Back
Ignite Talk
Session: Ignite Session 2B
0762: Rituximab-treated Rheumatic Patients: B-cell Levels Predict Sero-conversion After COVID-19 Boost or Re-vaccination in Initial Vaccine Non-responders
Saturday, November 12, 2022
2:00 PM – 2:05 PM Eastern Time
Location: Center City Stage
- CA
Christian Ammitzbøll, MD, PhD
Aarhus University Hospital
Aarhus V, DenmarkDisclosure: Disclosure information not submitted.
Ignite Speaker(s)
Christian Ammitzboell1, marianne Kragh thomsen2, Jakob Bøgn Andersen1, Jens Magnus Berth Jensen3, marie-Louise From Hermansen1, anders Dahl Johannsen1, Mads Lamm Larsen1, Clara Elbæl Mistegaard1, Susan Mikkelsen3, Fruzsina Szabados3, Signe Risbøl Vils1, Christian Erikstrup3, Ellen-Margrethe Hauge1 and Anne Troldborg1, 1Department of Rheumatology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, 2Department of Clinical Microbiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, 3Department of Clinical Immunology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark
Background/Purpose: Treatment with rituximab (RTX) has presented a challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic, as antibody response after primary vaccination are markedly reduced and often undetectable.The primary outcome of this study was to investigate the percentage of RTX treated RD patients without detectable antibody responses after two vaccinations that mounted detectable antibody responses after a booster vaccination (3rd dose) or revaccination (3rd and 4th) vaccine dose. The secondary outcome was to examine if the level of B-cells in peripheral blood predicted the antibody response.
Methods: We included 91 RD patients, who had recieved RTX within the past 24 months and were vaccinated against COVID-19 with an mRNA vaccine. Patients were offered revaccination or a single booster vaccination with an mRNA vaccine. Serum total antibodies and specific IgG against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were measured before and six weeks after the last vaccine dose. B-cells (CD19+CD45+) were measured by flow cytometry at inclusion. Logistic regression analyses were performed with the presence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after vaccination as the dependent variable.
The study was supported by an urestricted grant from the The Danish Rheumatism Association.
Results: Patient characteristics are given in Table 1. Most participants were female (69%) with a median age of 61 years, and the most common diagnosis were vasculitis (45%), rheumatoid arthritis (19%) and myositis (19%).
Sixty-nine patients had undetectable anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels after the initial vaccination. In these patients, 5 out 13 (38%) who recieved a booster dose and 18/56 (32%) who recieved a revaccination seroconverted, Figure 1A. This difference was not significant (p=0.67). Patients receiving re-vaccination had significantly higher antibody levels than patients receiving a booster dose (p< 0.001), Figure 1A.
Nearly all patients (7/8, 87.5 %), who had quantifiable B-lymphocytes but were seronegative before re-vaccination or boosting achieved detectable SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after six weeks (Fig. 1b). In contrast, 16 out of 58 patients (27.6%) with unquantifiable B-lymphocytes and unmeasurable antibodies before vaccination developed antibodies 6 weeks after booster/revaccination.
In both univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, only B-cells higher than 10/µL before boost or revaccination were associated with seroconversion (p=0.009 and p=0.01, respectively), Table 2. Seroconversion was independent of age, gender, diagnosis, cumulative RTX dose, RTX treatment time, and time since last RTX treatment.
Conclusion: Continuously impaired humoral response to mRNA vaccines was found in most RTX treated RD patients after a booster dose (one-dose) or revaccination (two-doses). Re-vaccination lead to significantly higher antibody levels in patients who did not have a detecable humoral responce after the first two vaccine doses, compared to a booster dose. CD19+ B-cells are a significant predictor of humoral responce to vaccination. However, more than half of the patients with no measureable B-cells pre-vaccination developed a detecable humoral responce after revaccination.
.jpg) Table 1. Patients Characteristics
Table 1. Patients Characteristics
.jpg) Figure 1. Seroconversion after boost or revaccination.
Figure 1. Seroconversion after boost or revaccination.
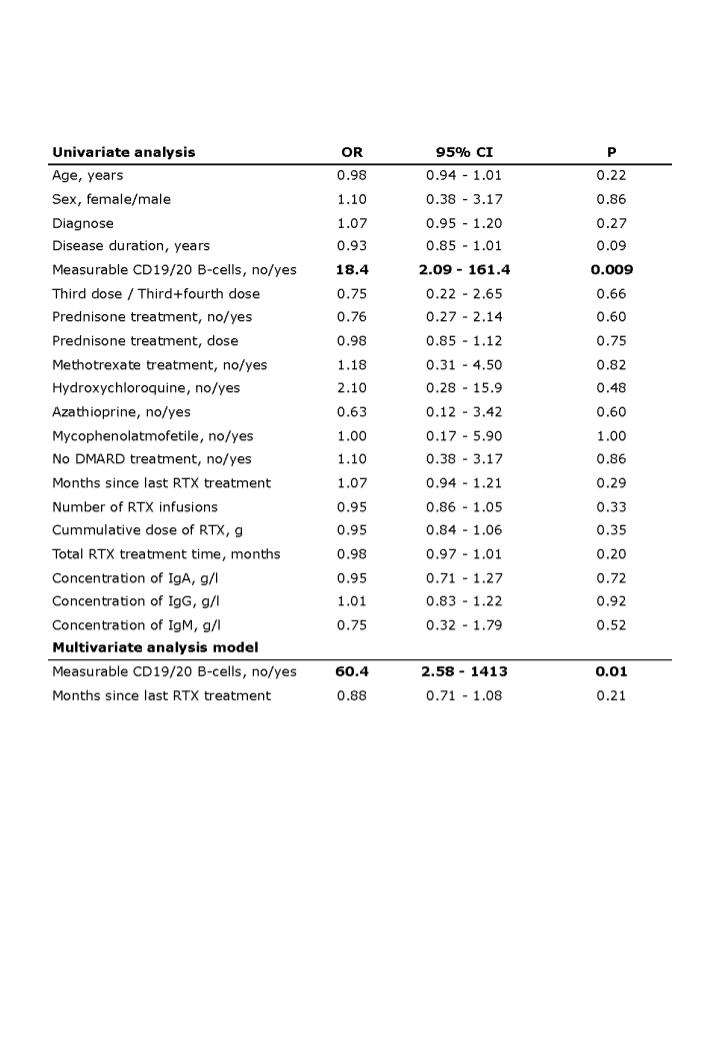 Table 2. Univariate and multivariate logistic analysis with seroconversion as dependent variable
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate logistic analysis with seroconversion as dependent variable
Disclosures: C. Ammitzboell, None; m. thomsen, None; J. Andersen, None; J. Jensen, None; m. Hermansen, None; a. Johannsen, None; M. Larsen, None; C. Mistegaard, None; S. Mikkelsen, None; F. Szabados, None; S. Vils, None; C. Erikstrup, None; E. Hauge, None; A. Troldborg, None.
Background/Purpose: Treatment with rituximab (RTX) has presented a challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic, as antibody response after primary vaccination are markedly reduced and often undetectable.The primary outcome of this study was to investigate the percentage of RTX treated RD patients without detectable antibody responses after two vaccinations that mounted detectable antibody responses after a booster vaccination (3rd dose) or revaccination (3rd and 4th) vaccine dose. The secondary outcome was to examine if the level of B-cells in peripheral blood predicted the antibody response.
Methods: We included 91 RD patients, who had recieved RTX within the past 24 months and were vaccinated against COVID-19 with an mRNA vaccine. Patients were offered revaccination or a single booster vaccination with an mRNA vaccine. Serum total antibodies and specific IgG against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were measured before and six weeks after the last vaccine dose. B-cells (CD19+CD45+) were measured by flow cytometry at inclusion. Logistic regression analyses were performed with the presence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after vaccination as the dependent variable.
The study was supported by an urestricted grant from the The Danish Rheumatism Association.
Results: Patient characteristics are given in Table 1. Most participants were female (69%) with a median age of 61 years, and the most common diagnosis were vasculitis (45%), rheumatoid arthritis (19%) and myositis (19%).
Sixty-nine patients had undetectable anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels after the initial vaccination. In these patients, 5 out 13 (38%) who recieved a booster dose and 18/56 (32%) who recieved a revaccination seroconverted, Figure 1A. This difference was not significant (p=0.67). Patients receiving re-vaccination had significantly higher antibody levels than patients receiving a booster dose (p< 0.001), Figure 1A.
Nearly all patients (7/8, 87.5 %), who had quantifiable B-lymphocytes but were seronegative before re-vaccination or boosting achieved detectable SARS-CoV-2 antibodies after six weeks (Fig. 1b). In contrast, 16 out of 58 patients (27.6%) with unquantifiable B-lymphocytes and unmeasurable antibodies before vaccination developed antibodies 6 weeks after booster/revaccination.
In both univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis, only B-cells higher than 10/µL before boost or revaccination were associated with seroconversion (p=0.009 and p=0.01, respectively), Table 2. Seroconversion was independent of age, gender, diagnosis, cumulative RTX dose, RTX treatment time, and time since last RTX treatment.
Conclusion: Continuously impaired humoral response to mRNA vaccines was found in most RTX treated RD patients after a booster dose (one-dose) or revaccination (two-doses). Re-vaccination lead to significantly higher antibody levels in patients who did not have a detecable humoral responce after the first two vaccine doses, compared to a booster dose. CD19+ B-cells are a significant predictor of humoral responce to vaccination. However, more than half of the patients with no measureable B-cells pre-vaccination developed a detecable humoral responce after revaccination.
.jpg) Table 1. Patients Characteristics
Table 1. Patients Characteristics.jpg) Figure 1. Seroconversion after boost or revaccination.
Figure 1. Seroconversion after boost or revaccination. Table 2. Univariate and multivariate logistic analysis with seroconversion as dependent variable
Table 2. Univariate and multivariate logistic analysis with seroconversion as dependent variableDisclosures: C. Ammitzboell, None; m. thomsen, None; J. Andersen, None; J. Jensen, None; m. Hermansen, None; a. Johannsen, None; M. Larsen, None; C. Mistegaard, None; S. Mikkelsen, None; F. Szabados, None; S. Vils, None; C. Erikstrup, None; E. Hauge, None; A. Troldborg, None.

