lotfi-Emran1 and David Masopust2, 1University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, 2University of Minnesota, Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Minneapolis, MN
Background/Purpose: Mice exposed to natural microbes (NME) develop an appropriately mature immune system, one that resembles that of a non-neonatal human.1,2 Collagen induced arthritis is a standard protocol for induction of inflammatory arthritis in susceptible mouse strains that notably does not develop in germ free conditions and whose clinical expression can be altered with manipulation of mouse microbiome.3-7 The mouse strain with the most tools, C57BL/6 (BL6), is not susceptible to CIA.8 We demonstrate that despite comparable anti-collagen antibody production to their SPF counterparts, NME BL6 mice readily develop CIA. In addition, NME CIA mice harbor more neutrophils and CD8+ T cells in joints compared to SPF counterparts.
Methods: In a BSL-3 facility, petstore mice were introduced into the cages of 8 week (wk) old BL6 mice for 8 wks. Controls remained in SPF facilities. Following co-housing, mice received intradermal (i.d.) injection of 100 ug chicken collagen II in complete freund's adjuvant (CFA) and concurrent intraperitoneal (i.p.) pertussis toxin (PTx). 2-3 wks later, they received i.d. collagen II in incomplete FA (IFA) and i.p. PTx. Collagen-absent CFA and IFA served as control. (Fig 1A). Mice were clinically scored and weighed weekly as described.8 Prior to tissue harvest, mice received intravascular anti-CD45.2 antibody to discriminate between tissue and intravascular cells.9 Knee synovial tissue was harvested as described10, digested in collagenase II, stained with live-dead discrimination reagent and antibodies for surface protein expression, then evaluated with flow cytometry. Serum was collected at multiple time points and assessed for anti-Collagen II IgG by ELISA (Chondrex, Woodinville, WA). Data was analyzed and visualized with Graphpad prism 9.
Results: NME CIA mice weigh less than their SPF and CIA-control counterparts (Fig 1B). 73% (8 of 11) dirty mice developed CIA, starting 28 days after induction, whereas none of the SPF or control NME mice developed disease (Fig 1C). No difference was detected in serum anti-Collagen II IgG between SPF and NME CIA mice. (Fig 1D) Comparison of synovial cells in NME versus SPF CIA demonstrates a significant increase in neutrophils and CD8+ T cells (Fig 2). Neither B cells nor CD4+ T cells were increased in joints (Fig 2). Neither CD4+ T cells nor CD8+ T cells expressed CD25, an activation marker and a marker of T regulatory cells. Joint CD8+ T cells are antigen experienced cells, CD44+ and CD62L low (Fig 3A). A subset express CD69 resembling resident memory CD8+ T cells (TRM, Fig 3B). Notably, they do not express CD103, a hallmark of CD8+ TRM in some tissues.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that NME renders BL6 mice susceptible to CIA induced inflammatory arthritis. This susceptibility is not associated with a difference in anti-collagen II antibody production but is associated with an accumulation of joint neutrophils and CD8+ T cells resembling TRM. The disjuncture between pathologic antibody production and clinical disease in NME CIA parallels the noted presence of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies decades prior to clinical disease expression in human Rheumatoid Arthritis.
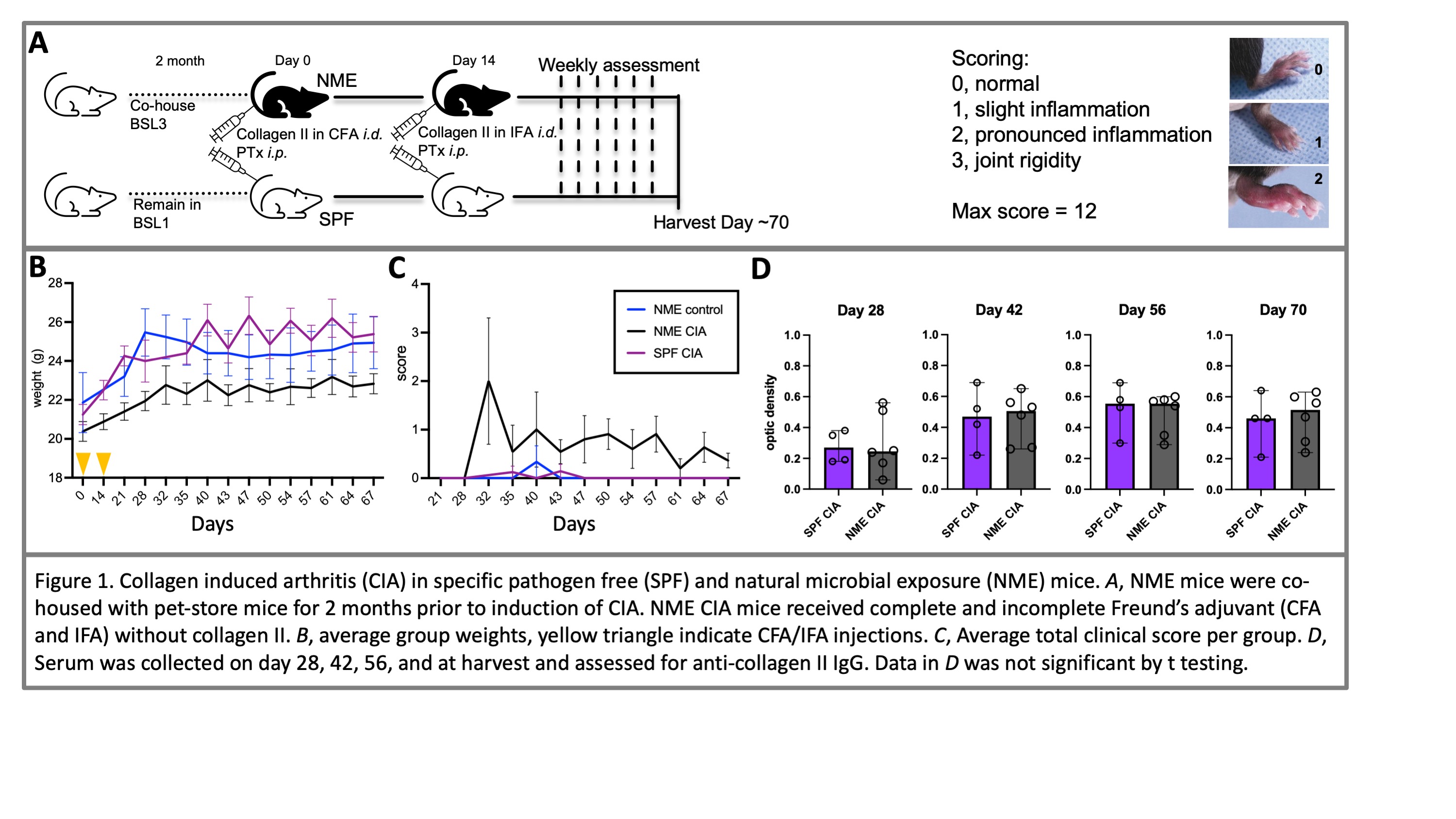 Figure 1. Collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in specific pathogen free (SPF) and natural microbial exposure (NME) mice. A, NME mice were co-housed with pet-store mice for 2 months prior to induction of CIA. NME CIA mice received complete and incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA and IFA) without collagen II. B, average group weights, yellow triangle indicate CFA/IFA injections. C, Average total clinical score per group. D, Serum was collected on day 28, 42, 56, and at harvest and assessed for anti-collagen II IgG. Data in D was not significant by t testing.
Figure 1. Collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in specific pathogen free (SPF) and natural microbial exposure (NME) mice. A, NME mice were co-housed with pet-store mice for 2 months prior to induction of CIA. NME CIA mice received complete and incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA and IFA) without collagen II. B, average group weights, yellow triangle indicate CFA/IFA injections. C, Average total clinical score per group. D, Serum was collected on day 28, 42, 56, and at harvest and assessed for anti-collagen II IgG. Data in D was not significant by t testing.
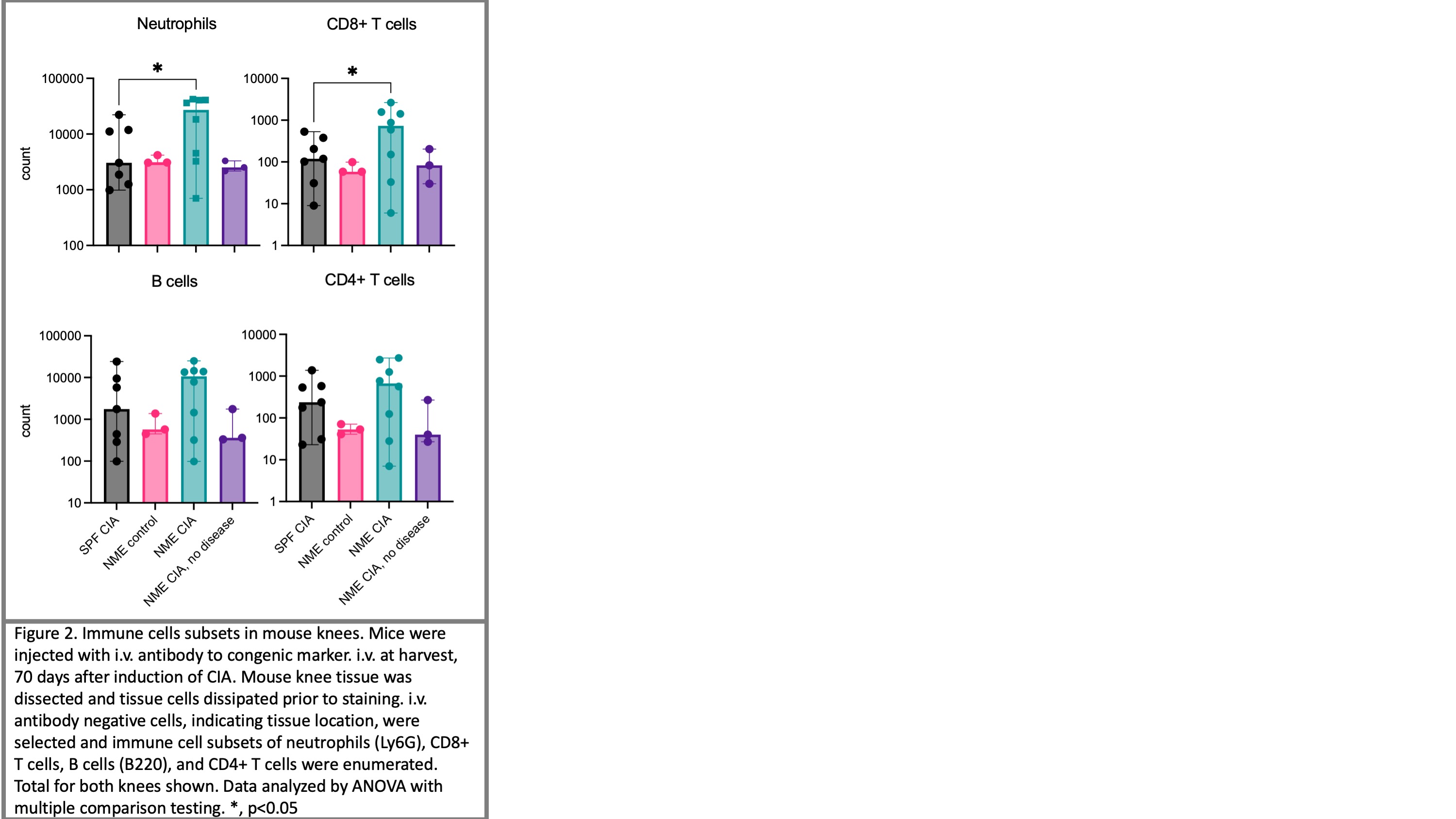 Figure 2. Immune cells subsets in mouse knees. Mice were injected with i.v. antibody to congenic marker. i.v. at harvest, 70 days after induction of CIA. Mouse knee tissue was dissected and tissue cells dissipated prior to staining. i.v. antibody negative cells, indicating tissue location, were selected and immune cell subsets of neutrophils (Ly6G), CD8+ T cells, B cells (B220), and CD4+ T cells were enumerated. Total for both knees shown. Data analyzed by ANOVA with multiple comparison testing. *, p < 0.05
Figure 2. Immune cells subsets in mouse knees. Mice were injected with i.v. antibody to congenic marker. i.v. at harvest, 70 days after induction of CIA. Mouse knee tissue was dissected and tissue cells dissipated prior to staining. i.v. antibody negative cells, indicating tissue location, were selected and immune cell subsets of neutrophils (Ly6G), CD8+ T cells, B cells (B220), and CD4+ T cells were enumerated. Total for both knees shown. Data analyzed by ANOVA with multiple comparison testing. *, p < 0.05
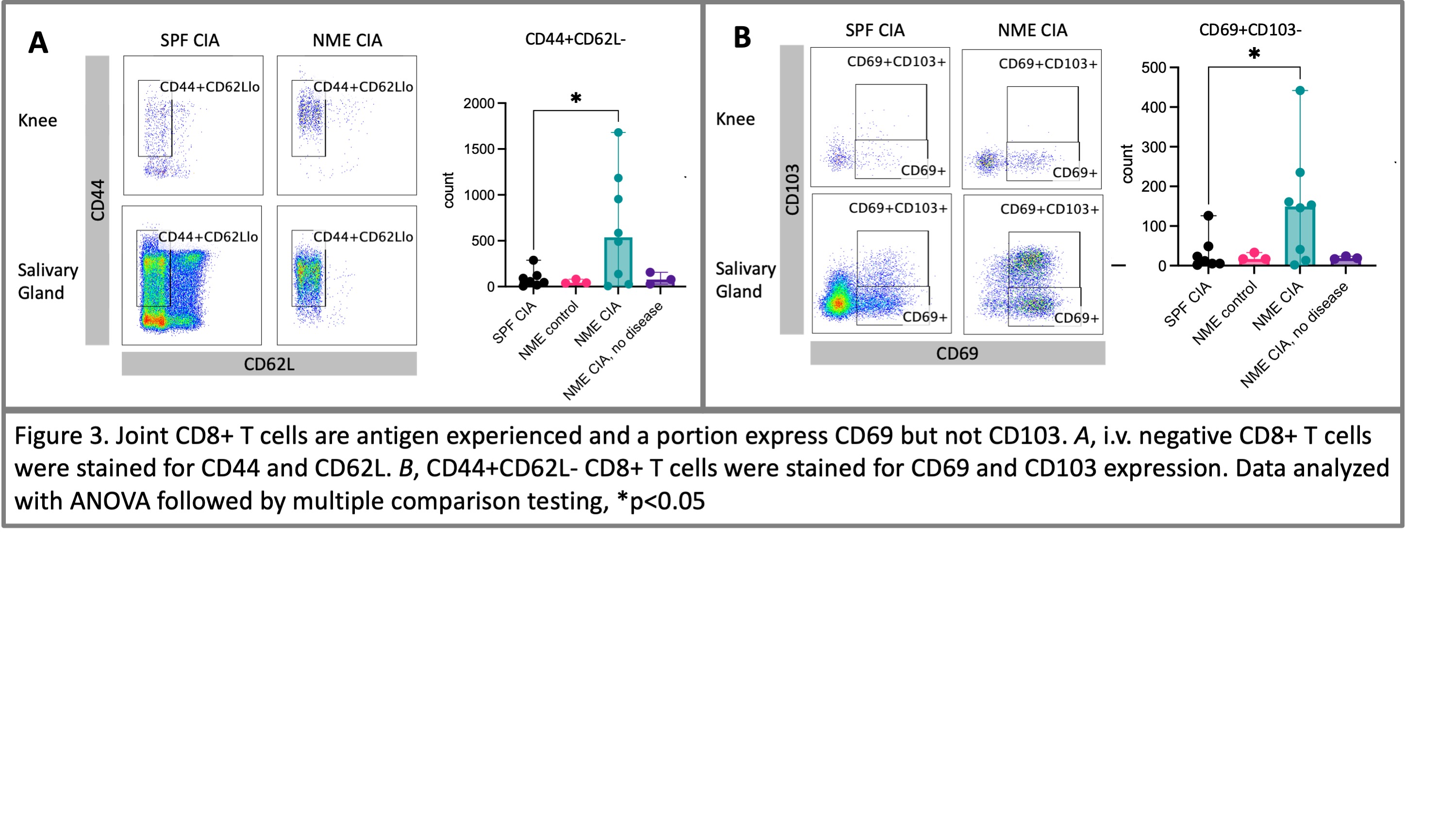 Figure 3. Joint CD8+ T cells are antigen experienced and a portion express CD69 but not CD103. A, i.v. negative CD8+ T cells were stained for CD44 and CD62L. B, CD44+CD62L- CD8+ T cells were stained for CD69 and CD103 expression. Data analyzed with ANOVA followed by multiple comparison testing, *p < 0.05
Figure 3. Joint CD8+ T cells are antigen experienced and a portion express CD69 but not CD103. A, i.v. negative CD8+ T cells were stained for CD44 and CD62L. B, CD44+CD62L- CD8+ T cells were stained for CD69 and CD103 expression. Data analyzed with ANOVA followed by multiple comparison testing, *p < 0.05
Disclosures: S. Lotfi-Emran, None; D. Masopust, None.
Background/Purpose: Mice exposed to natural microbes (NME) develop an appropriately mature immune system, one that resembles that of a non-neonatal human.1,2 Collagen induced arthritis is a standard protocol for induction of inflammatory arthritis in susceptible mouse strains that notably does not develop in germ free conditions and whose clinical expression can be altered with manipulation of mouse microbiome.3-7 The mouse strain with the most tools, C57BL/6 (BL6), is not susceptible to CIA.8 We demonstrate that despite comparable anti-collagen antibody production to their SPF counterparts, NME BL6 mice readily develop CIA. In addition, NME CIA mice harbor more neutrophils and CD8+ T cells in joints compared to SPF counterparts.
Methods: In a BSL-3 facility, petstore mice were introduced into the cages of 8 week (wk) old BL6 mice for 8 wks. Controls remained in SPF facilities. Following co-housing, mice received intradermal (i.d.) injection of 100 ug chicken collagen II in complete freund's adjuvant (CFA) and concurrent intraperitoneal (i.p.) pertussis toxin (PTx). 2-3 wks later, they received i.d. collagen II in incomplete FA (IFA) and i.p. PTx. Collagen-absent CFA and IFA served as control. (Fig 1A). Mice were clinically scored and weighed weekly as described.8 Prior to tissue harvest, mice received intravascular anti-CD45.2 antibody to discriminate between tissue and intravascular cells.9 Knee synovial tissue was harvested as described10, digested in collagenase II, stained with live-dead discrimination reagent and antibodies for surface protein expression, then evaluated with flow cytometry. Serum was collected at multiple time points and assessed for anti-Collagen II IgG by ELISA (Chondrex, Woodinville, WA). Data was analyzed and visualized with Graphpad prism 9.
Results: NME CIA mice weigh less than their SPF and CIA-control counterparts (Fig 1B). 73% (8 of 11) dirty mice developed CIA, starting 28 days after induction, whereas none of the SPF or control NME mice developed disease (Fig 1C). No difference was detected in serum anti-Collagen II IgG between SPF and NME CIA mice. (Fig 1D) Comparison of synovial cells in NME versus SPF CIA demonstrates a significant increase in neutrophils and CD8+ T cells (Fig 2). Neither B cells nor CD4+ T cells were increased in joints (Fig 2). Neither CD4+ T cells nor CD8+ T cells expressed CD25, an activation marker and a marker of T regulatory cells. Joint CD8+ T cells are antigen experienced cells, CD44+ and CD62L low (Fig 3A). A subset express CD69 resembling resident memory CD8+ T cells (TRM, Fig 3B). Notably, they do not express CD103, a hallmark of CD8+ TRM in some tissues.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that NME renders BL6 mice susceptible to CIA induced inflammatory arthritis. This susceptibility is not associated with a difference in anti-collagen II antibody production but is associated with an accumulation of joint neutrophils and CD8+ T cells resembling TRM. The disjuncture between pathologic antibody production and clinical disease in NME CIA parallels the noted presence of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies decades prior to clinical disease expression in human Rheumatoid Arthritis.
 Figure 1. Collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in specific pathogen free (SPF) and natural microbial exposure (NME) mice. A, NME mice were co-housed with pet-store mice for 2 months prior to induction of CIA. NME CIA mice received complete and incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA and IFA) without collagen II. B, average group weights, yellow triangle indicate CFA/IFA injections. C, Average total clinical score per group. D, Serum was collected on day 28, 42, 56, and at harvest and assessed for anti-collagen II IgG. Data in D was not significant by t testing.
Figure 1. Collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in specific pathogen free (SPF) and natural microbial exposure (NME) mice. A, NME mice were co-housed with pet-store mice for 2 months prior to induction of CIA. NME CIA mice received complete and incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA and IFA) without collagen II. B, average group weights, yellow triangle indicate CFA/IFA injections. C, Average total clinical score per group. D, Serum was collected on day 28, 42, 56, and at harvest and assessed for anti-collagen II IgG. Data in D was not significant by t testing. Figure 2. Immune cells subsets in mouse knees. Mice were injected with i.v. antibody to congenic marker. i.v. at harvest, 70 days after induction of CIA. Mouse knee tissue was dissected and tissue cells dissipated prior to staining. i.v. antibody negative cells, indicating tissue location, were selected and immune cell subsets of neutrophils (Ly6G), CD8+ T cells, B cells (B220), and CD4+ T cells were enumerated. Total for both knees shown. Data analyzed by ANOVA with multiple comparison testing. *, p < 0.05
Figure 2. Immune cells subsets in mouse knees. Mice were injected with i.v. antibody to congenic marker. i.v. at harvest, 70 days after induction of CIA. Mouse knee tissue was dissected and tissue cells dissipated prior to staining. i.v. antibody negative cells, indicating tissue location, were selected and immune cell subsets of neutrophils (Ly6G), CD8+ T cells, B cells (B220), and CD4+ T cells were enumerated. Total for both knees shown. Data analyzed by ANOVA with multiple comparison testing. *, p < 0.05 Figure 3. Joint CD8+ T cells are antigen experienced and a portion express CD69 but not CD103. A, i.v. negative CD8+ T cells were stained for CD44 and CD62L. B, CD44+CD62L- CD8+ T cells were stained for CD69 and CD103 expression. Data analyzed with ANOVA followed by multiple comparison testing, *p < 0.05
Figure 3. Joint CD8+ T cells are antigen experienced and a portion express CD69 but not CD103. A, i.v. negative CD8+ T cells were stained for CD44 and CD62L. B, CD44+CD62L- CD8+ T cells were stained for CD69 and CD103 expression. Data analyzed with ANOVA followed by multiple comparison testing, *p < 0.05Disclosures: S. Lotfi-Emran, None; D. Masopust, None.

