Back
Poster Session B
Immunobiology
Session: (0578–0588) Cytokines and Cell Trafficking Poster
0580: 18F-FDG PET-MR Characterization of Aortitis in the IL1rn-/- Mouse Model of Giant-Cell Arteritis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AA
Achille Aouba
CHU de Caen Normandie
Caen, France
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Samuel Deshayes1, Caroline Baugé2, Pierre-Antoine Dupont2, Christophe Simard2, Hubert De Boysson1, Alain Manrique2 and Achille Aouba1, 1Department of Internal Medicine, UR4650 PSIR, Normandie Univ, UNICAEN, CHU de Caen Normandie, Caen, France, 2UR4650 PSIR, Normandie Univ, UNICAEN, Caen, France
Background/Purpose: Metabolic imaging is routinely used to demonstrate aortitis in patients with giant-cell arteritis. We aimed to investigate aortitis in BALB/c IL1rn-/- mice, a preclinical model of aortitis, using 18F-FDG Positron Emission Tomography–Magnetic Resonance (PET-MR).
Methods: Fifteen first-generation specific and opportunistic pathogen-free (SOPF) 9-week-old IL1rn-/- mice and 15 wild-type BALB/cAnN mice were investigated using 18F-FDG PET-MR imaging, gamma-counting and immunostainings (anti-CD4, -CD8, -CD11c, -CD20, -CD31, -CD63, -CD163, -interferon-γ, interleukin-1α, -1β, -6, -17A antibodies). In addition, 5 second-generation specific pathogen-free (SPF) 9-week-old IL1rn-/- mice also underwent 18F-FDG PET-MR. Aortic 18F-FDG uptake was assessed as the target-to-background ratio (TBR) using time-of-flight MR angiography as vascular landmarks.
Results: 18F-FDG uptake measured by PET or gamma-counting was similar in the first-generation SOPF IL1rn-/- mice and the wild-type group. However, the first-generation IL1rn-/- mice exhibited significantly more interleukin-1β (p=0.021) and interleukin-6 (p=0.019) positive cells within abdominal aorta compared to the wild-type group. In addition, the second-generation SPF group exhibited a significantly higher TBR (p=0.0068) than the wild-type mice on the descending thoracic aorta, unlike the first-generation SOPF IL1rn-/- mice.
Conclusion: Besides the involvement of IL-1 and IL-6 in the mouse model of IL1rn-/- aortitis, this study validates 18F-FDG PET-MR as a useful tool for noninvasive monitoring of aortitis in this preclinical model. By demonstrating an increased aortic glucose metabolism, specifically in second-generation SPF 9-week-old IL1rn-/- mice, but not in the first-generation SOPF IL1rn-/- mice, compared to the wild-type group, our data suggest a pathophysiological role of the microbiota in this aortitis model and open perspectives for further pathophysiological and therapeutic investigations in this preclinical model.
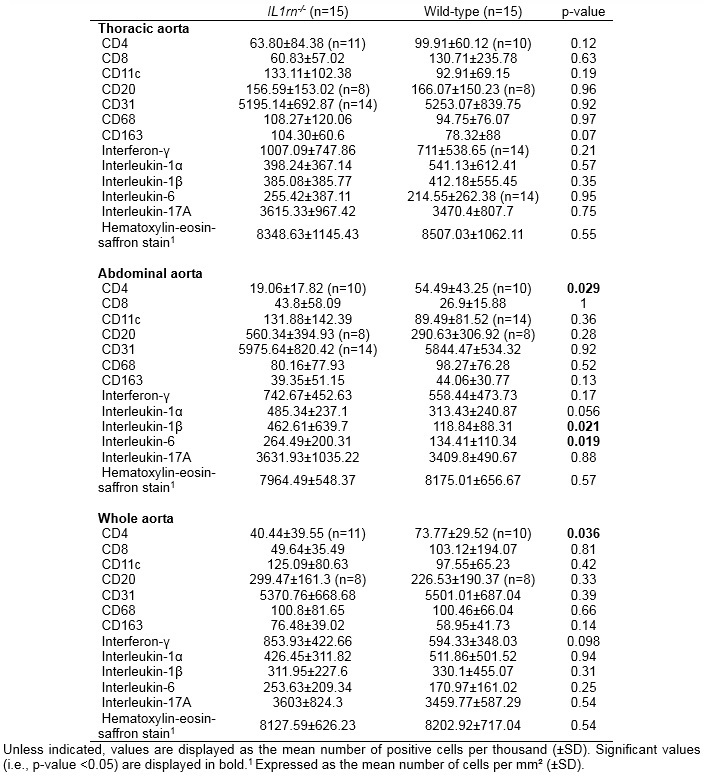 Results of histological stainings of mice aorta
Results of histological stainings of mice aorta
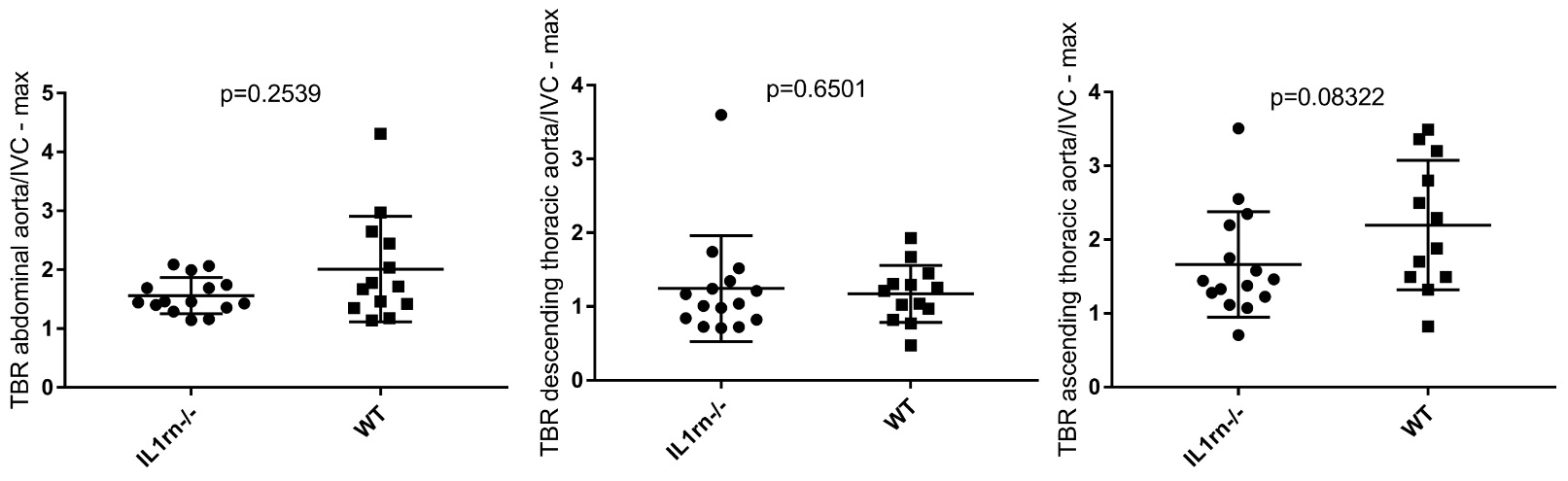 Results of the PET quantification in first-generation specific and opportunistic pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=15) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)
Results of the PET quantification in first-generation specific and opportunistic pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=15) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)
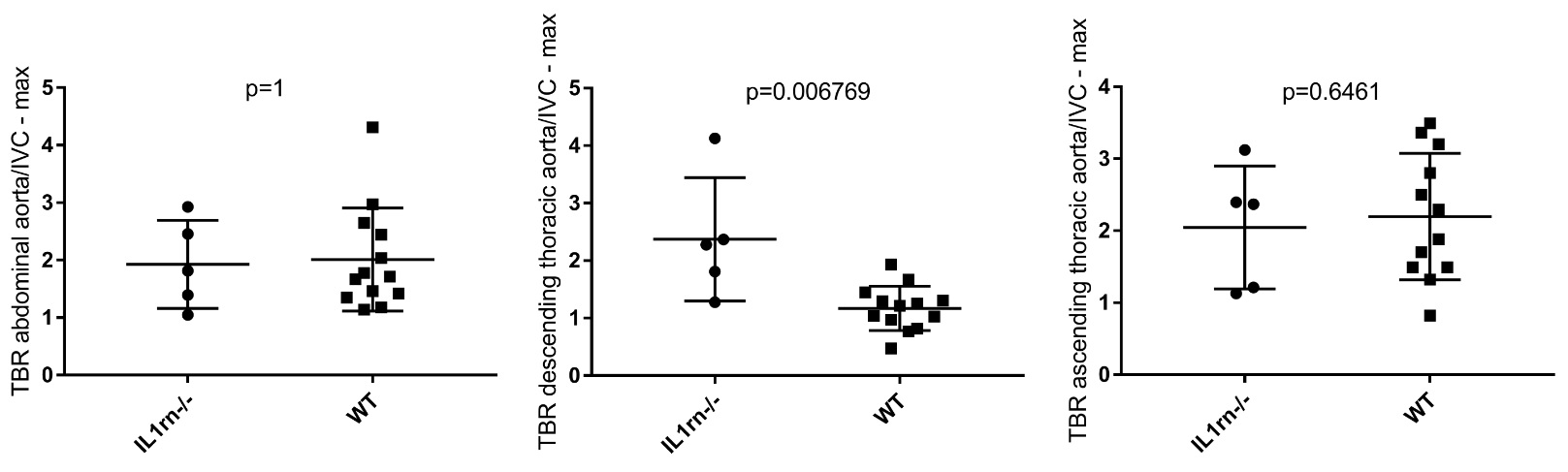 Results of the PET quantification in second-generation specific pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=5) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)
Results of the PET quantification in second-generation specific pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=5) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)
Disclosures: S. Deshayes, None; C. Baugé, None; P. Dupont, None; C. Simard, None; H. De Boysson, None; A. Manrique, None; A. Aouba, Roche.
Background/Purpose: Metabolic imaging is routinely used to demonstrate aortitis in patients with giant-cell arteritis. We aimed to investigate aortitis in BALB/c IL1rn-/- mice, a preclinical model of aortitis, using 18F-FDG Positron Emission Tomography–Magnetic Resonance (PET-MR).
Methods: Fifteen first-generation specific and opportunistic pathogen-free (SOPF) 9-week-old IL1rn-/- mice and 15 wild-type BALB/cAnN mice were investigated using 18F-FDG PET-MR imaging, gamma-counting and immunostainings (anti-CD4, -CD8, -CD11c, -CD20, -CD31, -CD63, -CD163, -interferon-γ, interleukin-1α, -1β, -6, -17A antibodies). In addition, 5 second-generation specific pathogen-free (SPF) 9-week-old IL1rn-/- mice also underwent 18F-FDG PET-MR. Aortic 18F-FDG uptake was assessed as the target-to-background ratio (TBR) using time-of-flight MR angiography as vascular landmarks.
Results: 18F-FDG uptake measured by PET or gamma-counting was similar in the first-generation SOPF IL1rn-/- mice and the wild-type group. However, the first-generation IL1rn-/- mice exhibited significantly more interleukin-1β (p=0.021) and interleukin-6 (p=0.019) positive cells within abdominal aorta compared to the wild-type group. In addition, the second-generation SPF group exhibited a significantly higher TBR (p=0.0068) than the wild-type mice on the descending thoracic aorta, unlike the first-generation SOPF IL1rn-/- mice.
Conclusion: Besides the involvement of IL-1 and IL-6 in the mouse model of IL1rn-/- aortitis, this study validates 18F-FDG PET-MR as a useful tool for noninvasive monitoring of aortitis in this preclinical model. By demonstrating an increased aortic glucose metabolism, specifically in second-generation SPF 9-week-old IL1rn-/- mice, but not in the first-generation SOPF IL1rn-/- mice, compared to the wild-type group, our data suggest a pathophysiological role of the microbiota in this aortitis model and open perspectives for further pathophysiological and therapeutic investigations in this preclinical model.
 Results of histological stainings of mice aorta
Results of histological stainings of mice aorta Results of the PET quantification in first-generation specific and opportunistic pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=15) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)
Results of the PET quantification in first-generation specific and opportunistic pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=15) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta) Results of the PET quantification in second-generation specific pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=5) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)
Results of the PET quantification in second-generation specific pathogen-free 9-week-old BALB/c IL1rn-/- (n=5) or wild-type mice (n=13 or n=12 for the ascending thoracic aorta)Disclosures: S. Deshayes, None; C. Baugé, None; P. Dupont, None; C. Simard, None; H. De Boysson, None; A. Manrique, None; A. Aouba, Roche.

