Back
Ignite Talk
Session: Ignite Session 8C
L14: Bimekizumab Maintains Improvements in Efficacy Endpoints and Has a Consistent Safety Profile Through 52 Weeks in Patients with Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis: Results from Two Parallel Phase 3 Studies
Monday, November 14, 2022
2:35 PM – 2:40 PM Eastern Time
Location: South Philly Stage
- XB
Xenofon Baraliakos, MD
Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne
Herne, GermanyDisclosure: Disclosure information not submitted.
Ignite Speaker(s)
Xenofon Baraliakos1, Atul Deodhar2, Désirée van der Heijde3, Marina Magrey4, Walter Maksymowych5, Tetsuya Tomita6, Huji Xu7, Marga Oortgiesen8, Ute Massow9, Carmen Fleurinck10, Alicia M Ellis8, Tom Vaux11, Julie Shepherd-Smith11, Alexander Marten9 and Lianne S Gensler12, 1Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany, 2Division of Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, 3Department of Rheumatology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 4Case Western Reserve University, MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, OH, US, Richfield, OH, 5Department of Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 6Graduate School of Health Science, Morinomiya University of Medical Science, Osaka City, Osaka City, Osaka, Japan, 7Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, Affiliated to Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China (People's Republic), 8UCB Pharma, Morrisvile, NC, 9UCB Pharma, Monheim am Rhein, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany, 10UCB Pharma, Brussels, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest, Belgium, 11UCB Pharma, Slough, United Kingdom, 12Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL‑17A. In the phase 3 BE MOBILE 1 and 2 studies, BKZ met all primary/secondary endpoints at Week (Wk)16 in patients (pts) with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS; also known as radiographic axSpA), respectively.1,2 Here, we present the first phase 3 results from up to Wk52 of BKZ treatment.
Methods: BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704; nr-axSpA) and 2 (NCT03928743; AS) were conducted in parallel and had similar designs, with a 16-wk placebo (PBO)-controlled and 36-wk maintenance period.1,2 Pts were randomized to subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg Q4W (BKZ) or to PBO then BKZ from Wk16 (PBO/BKZ). Efficacy endpoints were assessed through Wk52. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs; MedDRA v19.0) following first BKZ exposure are reported at the Wk52 data cut.
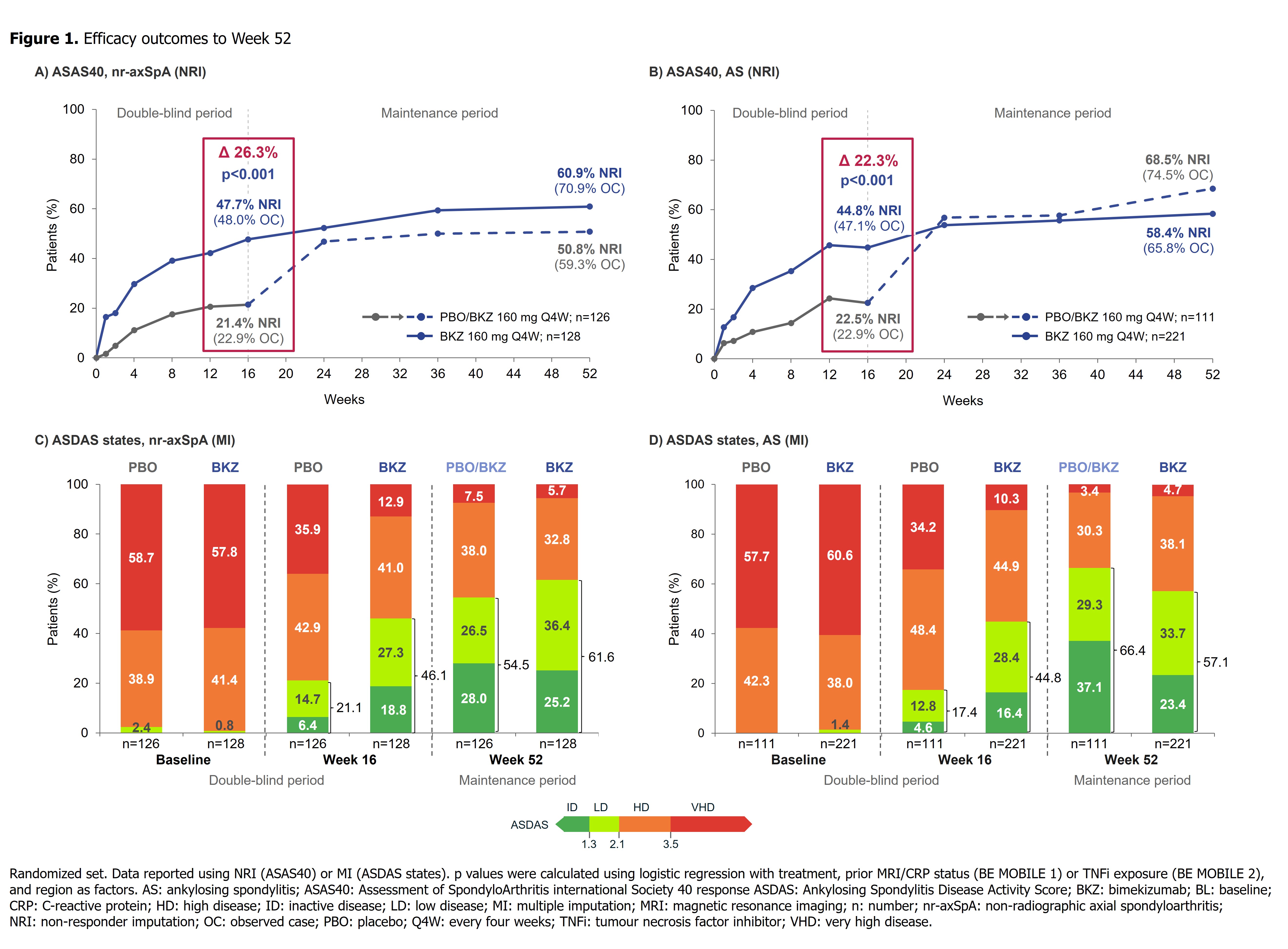
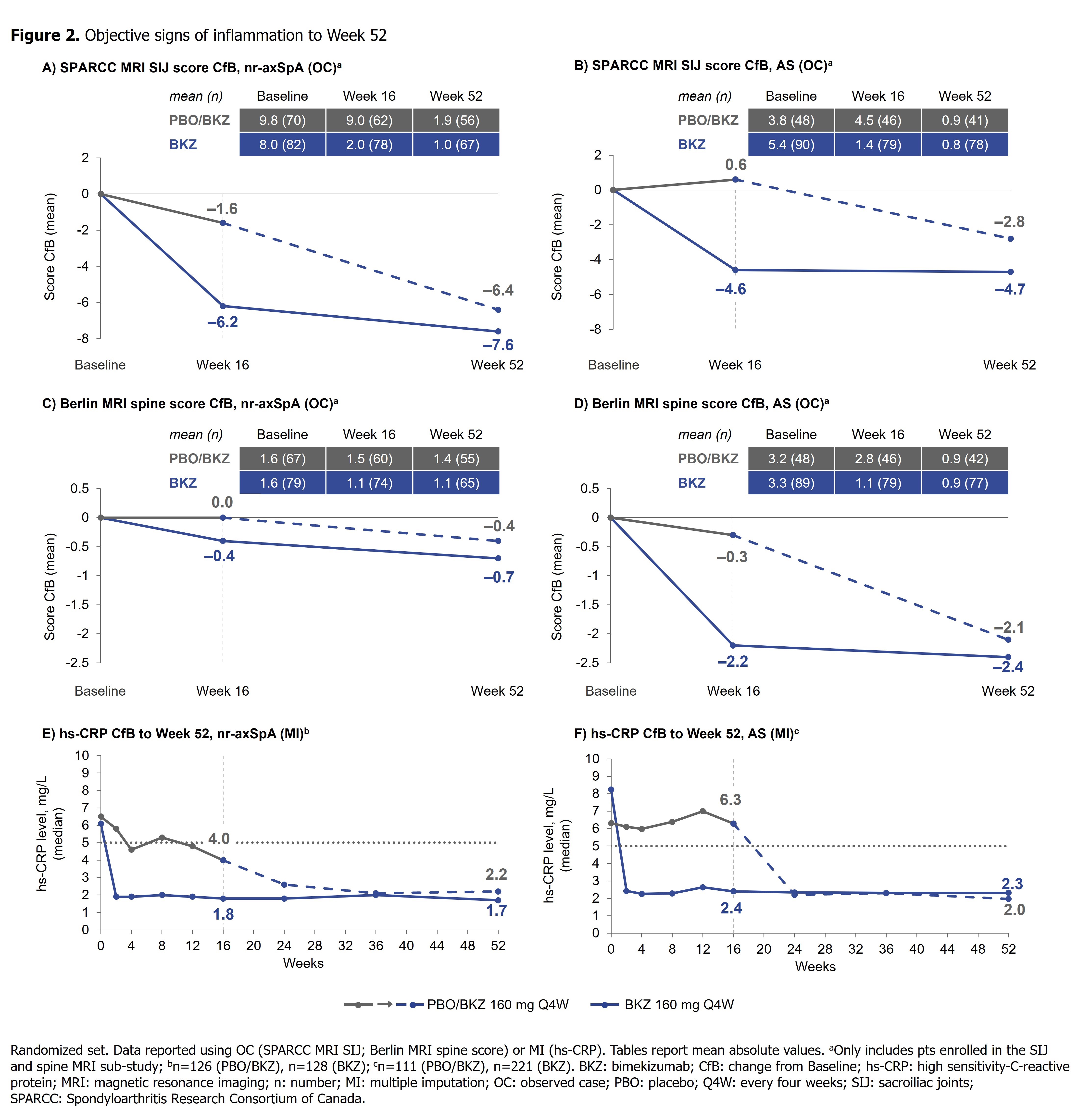
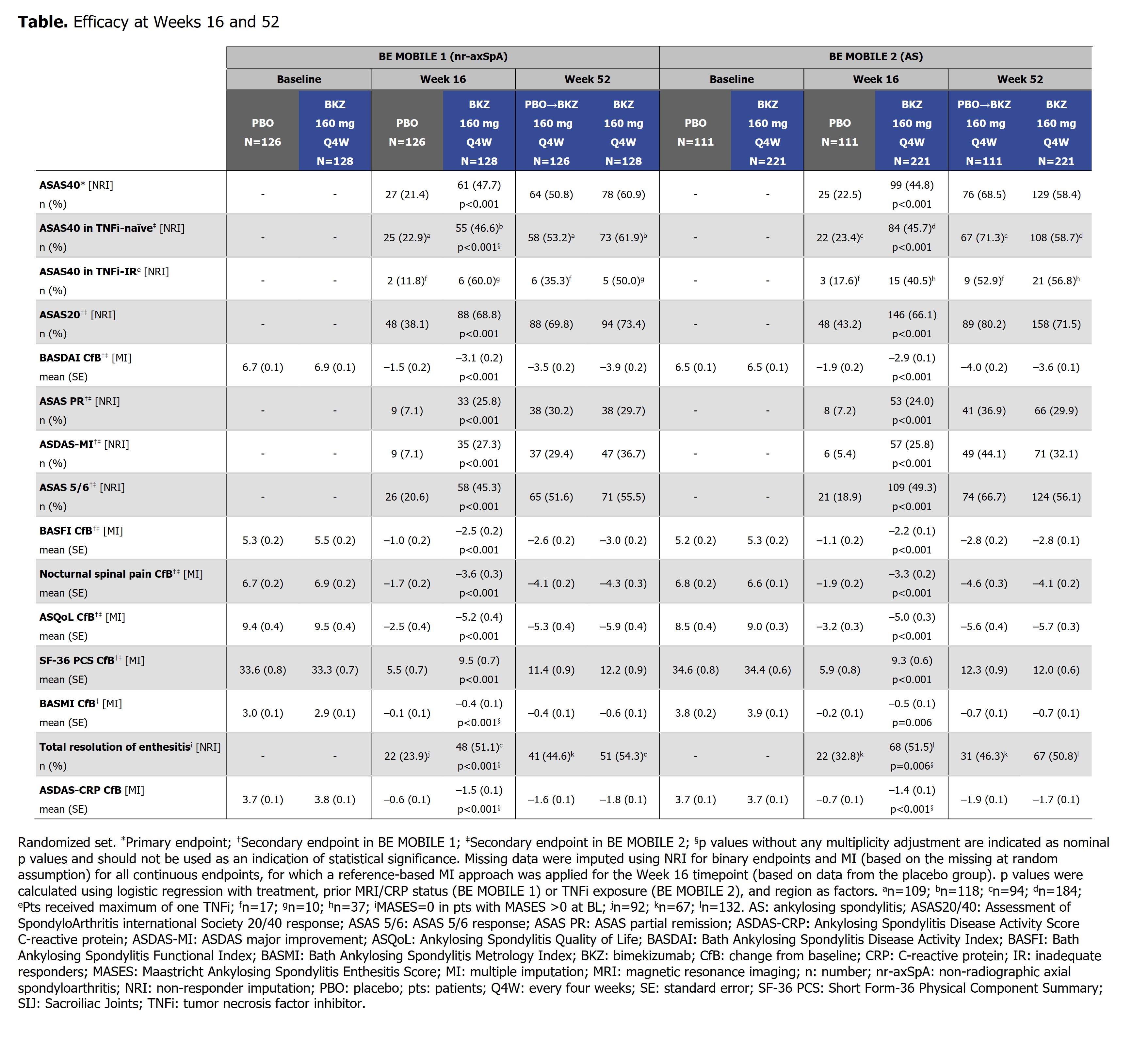
Results: 220/254 (86.6%) randomized pts with nr-axSpA and 298/332 (89.8%) with AS completed Wk52. In both studies, efficacy was sustained to Wk52 (Table). ASAS40 responses in BKZ-randomized pts increased from Wk16 (nr-axSpA: 47.7%; AS: 44.8%; non-responder imputation [NRI]) to Wk52 (nr-axSpA: 60.9%; AS: 58.4%; NRI) (Figure 1), with high levels of efficacy across both TNFi-naïve and TNFi-inadequate responder populations (Table). At Wk52, ASDAS < 2.1 was achieved by 61.6% and 57.1%, and ASDAS < 1.3 by 25.2% and 23.4%, of BKZ-randomized pts with nr-axSpA and AS, respectively (Figure 1). The Wk16 reductions from baseline in objective signs of inflammation (MRI, hs-CRP; Figure 2), and improvements in function (BASFI), and AS Quality of Life (Table), were maintained through 52 wks. Among PBO/BKZ-treated pts, efficacy at Wk52 was similar to that seen in BKZ-randomized pts (Figure 1; Table).
At the Wk52 data cut, 75.0% (183/244) of pts with nr-axSpA and 75.5% (249/330) of pts with AS had ≥1 TEAE on BKZ; the most frequent (by % pts) TEAEs by preferred term were nasopharyngitis (nr-axSpA: 12.3%; AS: 9.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (nr-axSpA: 9.4%; AS: 6.4%) and oral candidiasis (nr-axSpA: 7.4%; AS: 6.1%); few COVID-19 infections were reported (nr-axSpA: 7.0%; AS; 2.1%). Incidence (pts/100 patient years) of serious TEAEs were low (nr-axSpA: 4.4; AS: 7.1); no major adverse cardiovascular events, active tuberculosis cases, serious COVID-19 infections, or deaths were reported. Most incidences of fungal infection (nr-axSpA: 19.6; AS: 14.9; none serious or systemic) were Candida (nr-axSpA: 12.8; AS: 8.3) and mild to moderate; two pts with nr-axSpA and two with AS discontinued the study due to Candida infections. Incidence of IBD (nr-axSpA: 1.0; AS: 1.0) and uveitis (nr-axSpA: 1.5; AS: 2.4) were low.
Conclusion: Across the full axSpA disease spectrum, BKZ treatment resulted in sustained efficacy, including suppression of inflammation and improvements in function and quality of life, to Wk52. No new safety signals were observed, consistent with the safety profile established from Wk24 data.1,2
References: 1. Deodhar A. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:772–3; 2. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:12–3.
Disclosures: X. Baraliakos, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, MSD, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Celgene; A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GSK, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Amgen, Aurinia, Janssen, MoonLake; D. van der Heijde, AbbVie, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cyxone, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Imaging Rheumatology BV; M. Magrey, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Celgene, Galapagos, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, CARE Arthritis Limited, Boehringer-Ingelheim; T. Tomita, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Mitsubishi-Tanabe; H. Xu, AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Beigene, BioMap, IASO, Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences; M. Oortgiesen, UCB Pharma; U. Massow, UCB Pharma; C. Fleurinck, UCB Pharma; A. Ellis, UCB Pharma; T. Vaux, UCB Pharma; J. Shepherd-Smith, UCB Pharma; A. Marten, UCB Pharma; L. Gensler, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma.
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL‑17A. In the phase 3 BE MOBILE 1 and 2 studies, BKZ met all primary/secondary endpoints at Week (Wk)16 in patients (pts) with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS; also known as radiographic axSpA), respectively.1,2 Here, we present the first phase 3 results from up to Wk52 of BKZ treatment.
Methods: BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704; nr-axSpA) and 2 (NCT03928743; AS) were conducted in parallel and had similar designs, with a 16-wk placebo (PBO)-controlled and 36-wk maintenance period.1,2 Pts were randomized to subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg Q4W (BKZ) or to PBO then BKZ from Wk16 (PBO/BKZ). Efficacy endpoints were assessed through Wk52. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs; MedDRA v19.0) following first BKZ exposure are reported at the Wk52 data cut.
Results: 220/254 (86.6%) randomized pts with nr-axSpA and 298/332 (89.8%) with AS completed Wk52. In both studies, efficacy was sustained to Wk52 (Table). ASAS40 responses in BKZ-randomized pts increased from Wk16 (nr-axSpA: 47.7%; AS: 44.8%; non-responder imputation [NRI]) to Wk52 (nr-axSpA: 60.9%; AS: 58.4%; NRI) (Figure 1), with high levels of efficacy across both TNFi-naïve and TNFi-inadequate responder populations (Table). At Wk52, ASDAS < 2.1 was achieved by 61.6% and 57.1%, and ASDAS < 1.3 by 25.2% and 23.4%, of BKZ-randomized pts with nr-axSpA and AS, respectively (Figure 1). The Wk16 reductions from baseline in objective signs of inflammation (MRI, hs-CRP; Figure 2), and improvements in function (BASFI), and AS Quality of Life (Table), were maintained through 52 wks. Among PBO/BKZ-treated pts, efficacy at Wk52 was similar to that seen in BKZ-randomized pts (Figure 1; Table).
At the Wk52 data cut, 75.0% (183/244) of pts with nr-axSpA and 75.5% (249/330) of pts with AS had ≥1 TEAE on BKZ; the most frequent (by % pts) TEAEs by preferred term were nasopharyngitis (nr-axSpA: 12.3%; AS: 9.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (nr-axSpA: 9.4%; AS: 6.4%) and oral candidiasis (nr-axSpA: 7.4%; AS: 6.1%); few COVID-19 infections were reported (nr-axSpA: 7.0%; AS; 2.1%). Incidence (pts/100 patient years) of serious TEAEs were low (nr-axSpA: 4.4; AS: 7.1); no major adverse cardiovascular events, active tuberculosis cases, serious COVID-19 infections, or deaths were reported. Most incidences of fungal infection (nr-axSpA: 19.6; AS: 14.9; none serious or systemic) were Candida (nr-axSpA: 12.8; AS: 8.3) and mild to moderate; two pts with nr-axSpA and two with AS discontinued the study due to Candida infections. Incidence of IBD (nr-axSpA: 1.0; AS: 1.0) and uveitis (nr-axSpA: 1.5; AS: 2.4) were low.
Conclusion: Across the full axSpA disease spectrum, BKZ treatment resulted in sustained efficacy, including suppression of inflammation and improvements in function and quality of life, to Wk52. No new safety signals were observed, consistent with the safety profile established from Wk24 data.1,2
References: 1. Deodhar A. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:772–3; 2. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:12–3.



Disclosures: X. Baraliakos, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, MSD, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Celgene; A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, GSK, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Amgen, Aurinia, Janssen, MoonLake; D. van der Heijde, AbbVie, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cyxone, Eisai, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Imaging Rheumatology BV; M. Magrey, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Celgene, Galapagos, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, CARE Arthritis Limited, Boehringer-Ingelheim; T. Tomita, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Mitsubishi-Tanabe; H. Xu, AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Beigene, BioMap, IASO, Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences; M. Oortgiesen, UCB Pharma; U. Massow, UCB Pharma; C. Fleurinck, UCB Pharma; A. Ellis, UCB Pharma; T. Vaux, UCB Pharma; J. Shepherd-Smith, UCB Pharma; A. Marten, UCB Pharma; L. Gensler, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MoonLake, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma.

