Back
Poster Session A
Epidemiology, health policy and outcomes
Session: (0187–0213) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, and Attitudes Poster I
0191: Patient-reported Outcomes to Assess Dyspnea in Connective Tissue Diseases, Interstitial Lung Disease and Pulmonary Hypertension, a Systematic Literature Review of Measurement Properties
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- JL
Jacqueline Lemmers, MSc
Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen
Nijmegen, Netherlands
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Jacqueline Lemmers1, Madelon Vonk2 and Els Ende, van den3, 1Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen, Nijmegen, Netherlands, 2Department of Rheumatology, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands, 3Radboudumc, Nijmegen, Netherlands
Background/Purpose: This COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review aims to identify and summarize the quality of measurement properties of dyspnea-specific patient reported outcome measures (PROMS), for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), pulmonary hypertension (PH) or connective-tissue diseases (CTD).
Methods: A systematic literature search in PUBMED and EMBASE, was last updated in March 2022 to identify publications evaluating ≥1 measurement properties on dyspnea-specific PROMS in our target population. Based on COMIN analysis and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach, overall rating and level of evidence for identified measurement properties of included PROMS was assessed, and used to formulate recommendations.
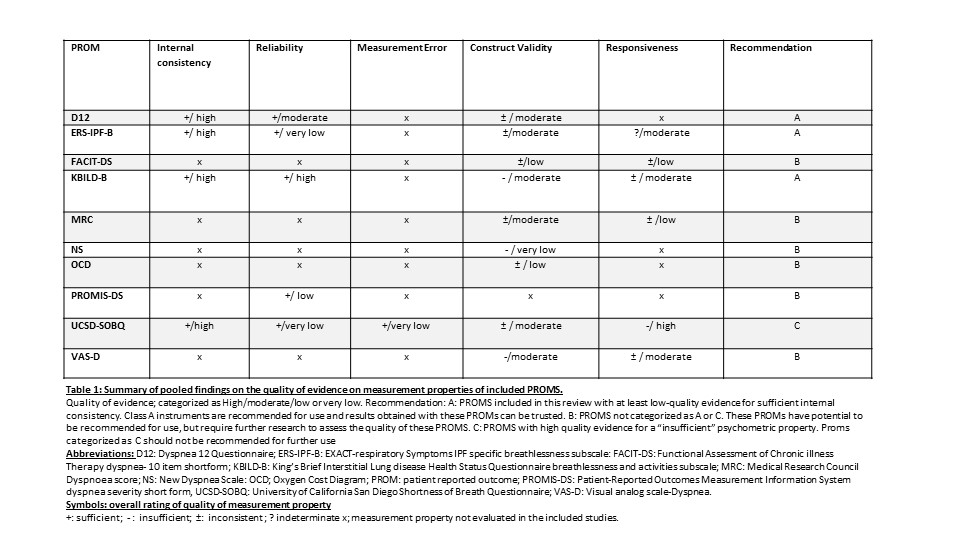
Results: We identified 26 publications on 10 PROMS. The Dyspnea-12 (D12), EXACT-respiratory Symptoms-IPF- breathlessness subscale (ERS-IPF-B) and King's Brief Interstitial Lung Disease Health Status Questionnaire - breathlessness and activities subscale (K-BILD-B) had high quality evidence for sufficient internal consistency, without high quality evidence of insufficient measurement properties, and can therefore be recommended for use. The University of California San Diego Shortness of Breath Questionnaire (UCSD-SOBQ) showed insufficient responsiveness in this target population. Most PROMS in this systematic review have moderate or low quality evidence on construct validity and responsiveness.
Conclusion: The K-BILD-B, despite lacking evidence on several important domains, is currently considered the best performing PROM. The UCSD-SOBQ is not recommended for use, due to high quality evidence on insufficient responsiveness in this population.
Disclosures: J. Lemmers, None; M. Vonk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ferrer, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck/MSD, Corbus, EUSTAR; E. Ende, van den, None.
Background/Purpose: This COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN)-based systematic review aims to identify and summarize the quality of measurement properties of dyspnea-specific patient reported outcome measures (PROMS), for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), pulmonary hypertension (PH) or connective-tissue diseases (CTD).
Methods: A systematic literature search in PUBMED and EMBASE, was last updated in March 2022 to identify publications evaluating ≥1 measurement properties on dyspnea-specific PROMS in our target population. Based on COMIN analysis and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach, overall rating and level of evidence for identified measurement properties of included PROMS was assessed, and used to formulate recommendations.
Results: We identified 26 publications on 10 PROMS. The Dyspnea-12 (D12), EXACT-respiratory Symptoms-IPF- breathlessness subscale (ERS-IPF-B) and King's Brief Interstitial Lung Disease Health Status Questionnaire - breathlessness and activities subscale (K-BILD-B) had high quality evidence for sufficient internal consistency, without high quality evidence of insufficient measurement properties, and can therefore be recommended for use. The University of California San Diego Shortness of Breath Questionnaire (UCSD-SOBQ) showed insufficient responsiveness in this target population. Most PROMS in this systematic review have moderate or low quality evidence on construct validity and responsiveness.
Conclusion: The K-BILD-B, despite lacking evidence on several important domains, is currently considered the best performing PROM. The UCSD-SOBQ is not recommended for use, due to high quality evidence on insufficient responsiveness in this population.

Disclosures: J. Lemmers, None; M. Vonk, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ferrer, Galapagos, Janssen, Merck/MSD, Corbus, EUSTAR; E. Ende, van den, None.

