Back
Poster Session D
Myopathic rheumatic diseases (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis)
Session: (1856–1887) Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II
1862: Lenabasum Reduces IFNγ and pIRF3 in Dermatomyositis Skin: Biomarker Results from a Double-Blind Phase 3 International Randomized Controlled Trial
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- TV
Thomas Vazquez, MD
University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Thomas Vazquez1, Meena Sharma1, Rui Feng2, DeAnna Diaz3, Nilesh Kodali1, Josh Dan3, Madison Grinnell3, Emily Keyes3, Grant Sprow3, Barbara White4 and Victoria Werth3, 1Philadelphia VAMC, Philadelphia, PA, USA and Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 2University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, 3Philadelphia VAMC, Philadelphia, PA, USA and Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, 4Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Pleasanton, CA
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that primarily affects the skin and lung; few effective treatment options are available. Lenabasum is a cannabinoid type 2 receptor agonist that activates the resolution phase of inflammation. Results from DETERMINE, a Phase 3 trial of lenabasum, demonstrated improvement in CDASI activity (CDASI-A) scores with treatment with lenabasum 20 mg twice daily compared to placebo. Our lab has previously demonstrated via immunohistochemistry (IHC) that lenabasum decreased CD4, IFNβ, IFNγ, and IL31 expression, p < 0.05 versus placebo, in involved skin at 12 weeks in a small Phase 2 study in DM patients, with no significant differences in IL4. Out hypothesis was that similar improvement in biomarkers would be seen in the larger Phase 3 study and would correlate with clinical improvement.
Methods: Skin biopsies from involved skin were obtained at baseline and Week 16 from 31 subjects with DM who enrolled in a double-blind, Phase 3 international randomized trial for lenabasum. Imaging mass cytometry was performed on 66 total formalin fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) skin biopsies, using a 37-marker panel that allowed quantification of expression of 12 intracellular biomarkers in 9 cell types. Statistical analysis was performed using a zero-based, mixed-effects negative binomial model for cell counts and a linear mixed-effects model for intracellular medians.
Results: Subjects in both lenabasum 20 mg BID and placebo treatment groups had similar immune infiltrates in the skin at baseline, except plasmacytoid dendritic cells were increased in the placebo group at baseline (p < 0.05). Lenabasum treatment did not decrease the number or alter the cell type of infiltrating immune cells at Week 16, but did reduce expression of other inflammatory biomarkers. At Week 16, subjects treated with lenabasum versus placebo had a significant decrease in IFNγ (p < 0.05) and phosphorylated-IRF3 (activated transcription factor for IFN-1) (p < 0.05) expression. There was a trend towards decrease in IL-31 expression with lenabasum treatment (p = 0.08). Change in CDASI-A scores was positively correlated with a change in IL-31 median pixel intensity (R = 0.636, p = 0.026) in subjects treated with lenabasum.
Conclusion: These results suggest clinical benefit of lenabasum on skin disease in DM may be mediated in part through reduction of IFNγ, pIRF3 (Type 1 Interferon related pathway), and IL-31 expression. These results support and extend previous findings.
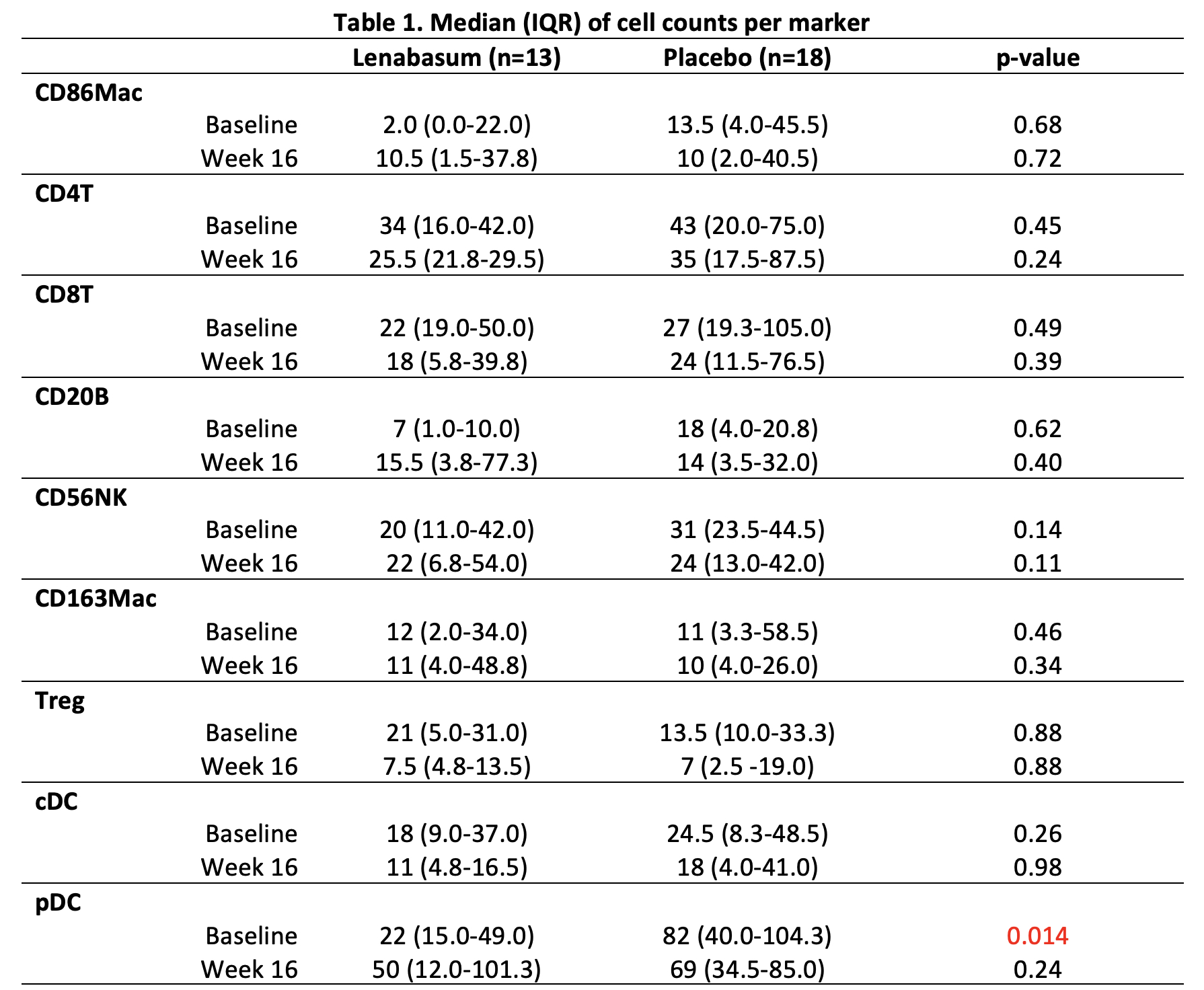 No significant change in cell counts from week 0 to 16 when comparing treatment with 20mg BID of Lenabasum to placebo.
No significant change in cell counts from week 0 to 16 when comparing treatment with 20mg BID of Lenabasum to placebo.
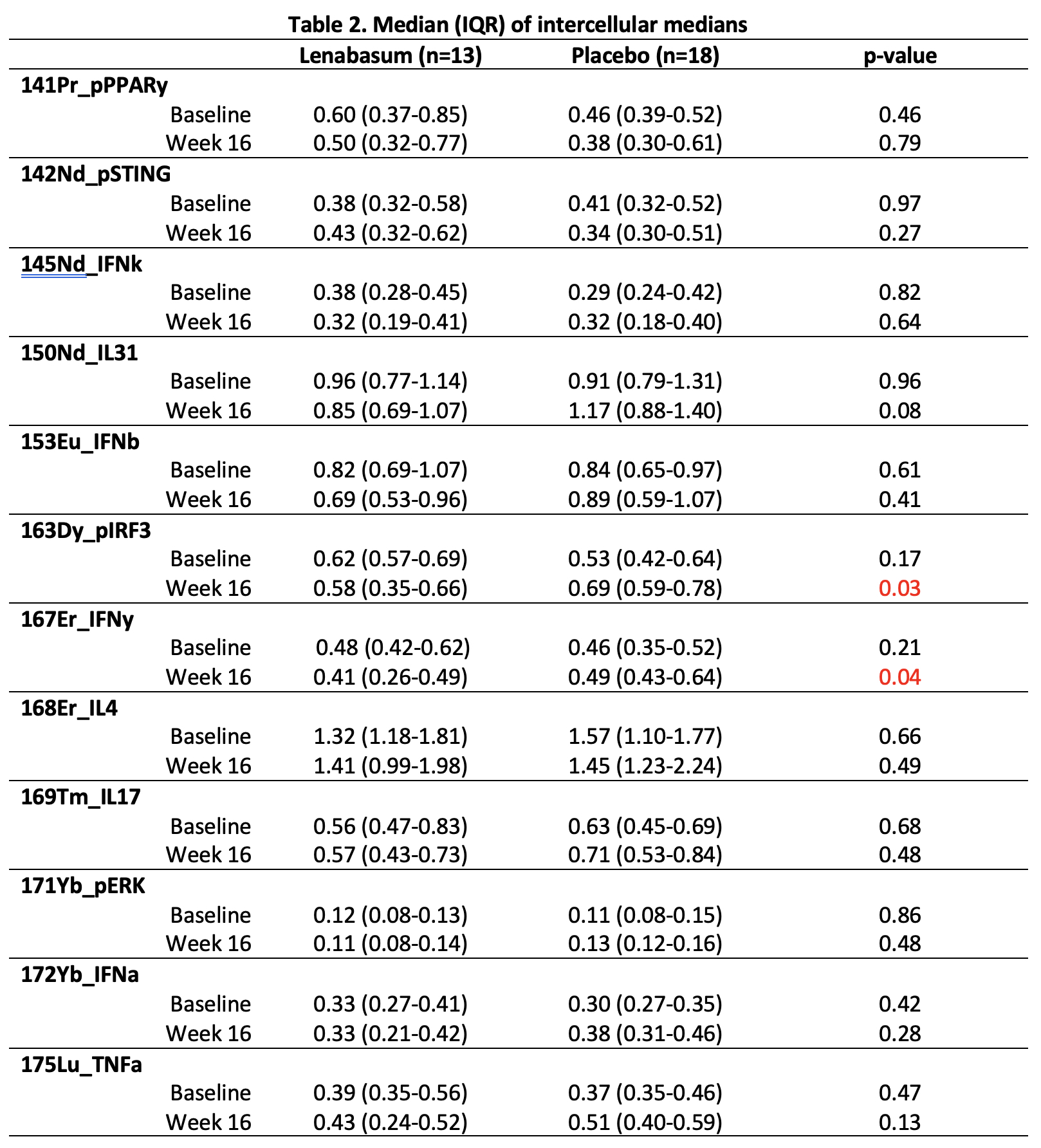 Lenabasum significantly decreased phosphorylated interferon regulatory transcription factor 3 (pIRF3) and interferon gamma (IFNy) (p < 0.05) at 16 weeks compared to placebo. There was a trend towards a decrease in interleukin (IL) -31 (p=0.08).
Lenabasum significantly decreased phosphorylated interferon regulatory transcription factor 3 (pIRF3) and interferon gamma (IFNy) (p < 0.05) at 16 weeks compared to placebo. There was a trend towards a decrease in interleukin (IL) -31 (p=0.08).
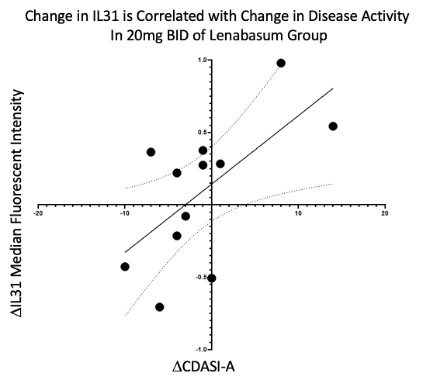 Subset analysis of subjects who received 20mg twice a day of Lenabasum showed that changes in the cutaneous dermatomyositis disease area and severity index activity (CDASI-A) score were positively correlated with change in the median pixel intensity in IL31. R = 0.636, p = 0.026
Subset analysis of subjects who received 20mg twice a day of Lenabasum showed that changes in the cutaneous dermatomyositis disease area and severity index activity (CDASI-A) score were positively correlated with change in the median pixel intensity in IL31. R = 0.636, p = 0.026
Disclosures: T. Vazquez, None; M. Sharma, None; R. Feng, None; D. Diaz, None; N. Kodali, None; J. Dan, None; M. Grinnell, None; E. Keyes, None; G. Sprow, None; B. White, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; V. Werth, GlaxoSmithKline, CLASI.
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease that primarily affects the skin and lung; few effective treatment options are available. Lenabasum is a cannabinoid type 2 receptor agonist that activates the resolution phase of inflammation. Results from DETERMINE, a Phase 3 trial of lenabasum, demonstrated improvement in CDASI activity (CDASI-A) scores with treatment with lenabasum 20 mg twice daily compared to placebo. Our lab has previously demonstrated via immunohistochemistry (IHC) that lenabasum decreased CD4, IFNβ, IFNγ, and IL31 expression, p < 0.05 versus placebo, in involved skin at 12 weeks in a small Phase 2 study in DM patients, with no significant differences in IL4. Out hypothesis was that similar improvement in biomarkers would be seen in the larger Phase 3 study and would correlate with clinical improvement.
Methods: Skin biopsies from involved skin were obtained at baseline and Week 16 from 31 subjects with DM who enrolled in a double-blind, Phase 3 international randomized trial for lenabasum. Imaging mass cytometry was performed on 66 total formalin fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) skin biopsies, using a 37-marker panel that allowed quantification of expression of 12 intracellular biomarkers in 9 cell types. Statistical analysis was performed using a zero-based, mixed-effects negative binomial model for cell counts and a linear mixed-effects model for intracellular medians.
Results: Subjects in both lenabasum 20 mg BID and placebo treatment groups had similar immune infiltrates in the skin at baseline, except plasmacytoid dendritic cells were increased in the placebo group at baseline (p < 0.05). Lenabasum treatment did not decrease the number or alter the cell type of infiltrating immune cells at Week 16, but did reduce expression of other inflammatory biomarkers. At Week 16, subjects treated with lenabasum versus placebo had a significant decrease in IFNγ (p < 0.05) and phosphorylated-IRF3 (activated transcription factor for IFN-1) (p < 0.05) expression. There was a trend towards decrease in IL-31 expression with lenabasum treatment (p = 0.08). Change in CDASI-A scores was positively correlated with a change in IL-31 median pixel intensity (R = 0.636, p = 0.026) in subjects treated with lenabasum.
Conclusion: These results suggest clinical benefit of lenabasum on skin disease in DM may be mediated in part through reduction of IFNγ, pIRF3 (Type 1 Interferon related pathway), and IL-31 expression. These results support and extend previous findings.
 No significant change in cell counts from week 0 to 16 when comparing treatment with 20mg BID of Lenabasum to placebo.
No significant change in cell counts from week 0 to 16 when comparing treatment with 20mg BID of Lenabasum to placebo. Lenabasum significantly decreased phosphorylated interferon regulatory transcription factor 3 (pIRF3) and interferon gamma (IFNy) (p < 0.05) at 16 weeks compared to placebo. There was a trend towards a decrease in interleukin (IL) -31 (p=0.08).
Lenabasum significantly decreased phosphorylated interferon regulatory transcription factor 3 (pIRF3) and interferon gamma (IFNy) (p < 0.05) at 16 weeks compared to placebo. There was a trend towards a decrease in interleukin (IL) -31 (p=0.08). Subset analysis of subjects who received 20mg twice a day of Lenabasum showed that changes in the cutaneous dermatomyositis disease area and severity index activity (CDASI-A) score were positively correlated with change in the median pixel intensity in IL31. R = 0.636, p = 0.026
Subset analysis of subjects who received 20mg twice a day of Lenabasum showed that changes in the cutaneous dermatomyositis disease area and severity index activity (CDASI-A) score were positively correlated with change in the median pixel intensity in IL31. R = 0.636, p = 0.026Disclosures: T. Vazquez, None; M. Sharma, None; R. Feng, None; D. Diaz, None; N. Kodali, None; J. Dan, None; M. Grinnell, None; E. Keyes, None; G. Sprow, None; B. White, Corbus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; V. Werth, GlaxoSmithKline, CLASI.

