Back
Poster Session C
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (1387–1416) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
1410: Subclinical Atherosclerosis Is Not Related with Acid Uric in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Study of 1005 Patients of a Single University Hospital
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- FB
Fabricio Benavides, MD
Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla
Santander, Spain
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Fabricio Benavides Villanueva1, Cristina Corrales1, Ivan Ferraz Amaro2, Nuria Vegas Revenga3, Ricardo Blanco4, Miguel Angel Gonzalez Gay5 and Alfonso Corrales6, 1Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, 2Division of Rheumatology. Hospital Universitario de Canarias. Spain., Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain, 3Hospital Galdakao- Usansolo, Galdakao, Spain, 4Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, IDIVAL, Santander, Spain, 5Hospital Universitario Marques de Valdecilla, Lugo, Spain, 6Research Group on Genetic Epidemiology and Atherosclerosis in Systemic Diseases and in Metabolic Bone Diseases of the Musculoskeletal System, IDIVAL; and Department of Rheumatology, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Gout are related with increased cardiovascular (CV) disease. Carotid plaques and increased carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) are surrogate markers of CV mortality. Serum uric acid (SUA) levels as an independent factor of subclinical Atherosclerosis and mortality in RA remains unclarified. Set the relation between SUA with CV risk factors and atherosclerosis.
Methods: Cross-sectional study with 1005 RA patients from a Single University Center. Atherosclerosis (c-IMT and carotid plaque) was explored by Carotid Ultrasonography. SUA and markers of subclinical atherosclerosis was studied by linear regression and logistic multivariate analysis.
Results: We studied 1005 RA patients (741 women, 74%), mean age 61±13. General features, CV risks factors, RA activity are included on TABLE. SUA as a dependent variable was significantly related with age, male gender and most of CV risk factors (body mass index, abdominal circumference, obesity) (single-variable analysis). Thus, a significate beta coef. [95%CI] positive relation with SUA was seen with hypertension (0.7 [0.5-0.8], p< 0.001), diabetes (0.5 [0.2-0.7], p< 0.001), dyslipidemia (0.2 [0.04-0.4], p=0.016), renal chronic insufficiency (1.5 [95CI 1,1-0.8], p< 0.001) and previous CV events (0.8 [0.4-1.2], p< 0.001). Subclinical Atherosclerosis, as a dependent variable, was significantly related with SUA (single-variable analysis). More, SUA showed a positive significate beta coef. [95%CI] relation with cIMT (18 [12-25], p< 0.001) and carotid plaques (1.29 [17-1.42], p< 0.001). But statistical significance was not seen in the multivariable analysis adjusted by Classic CV Risk Factors.
Conclusion: SUA is related with most of CV risk factors. But, is not associated with Subclinical Atherosclerosis.
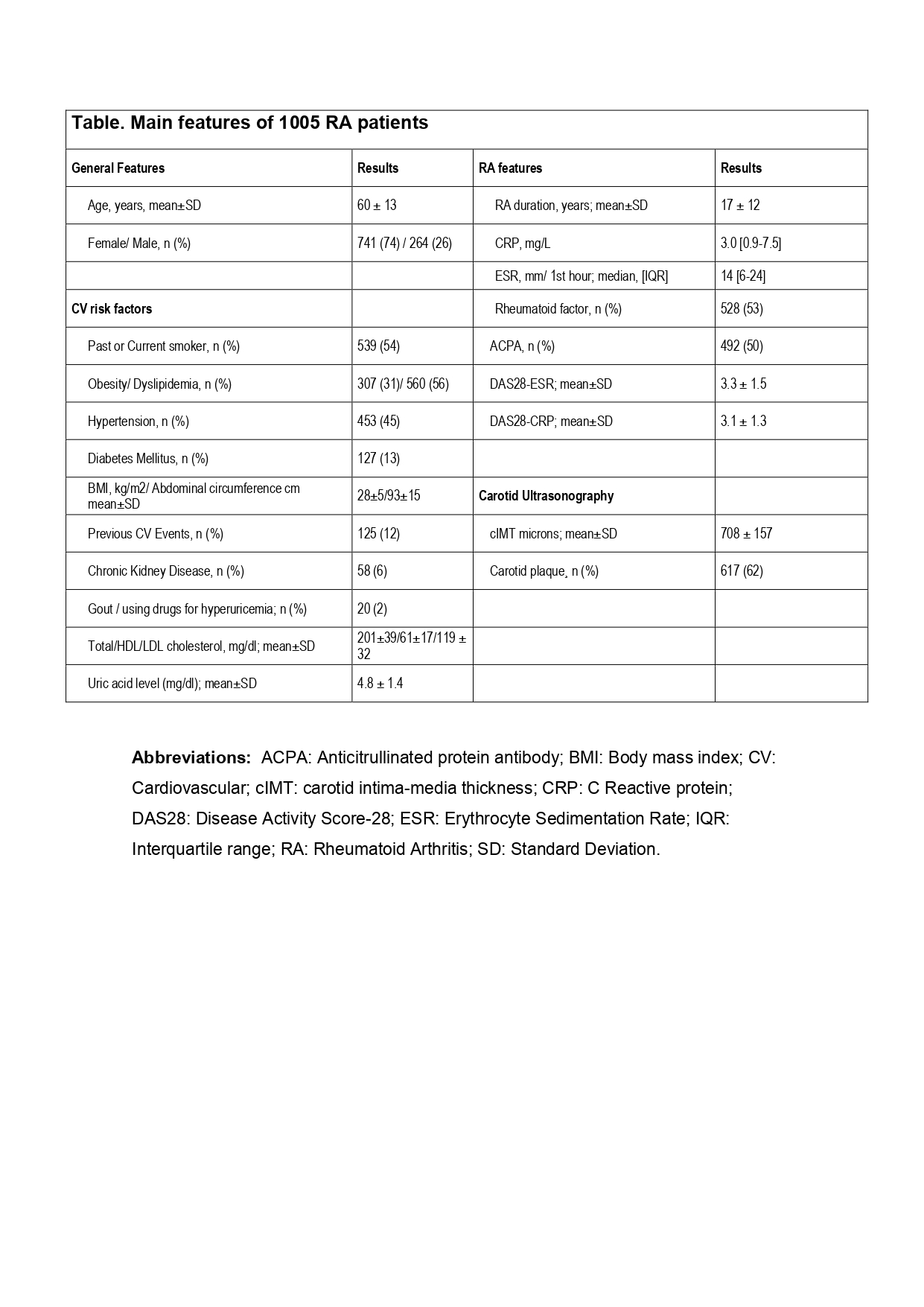 Table. Main features of 1005 RA patients
Table. Main features of 1005 RA patients
Disclosures: F. Benavides Villanueva, None; C. Corrales, None; I. Ferraz Amaro, AbbVie/Abbott, Merck/MSD, Janssen, Roche, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Roche, Amgen, Celgene, Merck/MSD; N. Vegas Revenga, None; R. Blanco, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Janssen, MSD, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Novartis, Sanofi; M. Gonzalez Gay, None; A. Corrales, None.
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Gout are related with increased cardiovascular (CV) disease. Carotid plaques and increased carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) are surrogate markers of CV mortality. Serum uric acid (SUA) levels as an independent factor of subclinical Atherosclerosis and mortality in RA remains unclarified. Set the relation between SUA with CV risk factors and atherosclerosis.
Methods: Cross-sectional study with 1005 RA patients from a Single University Center. Atherosclerosis (c-IMT and carotid plaque) was explored by Carotid Ultrasonography. SUA and markers of subclinical atherosclerosis was studied by linear regression and logistic multivariate analysis.
Results: We studied 1005 RA patients (741 women, 74%), mean age 61±13. General features, CV risks factors, RA activity are included on TABLE. SUA as a dependent variable was significantly related with age, male gender and most of CV risk factors (body mass index, abdominal circumference, obesity) (single-variable analysis). Thus, a significate beta coef. [95%CI] positive relation with SUA was seen with hypertension (0.7 [0.5-0.8], p< 0.001), diabetes (0.5 [0.2-0.7], p< 0.001), dyslipidemia (0.2 [0.04-0.4], p=0.016), renal chronic insufficiency (1.5 [95CI 1,1-0.8], p< 0.001) and previous CV events (0.8 [0.4-1.2], p< 0.001). Subclinical Atherosclerosis, as a dependent variable, was significantly related with SUA (single-variable analysis). More, SUA showed a positive significate beta coef. [95%CI] relation with cIMT (18 [12-25], p< 0.001) and carotid plaques (1.29 [17-1.42], p< 0.001). But statistical significance was not seen in the multivariable analysis adjusted by Classic CV Risk Factors.
Conclusion: SUA is related with most of CV risk factors. But, is not associated with Subclinical Atherosclerosis.
 Table. Main features of 1005 RA patients
Table. Main features of 1005 RA patientsDisclosures: F. Benavides Villanueva, None; C. Corrales, None; I. Ferraz Amaro, AbbVie/Abbott, Merck/MSD, Janssen, Roche, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Roche, Amgen, Celgene, Merck/MSD; N. Vegas Revenga, None; R. Blanco, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Janssen, MSD, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Novartis, Sanofi; M. Gonzalez Gay, None; A. Corrales, None.

