Back
Poster Session A
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0272–0316) RA – Treatment Poster I
0301: Effectiveness and Safety of Tofacitinib Treatment in Adult Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Under Routine Clinical Care: Third Interim Analysis of a German Non-Interventional, Prospective, Multicenter Study (ESCALATE-RA)
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

Klaus Krüger, MD
Rheumatologisches Praxiszentrum München
Munich, Germany
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Klaus Krüger1, Ulrich Prothmann2, Thilo Klopsch3, Olaf Behmer4, Min-Jean Hsieh4, Jürgen Jobst4, Pascal Klaus4 and Thomas Meng4, 1Praxiszentrum St. Bonifatius, Rheumatology, München, Germany, 2Knappschaftsklinikum Saar, Püttlingen, Germany, 3Rheumatological Practice, Neubrandenburg, Germany, 4Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Berlin, Germany
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. ESCALATE-RA is the first prospective, non-interventional study with tofacitinib in Germany.
Methods: Enrollment of the planned 1500 patients took place Germany-wide at 88 recruiting sites between 2017 and 2021. Adult patients eligible for tofacitinib therapy are documented quarterly in a standardized manner from the first tofacitinib intake up to 24 months and remain within the study even after switching to another disease-modifying drug (DMARD) or combination of DMARDs. This third interim analysis (cut-off date 31 Jan 2022) evaluates patients who reached the final visit M24 after 24 months. Missing observations were not taken into account. Since this is an ongoing study, small changes in numbers may occur after the final data quality checks.
Results: At data cut-off, 1521 patients were enrolled, of whom 704 (51.4%) patients reached visit M24. Mean age was 59 years; approx. three quarters of patients were female. Other baseline characteristics are depicted in Table 1. Cardiovascular disease was present at baseline in 10.4% of patients: of these, 67.1% had ischemic cardiovascular disease, 16.4% had stroke or transient ischemic attack, and 11.0% each had lower limb peripheral arterial disease or cardiac defect (Table 1).
A reduction of disease activity and morning stiffness was observed over time while functional capacity according to FFbH (Hannover Functional Capacity Questionnaire, German short questionnaire for the assessment of functional capacity in the context of basic everyday activities (range: 0-100% functional capacity) [1]) increased (Table 2). Furthermore, an improvement of self-reported quality of life based on EQ-5D-3L and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT) Fatigue Scale was observed over time.
In the M24 population during 24 months of observation, 69.7% of patients experienced adverse events (AEs) and 17.5% experienced serious AEs. Apart from lack of efficacy (11.8%), the most common treatment-related AEs were influenza-like illness (4.4%), herpes zoster (4.8%), and nasopharyngitis (3.8%). Approximately one-third of patients discontinued tofacitinib treatment due to an AE. In the Overall Population, 6 out of 1491 patients (0.4%) died (Table 3).
Conclusion: This third interim analysis confirms effectiveness and increased quality of life with tofacitinib therapy. Safety results were consistent with the known safety profile of tofacitinib. These results are in line with those of the second interim analysis.
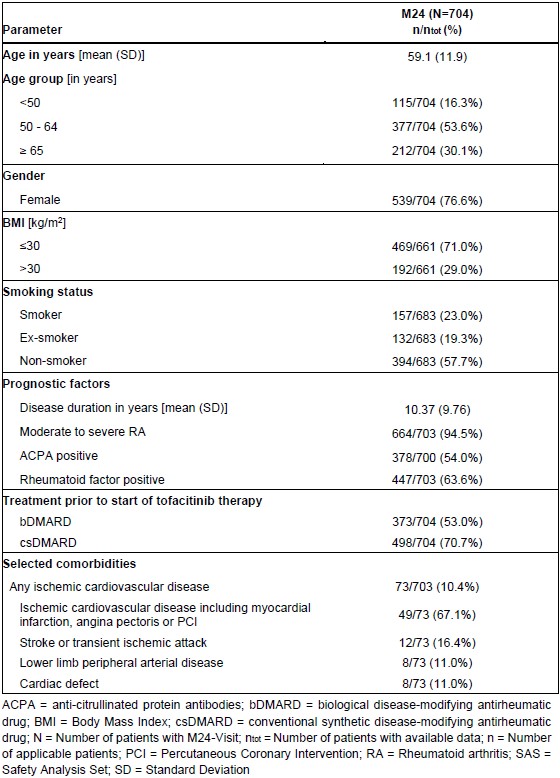 Table 1. Demographics and Clinical Data at Baseline
Table 1. Demographics and Clinical Data at Baseline
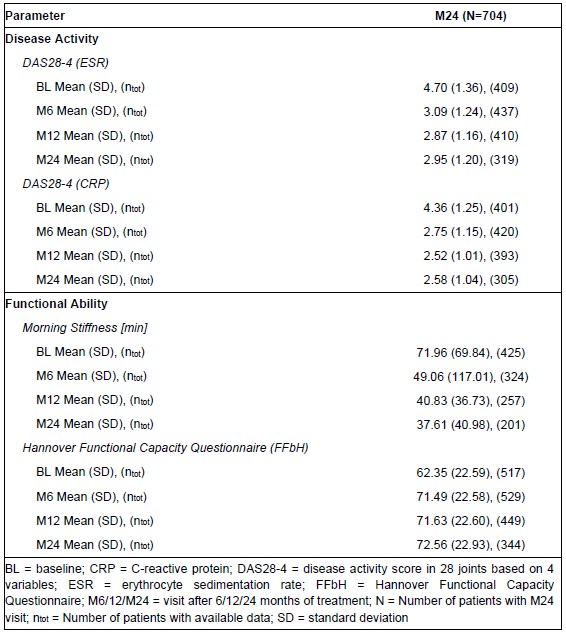 Table 2. Disease Activity, Functional Ability and Health-related Quality of Life
Table 2. Disease Activity, Functional Ability and Health-related Quality of Life
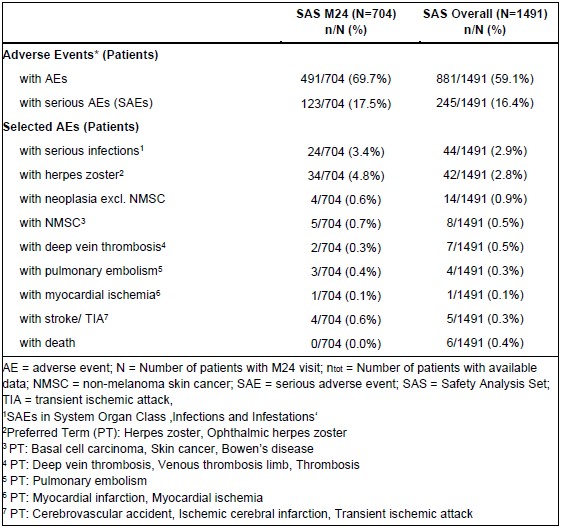 Table 3. Safety
Table 3. Safety
Disclosures: K. Krüger, AbbVie, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Hexal, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Celltrion, Janssen, Medac, Roche, UCB; U. Prothmann, None; T. Klopsch, Amgen, Evotec, Johnson Johnson, Morphosys, Novo Nordisk, AbbVie/Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB; O. Behmer, Pfizer; M. Hsieh, Pfizer; J. Jobst, Pfizer; P. Klaus, Pfizer; T. Meng, Pfizer.
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. ESCALATE-RA is the first prospective, non-interventional study with tofacitinib in Germany.
Methods: Enrollment of the planned 1500 patients took place Germany-wide at 88 recruiting sites between 2017 and 2021. Adult patients eligible for tofacitinib therapy are documented quarterly in a standardized manner from the first tofacitinib intake up to 24 months and remain within the study even after switching to another disease-modifying drug (DMARD) or combination of DMARDs. This third interim analysis (cut-off date 31 Jan 2022) evaluates patients who reached the final visit M24 after 24 months. Missing observations were not taken into account. Since this is an ongoing study, small changes in numbers may occur after the final data quality checks.
Results: At data cut-off, 1521 patients were enrolled, of whom 704 (51.4%) patients reached visit M24. Mean age was 59 years; approx. three quarters of patients were female. Other baseline characteristics are depicted in Table 1. Cardiovascular disease was present at baseline in 10.4% of patients: of these, 67.1% had ischemic cardiovascular disease, 16.4% had stroke or transient ischemic attack, and 11.0% each had lower limb peripheral arterial disease or cardiac defect (Table 1).
A reduction of disease activity and morning stiffness was observed over time while functional capacity according to FFbH (Hannover Functional Capacity Questionnaire, German short questionnaire for the assessment of functional capacity in the context of basic everyday activities (range: 0-100% functional capacity) [1]) increased (Table 2). Furthermore, an improvement of self-reported quality of life based on EQ-5D-3L and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT) Fatigue Scale was observed over time.
In the M24 population during 24 months of observation, 69.7% of patients experienced adverse events (AEs) and 17.5% experienced serious AEs. Apart from lack of efficacy (11.8%), the most common treatment-related AEs were influenza-like illness (4.4%), herpes zoster (4.8%), and nasopharyngitis (3.8%). Approximately one-third of patients discontinued tofacitinib treatment due to an AE. In the Overall Population, 6 out of 1491 patients (0.4%) died (Table 3).
Conclusion: This third interim analysis confirms effectiveness and increased quality of life with tofacitinib therapy. Safety results were consistent with the known safety profile of tofacitinib. These results are in line with those of the second interim analysis.
 Table 1. Demographics and Clinical Data at Baseline
Table 1. Demographics and Clinical Data at Baseline  Table 2. Disease Activity, Functional Ability and Health-related Quality of Life
Table 2. Disease Activity, Functional Ability and Health-related Quality of Life  Table 3. Safety
Table 3. SafetyDisclosures: K. Krüger, AbbVie, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Hexal, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Celltrion, Janssen, Medac, Roche, UCB; U. Prothmann, None; T. Klopsch, Amgen, Evotec, Johnson Johnson, Morphosys, Novo Nordisk, AbbVie/Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB; O. Behmer, Pfizer; M. Hsieh, Pfizer; J. Jobst, Pfizer; P. Klaus, Pfizer; T. Meng, Pfizer.

