Back
Poster Session D
Session: (2108–2153) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: PsA
2151: Izokibep Demonstrates Clinically Relevant Efficacy Benefits on Enthesitis, Dactylitis and Nail Outcomes in Active PsA Patients: A 16-week Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- Kd
Kurt de Vlam, MD, PhD
University Hospitals Leuven
Leuven, Belgium
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Kurt de Vlam1, Peter Taylor2, Philip J Mease3, Paul Peloso4, Dieter Wetzel5, Nicolai Brun5, Brian Wiens6, Jan Brandt-Juergens7, Edit Drescher8, Eva Dokoupilova9, Anna Rowinska-Osuch10, Nadia Abdel- Kader Martin11 and Frank Behrens12, 1University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3Swedish Medical Center/Providence St. Joseph Health, Seattle, WA, 4ACELYRIN, Naples, FL, 5Affibody AB, Solna, Sweden, 6ACELYRIN, Inc., Los Angeles, CA, 7Rheumatologische Schwerpunktpraxis, Berlin, Germany, 8Veszprem Megyei Csolnoky Ferenc Korhaz, Budapest, Hungary, 9Medical Plus, s.r.o. & Masaryk University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Brno, Prague, Czech Republic, 10ETG Network, Warsaw, Poland, 11Hospital Infanta Luisa Quiron, Rheumatology, Sevilla, Spain, 12Rheumatology University Hospital & Fraunhofer Institute Translational Medicine and Pharmacology, Goethe-University Frankfurt, Frankfurt Am Main, Germany
Background/Purpose: PsA is a chronic, inflammatory disease with multiple manifestations, with arthritis and skin involvement. Other areas of inflammation include enthesitis, dactylitis and nail involvement. Unresolved enthesitis leads to chronic pain and reduced quality of life1. IL-17 inhibitors have demonstrated benefits across multiple disease features. Izokibep is a unique IL-17A inhibitor with high potency (0.3 pM), small size (18.6 kD) and half-life extending albumin binding.
The purpose is to assess the efficacy of izokibep 40 mg Q2W and 80 mg Q2W versus placebo on measures of enthesitis (most common being Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI), as well as SPARCC), dactylitis and nails, and explore how these disease features impact quality of life (PsAID questionnaire) over 16 weeks. Drug safety was evaluated.
1McInnes, IB., J Rheumatol 2019;46:1458–61; doi:10.3899/jrheum.180792
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study was conducted with placebo (Pbo), izokibep 40 mg Q2W or 80 mg Q2W delivered subcutaneously to Week 16 (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04713072). Patients met CASPAR criteria and required ≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints (66/68 joint count), an inadequate response to NSAIDs, csDMARDs or TNF inhibitors to enroll. The presence of enthesitis, dactylitis or nail involvement was not required. Enthesitis was assessed by the LEI and SPARCC, dactylitis by the Leeds-B scale, and target nail involvement by NAPSI. Safety and tolerability were evaluated by history, exam, adverse events and lab findings.
Results: 135 patients were randomized across 28 European sites in 7 countries from June 2020 to July 2021. Mean age was 48.5, mean BMI 29.0 kg/m2, mean swollen joint count of 9.9 and mean tender joint count of 16.7 and mean PsA duration of 7.1 years. 80% were on csDMARD and 13% had failed TNF inhibitors. Enthesitis was present at baseline on the LEI in 32% (n=43) and in 77% (n=104) on the SPARCC with dactylitis present in 32% (n=43). NAPSI - target nail was collected on all patients. The ACR50 primary was met by 13% on placebo, 48% on izokibep 40 mg Q2W and 52% on izokibep 80 mg Q2W, p=0.0003. The LEI showed 88% with complete resolution at 16 weeks on izokibep 80 mg Q2W. SPARCC enthesitis also showed dose related improvement as did the Leeds Dactylitis Index (Table 1). Figure 1 shows those with enthesitis at baseline had a higher proportion of clinically meaningful improvements on the PsAID vs. all patients (53% vs. 41% respectively for izokibep 80 mg Q2W).
Safety evaluation showed no serious or severe adverse events up to week 16. AE rate overall was 52.3% for Pbo, 65.9% for 40 mg Q2W and 55.3% for 80 mg Q2W. The most common AEs (≥ 5% in any group) were injection site reaction or erythema, headache, hypertension, diarrhea, URTI. Two patients had AESI: one mild, transient vulvovaginal Candida infection; one injection site reaction leading to discontinuation.
Conclusion: Izokibep showed high levels of efficacy across enthesitis, dactylitis and nail scores that were clinically meaningful and statistically significant. Patients with enthesitis at baseline had the largest improvements in PsAID. The izokibep safety profile was generally consistent with other IL-17A inhibitors; in this trial, events were mostly similar to placebo.
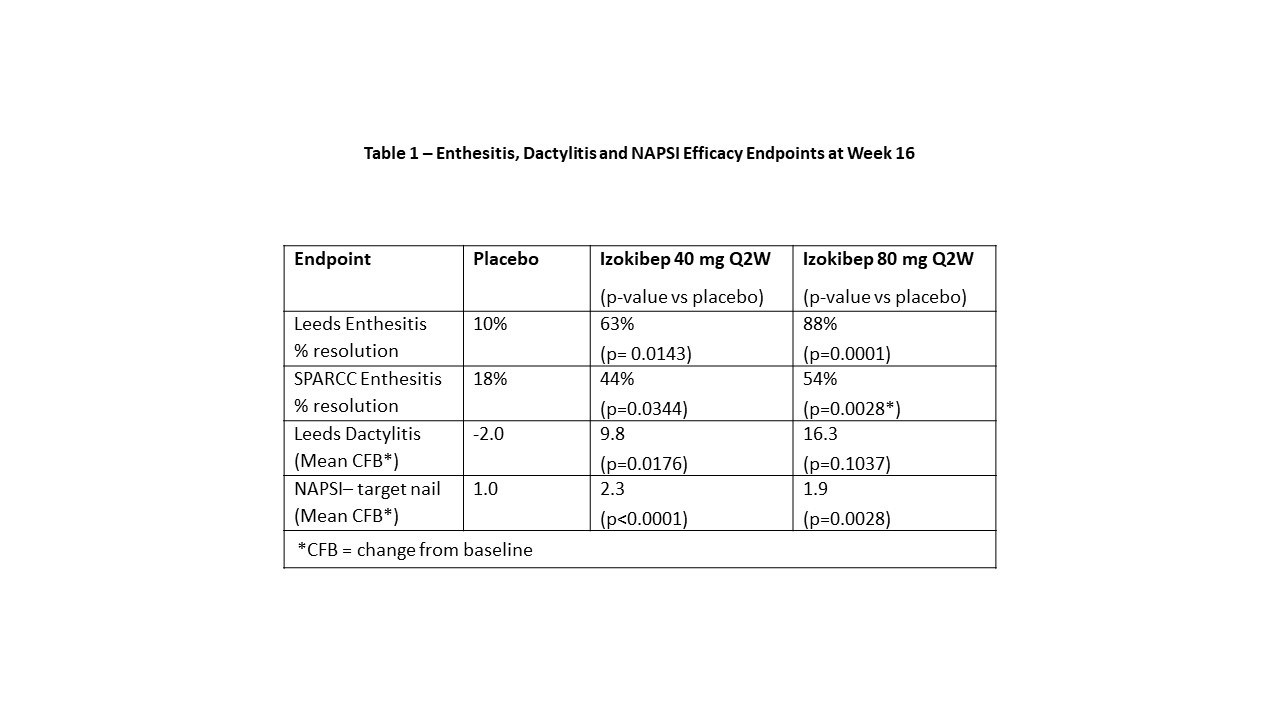 Table 1 – Enthesitis, Dactylitis and NAPSI Efficacy Endpoints at Week 16
Table 1 – Enthesitis, Dactylitis and NAPSI Efficacy Endpoints at Week 16
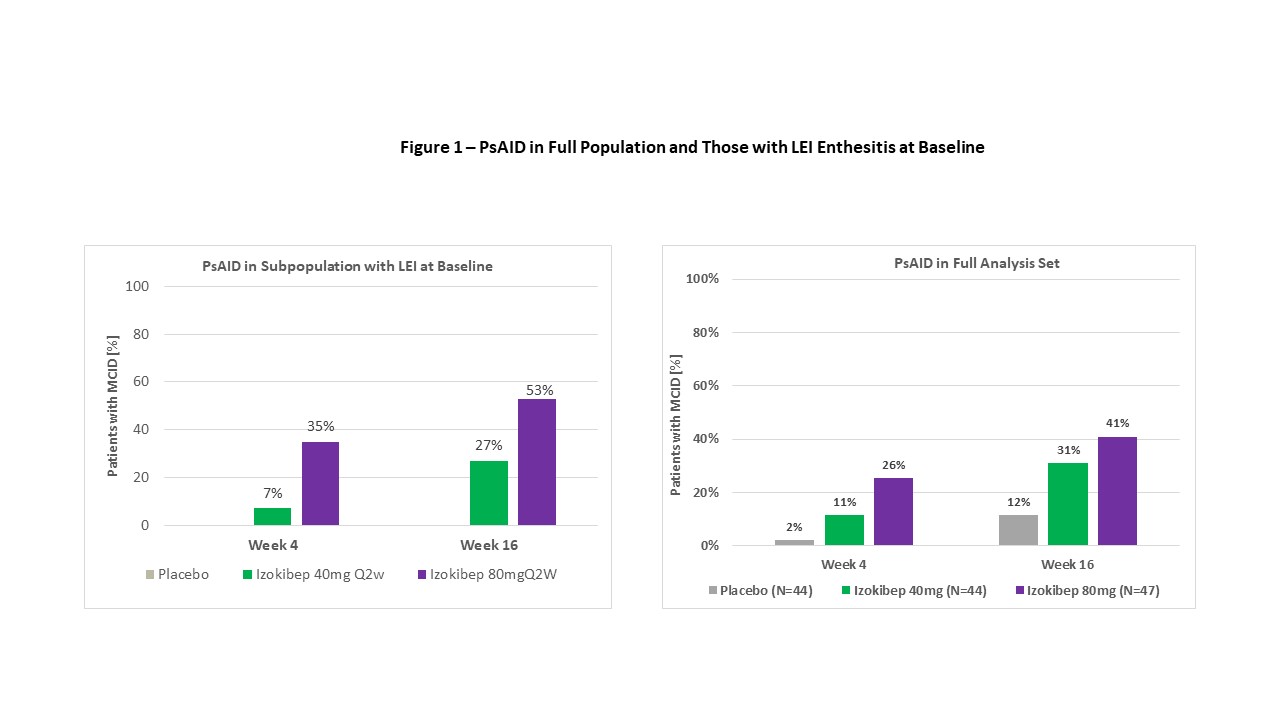 Figure 1 – PsAID in Full Population and Those with LEI Enthesitis at Baseline
Figure 1 – PsAID in Full Population and Those with LEI Enthesitis at Baseline
Disclosures: K. de Vlam, UCB, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, AbbVie/Abbott, Merck/MSD, johnson and johnson; P. Taylor, Biogen, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Janssen, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, UCB, Galapagos, Abbvie; P. Mease, AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB, Sun Pharma, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Genentech; P. Peloso, ACELYRIN, ACELYRIN; D. Wetzel, Affibody; N. Brun, Affibody AB, Affibody AB; B. Wiens, ACELYRIN; J. Brandt-Juergens, AbbVie/Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Sanofi-Aventis, Medac, Gilead, Gilead, Affibody; E. Drescher, None; E. Dokoupilova, None; A. Rowinska-Osuch, None; N. Abdel- Kader Martin, Pfizer; F. Behrens, AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Galapagos, Gilead, UCB, Affibody, MoonLake, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK).
Background/Purpose: PsA is a chronic, inflammatory disease with multiple manifestations, with arthritis and skin involvement. Other areas of inflammation include enthesitis, dactylitis and nail involvement. Unresolved enthesitis leads to chronic pain and reduced quality of life1. IL-17 inhibitors have demonstrated benefits across multiple disease features. Izokibep is a unique IL-17A inhibitor with high potency (0.3 pM), small size (18.6 kD) and half-life extending albumin binding.
The purpose is to assess the efficacy of izokibep 40 mg Q2W and 80 mg Q2W versus placebo on measures of enthesitis (most common being Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI), as well as SPARCC), dactylitis and nails, and explore how these disease features impact quality of life (PsAID questionnaire) over 16 weeks. Drug safety was evaluated.
1McInnes, IB., J Rheumatol 2019;46:1458–61; doi:10.3899/jrheum.180792
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study was conducted with placebo (Pbo), izokibep 40 mg Q2W or 80 mg Q2W delivered subcutaneously to Week 16 (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04713072). Patients met CASPAR criteria and required ≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints (66/68 joint count), an inadequate response to NSAIDs, csDMARDs or TNF inhibitors to enroll. The presence of enthesitis, dactylitis or nail involvement was not required. Enthesitis was assessed by the LEI and SPARCC, dactylitis by the Leeds-B scale, and target nail involvement by NAPSI. Safety and tolerability were evaluated by history, exam, adverse events and lab findings.
Results: 135 patients were randomized across 28 European sites in 7 countries from June 2020 to July 2021. Mean age was 48.5, mean BMI 29.0 kg/m2, mean swollen joint count of 9.9 and mean tender joint count of 16.7 and mean PsA duration of 7.1 years. 80% were on csDMARD and 13% had failed TNF inhibitors. Enthesitis was present at baseline on the LEI in 32% (n=43) and in 77% (n=104) on the SPARCC with dactylitis present in 32% (n=43). NAPSI - target nail was collected on all patients. The ACR50 primary was met by 13% on placebo, 48% on izokibep 40 mg Q2W and 52% on izokibep 80 mg Q2W, p=0.0003. The LEI showed 88% with complete resolution at 16 weeks on izokibep 80 mg Q2W. SPARCC enthesitis also showed dose related improvement as did the Leeds Dactylitis Index (Table 1). Figure 1 shows those with enthesitis at baseline had a higher proportion of clinically meaningful improvements on the PsAID vs. all patients (53% vs. 41% respectively for izokibep 80 mg Q2W).
Safety evaluation showed no serious or severe adverse events up to week 16. AE rate overall was 52.3% for Pbo, 65.9% for 40 mg Q2W and 55.3% for 80 mg Q2W. The most common AEs (≥ 5% in any group) were injection site reaction or erythema, headache, hypertension, diarrhea, URTI. Two patients had AESI: one mild, transient vulvovaginal Candida infection; one injection site reaction leading to discontinuation.
Conclusion: Izokibep showed high levels of efficacy across enthesitis, dactylitis and nail scores that were clinically meaningful and statistically significant. Patients with enthesitis at baseline had the largest improvements in PsAID. The izokibep safety profile was generally consistent with other IL-17A inhibitors; in this trial, events were mostly similar to placebo.
 Table 1 – Enthesitis, Dactylitis and NAPSI Efficacy Endpoints at Week 16
Table 1 – Enthesitis, Dactylitis and NAPSI Efficacy Endpoints at Week 16 Figure 1 – PsAID in Full Population and Those with LEI Enthesitis at Baseline
Figure 1 – PsAID in Full Population and Those with LEI Enthesitis at BaselineDisclosures: K. de Vlam, UCB, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, AbbVie/Abbott, Merck/MSD, johnson and johnson; P. Taylor, Biogen, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Janssen, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, UCB, Galapagos, Abbvie; P. Mease, AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB, Sun Pharma, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Genentech; P. Peloso, ACELYRIN, ACELYRIN; D. Wetzel, Affibody; N. Brun, Affibody AB, Affibody AB; B. Wiens, ACELYRIN; J. Brandt-Juergens, AbbVie/Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck/MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Sanofi-Aventis, Medac, Gilead, Gilead, Affibody; E. Drescher, None; E. Dokoupilova, None; A. Rowinska-Osuch, None; N. Abdel- Kader Martin, Pfizer; F. Behrens, AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Galapagos, Gilead, UCB, Affibody, MoonLake, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK).

