Back
Ignite Talk
Session: Ignite Session 5A
0020: Redoxosomes Mediate a Feed-forward Loop of Cartilage Matrix Destruction Through α5β1 Integrin Signaling in Response to a Fibronectin Matrikine
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:45 PM – 1:50 PM Eastern Time
Location: Northern Liberties Stage
- RL
Richard Loeser, Jr., MD
University of North Carolina
Chapel Hill, NC, United StatesDisclosure: Disclosure information not submitted.
Ignite Speaker(s)
Michael Miao1, Peter Su2, Yang Cui1, John Collins3, Edward Bahnson1, Susan Chubinskaya4 and Richard Loeser1, 1University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, 2University of Technology, Ultimo, Australia, 3Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA, 4Rush University, Chicago, IL
Background/Purpose: Degradation of pericellular matrix proteins creates bioactive fragments called "matrikines" that include fibronectin fragments (FN-f). FN-f found in OA cartilage and synovial fluid exhibit properties of matrikines by binding to the chondrocyte α5β1 integrin receptor to activate signaling that upregulates expression of cytokines and proteases including MMP-13. We found that FN-f, but not intact FN, induces MAPK and Src signaling that is redox regulated by H2O2 produced by Nox-2. The purpose of the present study was to determine the mechanism by which α5β1 integrin activation by a FN matrikine produces H2O2 in a temporospatial manner to control signaling that upregulates MMP-13 production.
Methods: Primary human chondrocytes were serum starved prior to treatment with a purified 42kD recombinant FN-f (FN7-10) containing the α5β1 integrin binding region or intact FN for comparison. Plasmid constructs expressing fluorescent tagged proteins were used to locate the α5 integrin subunit, FN7-10, Nox2, early and late endosomes, and Src by confocal microscopy. Compartmentalized redox biosensors (HyPer3-tk, HyPer-cyto, and Hyper-Rab5) were used to track H2O2 production using time-lapse live cell imaging. The dynamin inhibitor Dynasore (60 µM) and transfection with dominant negative Rab5 (Rab5DN(S43N)) were used to inhibit endocytosis.
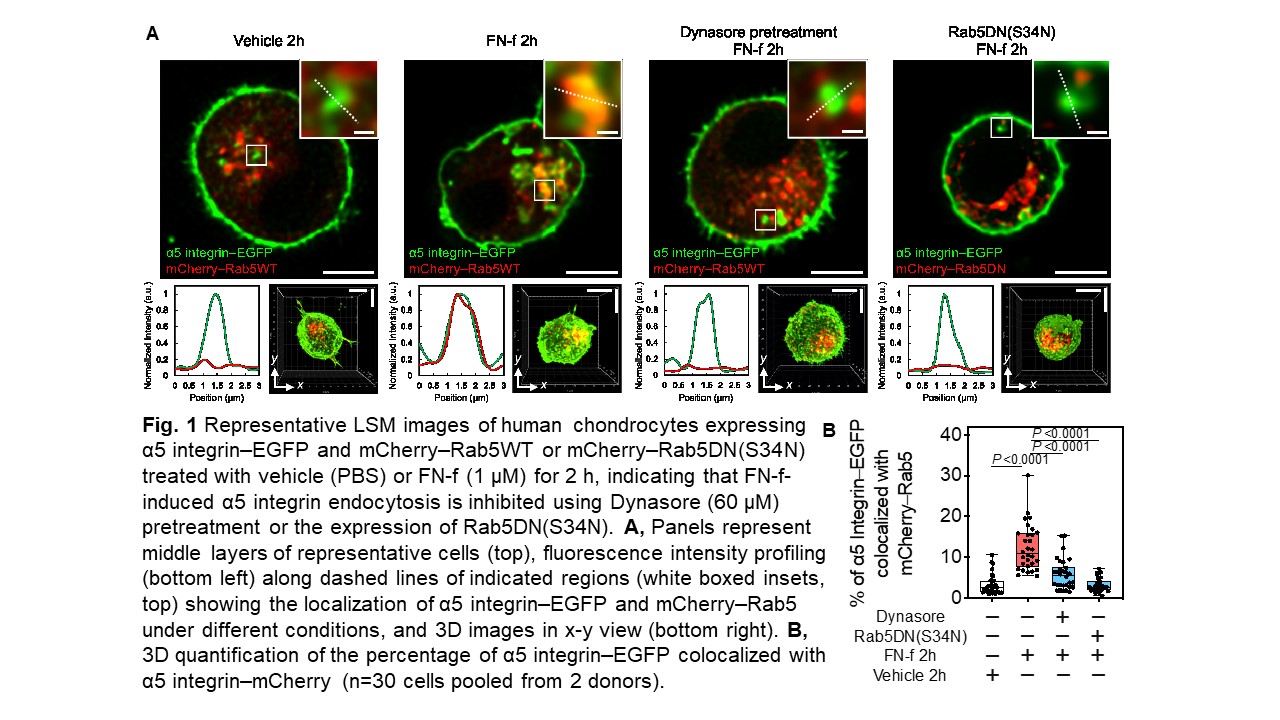
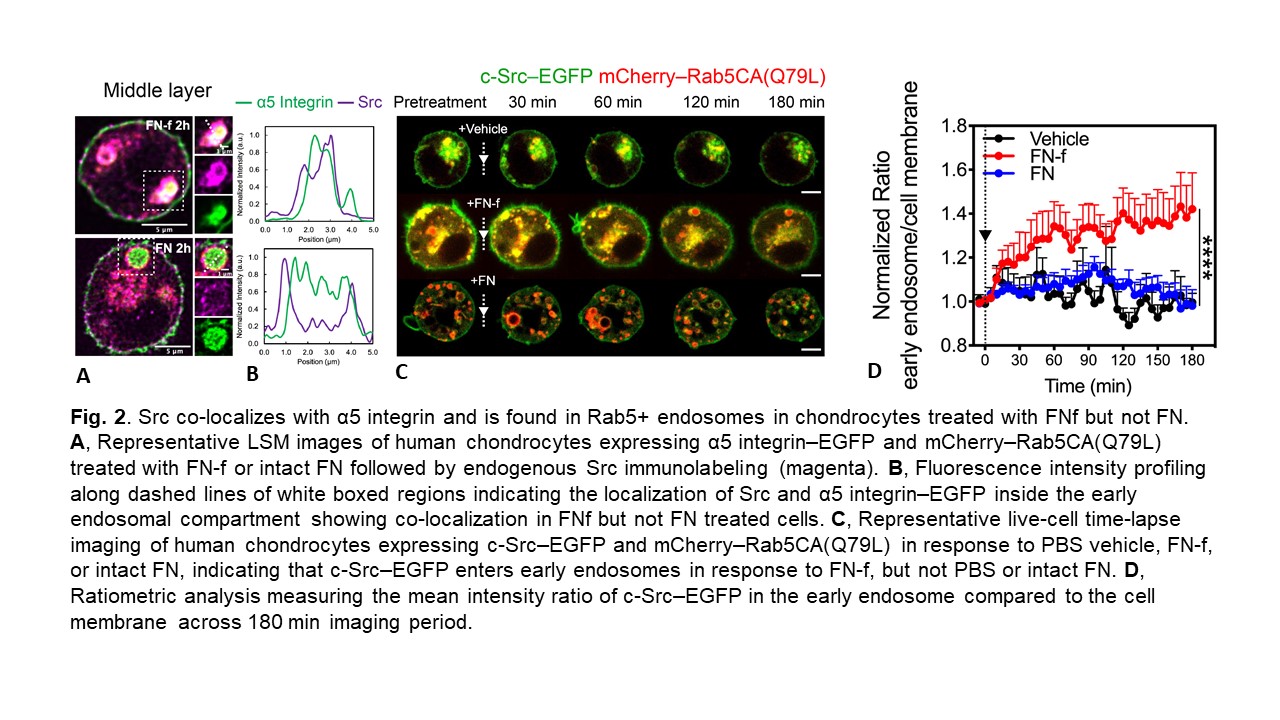
Results: FN-f and intact FN both induced α5-EGFP to enter early (Rab5+) endosomes but co-localization with Nox2 only occurred with FN-f. FN-f-EGFP also demonstrated co-localization with Rab5 indicating FN-f and α5 were endocytosed into early endosomes. Endocytosis of FN-f and α5 integrin was significantly reduced by Dynasore or by expression of dominant negative Rab5 (Fig.1) and this inhibited FN-f activation of MAPK signaling and MMP-13 production. The H2O2 biosensors indicated that FN-f induced H2O2 at the plasma membrane and then localization in the cytosol and early endosomes. EGFP-Nox2 gradually entered α5 integrin+/Rab5+ vesicles at the time point when endosomal H2O2 was detected, consistent with the formation of "redoxosomes". Inhibition of H2O2 or Nox2 blocked FN-f induced MMP-13 production. The redox regulated tyrosine kinase Src co-localized with α5 integrin in early endosomes in response to FN-f but not intact FN (Fig. 2). Co-localization of Src and Nox2 were significantly increased in endosomes from chondrocytes treated with FN-f and in OA cartilage sections. Different from FN-f induced integrin endocytosis, in which a degradative pathway was followed through Rab7+ vesicles, α5 endocytosis with intact FN followed a recycling pathway through Rab11+ vesicles which would return the integrin to the cell surface.
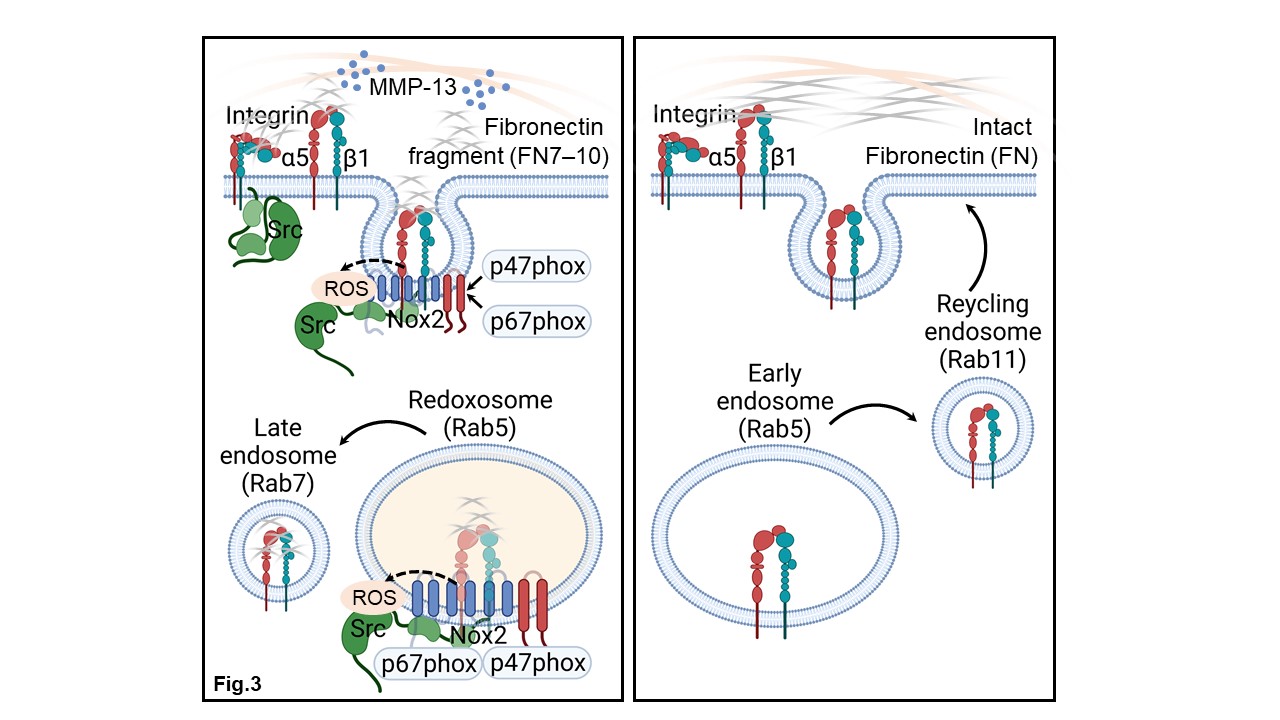
Conclusion: Chondrocytes endocytosed the FN7-10 matrikine along with the α5β1 integrin to generate signaling redoxosomes for the generation of H2O2 by Nox2 in a temporospatial pattern (Fig.3). In contrast, binding of intact FN did not activate redox signaling and resulted in recycling of the α5β1 integrin to the chondrocyte cell surface. These findings reveal an intricate redox regulated mechanism by which chondrocytes respond to a FN matrikine and provide novel targets to control the progressive cartilage degradation seen in OA.
Disclosures: M. Miao, None; P. Su, None; Y. Cui, None; J. Collins, None; E. Bahnson, None; S. Chubinskaya, None; R. Loeser, None.
Background/Purpose: Degradation of pericellular matrix proteins creates bioactive fragments called "matrikines" that include fibronectin fragments (FN-f). FN-f found in OA cartilage and synovial fluid exhibit properties of matrikines by binding to the chondrocyte α5β1 integrin receptor to activate signaling that upregulates expression of cytokines and proteases including MMP-13. We found that FN-f, but not intact FN, induces MAPK and Src signaling that is redox regulated by H2O2 produced by Nox-2. The purpose of the present study was to determine the mechanism by which α5β1 integrin activation by a FN matrikine produces H2O2 in a temporospatial manner to control signaling that upregulates MMP-13 production.
Methods: Primary human chondrocytes were serum starved prior to treatment with a purified 42kD recombinant FN-f (FN7-10) containing the α5β1 integrin binding region or intact FN for comparison. Plasmid constructs expressing fluorescent tagged proteins were used to locate the α5 integrin subunit, FN7-10, Nox2, early and late endosomes, and Src by confocal microscopy. Compartmentalized redox biosensors (HyPer3-tk, HyPer-cyto, and Hyper-Rab5) were used to track H2O2 production using time-lapse live cell imaging. The dynamin inhibitor Dynasore (60 µM) and transfection with dominant negative Rab5 (Rab5DN(S43N)) were used to inhibit endocytosis.
Results: FN-f and intact FN both induced α5-EGFP to enter early (Rab5+) endosomes but co-localization with Nox2 only occurred with FN-f. FN-f-EGFP also demonstrated co-localization with Rab5 indicating FN-f and α5 were endocytosed into early endosomes. Endocytosis of FN-f and α5 integrin was significantly reduced by Dynasore or by expression of dominant negative Rab5 (Fig.1) and this inhibited FN-f activation of MAPK signaling and MMP-13 production. The H2O2 biosensors indicated that FN-f induced H2O2 at the plasma membrane and then localization in the cytosol and early endosomes. EGFP-Nox2 gradually entered α5 integrin+/Rab5+ vesicles at the time point when endosomal H2O2 was detected, consistent with the formation of "redoxosomes". Inhibition of H2O2 or Nox2 blocked FN-f induced MMP-13 production. The redox regulated tyrosine kinase Src co-localized with α5 integrin in early endosomes in response to FN-f but not intact FN (Fig. 2). Co-localization of Src and Nox2 were significantly increased in endosomes from chondrocytes treated with FN-f and in OA cartilage sections. Different from FN-f induced integrin endocytosis, in which a degradative pathway was followed through Rab7+ vesicles, α5 endocytosis with intact FN followed a recycling pathway through Rab11+ vesicles which would return the integrin to the cell surface.
Conclusion: Chondrocytes endocytosed the FN7-10 matrikine along with the α5β1 integrin to generate signaling redoxosomes for the generation of H2O2 by Nox2 in a temporospatial pattern (Fig.3). In contrast, binding of intact FN did not activate redox signaling and resulted in recycling of the α5β1 integrin to the chondrocyte cell surface. These findings reveal an intricate redox regulated mechanism by which chondrocytes respond to a FN matrikine and provide novel targets to control the progressive cartilage degradation seen in OA.



Disclosures: M. Miao, None; P. Su, None; Y. Cui, None; J. Collins, None; E. Bahnson, None; S. Chubinskaya, None; R. Loeser, None.

