Back
Poster Session C
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (1417–1439) RA – Treatment Poster III
1439: Lymphatic Delivery of Etanercept Achieves Significant Improvements in Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Measures at 50% of the Standard Dose for Patients with an Inadequate Response to Subcutaneous Injections
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- RR
Russell Ross, PhD
Sorrento Therapeutics
Sandy Springs, GA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Alan Smith1, Pei-Ling Roerig1, Jacob Cason2, David Fancis2, Brian Cooley2, Mike Royal3, Vibeke Strand4, John Goldman5, Roel Querubin6 and Russell Ross2, 14P Therapeutics, Peachtree Corners, GA, 2Sorrento Therapeutics, Atlanta, GA, 3Sorrento Therapeutics, San Diego, CA, 4Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, 5Northside Hospital, Atlanta, GA, 6Atlanta Research Center for Rheumatology, Marietta, GA
Background/Purpose: The lymphatic system plays an integral role in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)1 and mediates local RA flares2, yet most biologic therapies are dosed subcutaneously (SC) or intravenously (IV). Nanotopography-microneedles (NTM) have previously been shown to enhance local lymphatic delivery and improve therapeutic efficacy in collagen-induced arthritic rats3. Here we report interim results from a 10-patient Phase 1b clinical trial in patients with high to moderate RA activity and with a history of an inadequate response to weekly SC injections of 50 mg of etanercept who were switched to weekly NTM-device-facilitated lymphatic delivery of 25 mg of etanercept for 12 weeks.
Methods: The NTM device was applied to the dorsal forearm and etanercept infused for 1.25 hours. The device was alternately applied between the left and right forearms every other week. Lymphatic imaging was conducted using Near-Infrared Fluorescence (NIRF) imaging techniques with indocyanine green dye3 to evaluate delivery into the lymphatic vessels and draining axillary lymph nodes, and to determine if lymphatic function (pump rates) improved after treatment. Data from the first 7 patients enrolled are included in this analysis. The patient baseline demographics and disease characteristics are given in Table 1. The remaining 3 patients are currently completing 12 weeks of dosing.
Results: Switching from once weekly 50 mg SC injections to once weekly 25 mg lymphatic delivery significantly reduced disease activity without local adverse events or drug delivery-related immune responses. Patients with high DAS28(CRP) baseline scores were reduced to moderate levels and patients with moderate DAS28(CRP) baseline scores were reduced to low disease activity levels (Figure 1A). Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity and Patient Disease Pain concomitantly decreased (Figure 1B). Lymphatic function, based on average pump rates, increased from a baseline of 1.0 to 2.9 pumps/minute after 12 weeks of treatment (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The NTM device effectively delivers lymphatically based on NIRF imaging results. RA disease activity and lymphatic function were improved in all patients. These improvements resulting from use of the NTM device underscore the importance of directing TNFα inhibitors locoregionally to lymphatics and lymph nodes in the treatment of RA.
1. Yousef, M et al.: J Pharm Pharm Sci 2021; 24: 533-47 (ww.capsCanada.org)
2. Rahimi, H et al.: Arth Res Ther 2016; 18:194-203
3. Aldrich, MB et al.: Arth Res Ther 2017; 19:1–13
.jpg) Table 1: Baseline demographics and disease characteristics for first 7 patients. “Other RA Medications” column includes additional therapies patients were using at W0 (baseline) to treat RA; “Comorbidities” column includes ongoing medical conditions at W0; “Disease State” column represents disease activity at W0 (baseline), as measured by DAS28(CRP).
Table 1: Baseline demographics and disease characteristics for first 7 patients. “Other RA Medications” column includes additional therapies patients were using at W0 (baseline) to treat RA; “Comorbidities” column includes ongoing medical conditions at W0; “Disease State” column represents disease activity at W0 (baseline), as measured by DAS28(CRP).
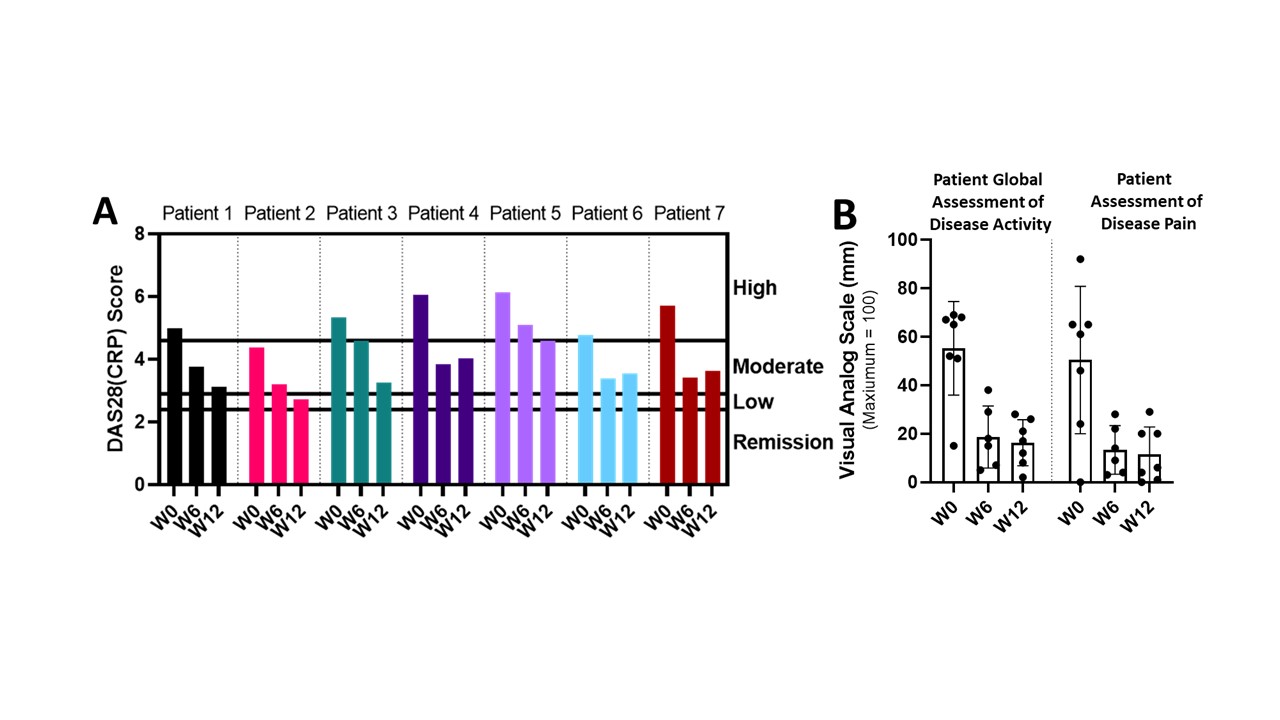 Figure 1: Disease scoring and metrics in patients treated using lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) DAS28(CRP) levels at W0 (baseline), W6, and W12, and B) Left) Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity, Right) Patient Assessment of Disease Pain. Data are represented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).
Figure 1: Disease scoring and metrics in patients treated using lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) DAS28(CRP) levels at W0 (baseline), W6, and W12, and B) Left) Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity, Right) Patient Assessment of Disease Pain. Data are represented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).
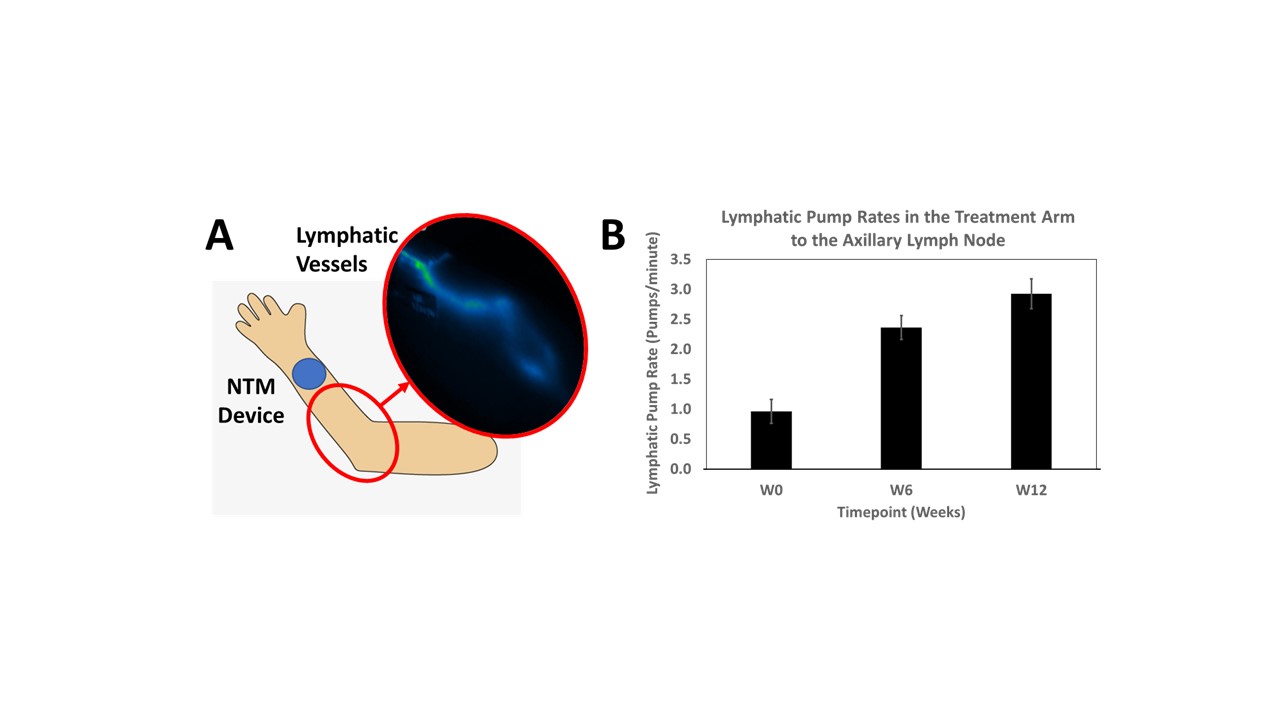 Figure 2: Improvements in lymphatic function from week 0 (W0) to 12 (W12) from lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) Shows the nanotopography-microneedle (NTM) device dosing location on the patient and where the lymphatic vessels were imaged with indocyanine green dye. B) Comparison of lymphatic pump rates at W0 (baseline), 6 weeks (W6) and 12 weeks (W12) dosing. Data is presented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).
Figure 2: Improvements in lymphatic function from week 0 (W0) to 12 (W12) from lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) Shows the nanotopography-microneedle (NTM) device dosing location on the patient and where the lymphatic vessels were imaged with indocyanine green dye. B) Comparison of lymphatic pump rates at W0 (baseline), 6 weeks (W6) and 12 weeks (W12) dosing. Data is presented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).
Disclosures: A. Smith, Sorrento Therapeutics; P. Roerig, None; J. Cason, Sorrento Therapeutics; D. Fancis, Sorrento Therapeutics; B. Cooley, Sorrento Therapeutics; M. Royal, Sorrento Therapeutics; V. Strand, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chemocentryx, Celltrion, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Inmedix, Janssen, Kiniksa, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Rheos, R-Pharma, Samsung, Sandoz, Sanofi, Scipher, Setpoint, Spherix, Aria, Bioventus, Blackrock, Equilium, Glenmark, Horizon, Kypha, Lilly, MiMedx, Sorrento, Tonix, Priovant; J. Goldman, Sorrento Therapeutics; R. Querubin, Sorrento Therapeutics; R. Ross, Sorrento Therapeutics.
Background/Purpose: The lymphatic system plays an integral role in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)1 and mediates local RA flares2, yet most biologic therapies are dosed subcutaneously (SC) or intravenously (IV). Nanotopography-microneedles (NTM) have previously been shown to enhance local lymphatic delivery and improve therapeutic efficacy in collagen-induced arthritic rats3. Here we report interim results from a 10-patient Phase 1b clinical trial in patients with high to moderate RA activity and with a history of an inadequate response to weekly SC injections of 50 mg of etanercept who were switched to weekly NTM-device-facilitated lymphatic delivery of 25 mg of etanercept for 12 weeks.
Methods: The NTM device was applied to the dorsal forearm and etanercept infused for 1.25 hours. The device was alternately applied between the left and right forearms every other week. Lymphatic imaging was conducted using Near-Infrared Fluorescence (NIRF) imaging techniques with indocyanine green dye3 to evaluate delivery into the lymphatic vessels and draining axillary lymph nodes, and to determine if lymphatic function (pump rates) improved after treatment. Data from the first 7 patients enrolled are included in this analysis. The patient baseline demographics and disease characteristics are given in Table 1. The remaining 3 patients are currently completing 12 weeks of dosing.
Results: Switching from once weekly 50 mg SC injections to once weekly 25 mg lymphatic delivery significantly reduced disease activity without local adverse events or drug delivery-related immune responses. Patients with high DAS28(CRP) baseline scores were reduced to moderate levels and patients with moderate DAS28(CRP) baseline scores were reduced to low disease activity levels (Figure 1A). Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity and Patient Disease Pain concomitantly decreased (Figure 1B). Lymphatic function, based on average pump rates, increased from a baseline of 1.0 to 2.9 pumps/minute after 12 weeks of treatment (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The NTM device effectively delivers lymphatically based on NIRF imaging results. RA disease activity and lymphatic function were improved in all patients. These improvements resulting from use of the NTM device underscore the importance of directing TNFα inhibitors locoregionally to lymphatics and lymph nodes in the treatment of RA.
1. Yousef, M et al.: J Pharm Pharm Sci 2021; 24: 533-47 (ww.capsCanada.org)
2. Rahimi, H et al.: Arth Res Ther 2016; 18:194-203
3. Aldrich, MB et al.: Arth Res Ther 2017; 19:1–13
.jpg) Table 1: Baseline demographics and disease characteristics for first 7 patients. “Other RA Medications” column includes additional therapies patients were using at W0 (baseline) to treat RA; “Comorbidities” column includes ongoing medical conditions at W0; “Disease State” column represents disease activity at W0 (baseline), as measured by DAS28(CRP).
Table 1: Baseline demographics and disease characteristics for first 7 patients. “Other RA Medications” column includes additional therapies patients were using at W0 (baseline) to treat RA; “Comorbidities” column includes ongoing medical conditions at W0; “Disease State” column represents disease activity at W0 (baseline), as measured by DAS28(CRP). Figure 1: Disease scoring and metrics in patients treated using lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) DAS28(CRP) levels at W0 (baseline), W6, and W12, and B) Left) Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity, Right) Patient Assessment of Disease Pain. Data are represented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).
Figure 1: Disease scoring and metrics in patients treated using lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) DAS28(CRP) levels at W0 (baseline), W6, and W12, and B) Left) Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity, Right) Patient Assessment of Disease Pain. Data are represented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).  Figure 2: Improvements in lymphatic function from week 0 (W0) to 12 (W12) from lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) Shows the nanotopography-microneedle (NTM) device dosing location on the patient and where the lymphatic vessels were imaged with indocyanine green dye. B) Comparison of lymphatic pump rates at W0 (baseline), 6 weeks (W6) and 12 weeks (W12) dosing. Data is presented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).
Figure 2: Improvements in lymphatic function from week 0 (W0) to 12 (W12) from lymphatic delivery of etanercept. A) Shows the nanotopography-microneedle (NTM) device dosing location on the patient and where the lymphatic vessels were imaged with indocyanine green dye. B) Comparison of lymphatic pump rates at W0 (baseline), 6 weeks (W6) and 12 weeks (W12) dosing. Data is presented as mean ± SE (SE is the standard error).Disclosures: A. Smith, Sorrento Therapeutics; P. Roerig, None; J. Cason, Sorrento Therapeutics; D. Fancis, Sorrento Therapeutics; B. Cooley, Sorrento Therapeutics; M. Royal, Sorrento Therapeutics; V. Strand, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Boehringer-Ingelheim, Chemocentryx, Celltrion, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Inmedix, Janssen, Kiniksa, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Rheos, R-Pharma, Samsung, Sandoz, Sanofi, Scipher, Setpoint, Spherix, Aria, Bioventus, Blackrock, Equilium, Glenmark, Horizon, Kypha, Lilly, MiMedx, Sorrento, Tonix, Priovant; J. Goldman, Sorrento Therapeutics; R. Querubin, Sorrento Therapeutics; R. Ross, Sorrento Therapeutics.

