Back
Poster Session B
Session: (0752–0778) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
0773: Additional Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Improves Cross-Variant Neutralization Titers in Immunosuppressed Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Disease
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

Michael Paley, MD, PhD
Washington University in St. Louis
Saint Louis, MO, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Michael Paley1, Parakkal Deepak2, Wooseob Kim3, Monica Yang4, Vinay Chandrasekaran3, Guadalupe Oliva Escudero3, Katherine Huang3, Zhuoming Liu3, Lily McMorrow5, Mahima Thapa3, Matthew Ciorba3, Mehrdad Matloubian6, Lianne Gensler7, Mary Nakamura8, Sean Whelan3, William Buchser3, Ali Ellebedy3 and Alfred Kim5, 1Washington University in St. Louis, Saint Louis, MO, 2Washington University in St. Louis, Saint Louis, 3Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO, 4UCSF, SF, CA, 5Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, 6UCSF, San Francisco, CA, 7Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 8UCSF/SFVAHCS, San Francisco, CA
Background/Purpose: Most immunosuppressed patients with chronic inflammatory diseases (CID) mount total anti-Spike (S) IgG responses following vaccination with mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Less is known, however, about cross-variant neutralization potential, an immune correlate of protection that highly associates with efficacy of vaccination. Here, we describe how an additional dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination influences both total anti-S IgG and neutralizing titers to variants of concern.
Methods: The COVID-19 Vaccine Responses in Patients with Autoimmune Disease (COVaRiPAD) study is a prospective assessment of mRNA-based vaccine immunogenicity and reactogenicity in patients with CID. A total of 340 adults with CIDs were enrolled, with 81 participants having samples available at both 5 months after completion of the initial series and 4 weeks after the third dose. Serum anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) IgG+ binding and neutralizing antibody titers to vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotyped with S protein from D614G (common), (Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta), B.1.617.2 (Delta), P.1 (Gamma), and B.1.1.519 subvariant (Omicron) were quantified.
Results: When examining the effect of a third dose of vaccine, total anti-S IgG titers increased >100-fold for most classes with exception of those on B cell depleting therapies. The additional dose did increase neutralization titers to all variants tested in most immunosuppressive classes with n ≥ 4 (Table 2), including 3- to 9-fold increases in neutralization against Omicron.
Conclusion: Reassuringly, immunosuppressed patients with CID mounted improved total anti-S IgG and neutralizing antibody titers to variants of concern broadly across various immunosuppressive classes. This highlights the necessity to provide additional doses beyond the initial series, which likely will extend to doses beyond the third dose.
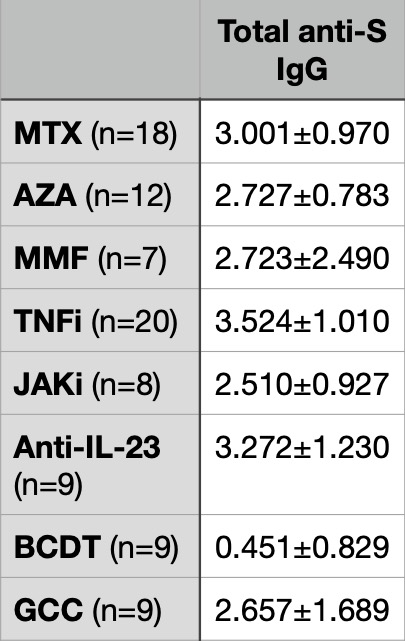 Table 1. Exponential fold change of total anti-S IgG titers between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
Table 1. Exponential fold change of total anti-S IgG titers between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
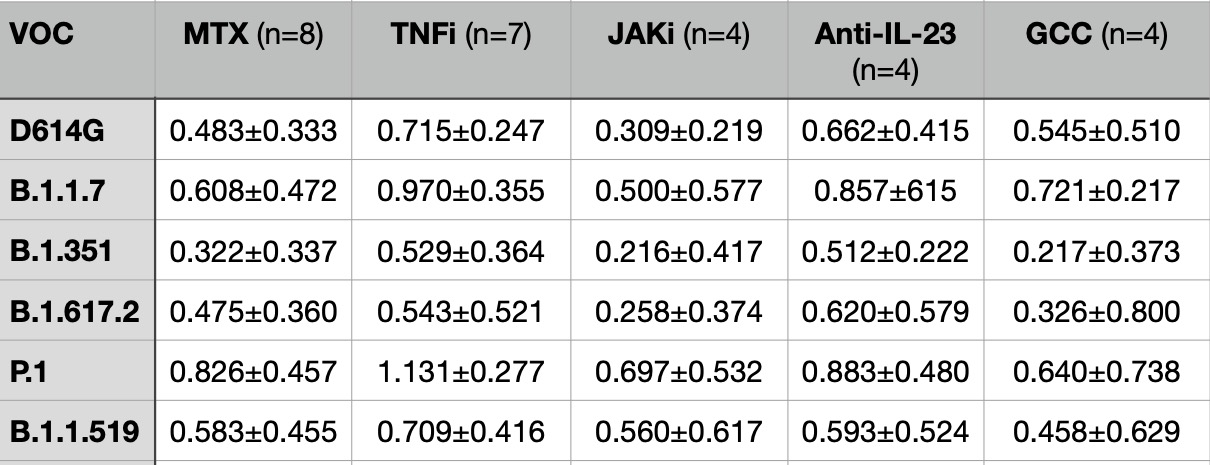 Table 2. Exponential fold change of neutralizing titers to variants of concern (VOC) between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
Table 2. Exponential fold change of neutralizing titers to variants of concern (VOC) between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
Disclosures: M. Paley, AbbVie/Abbott, Priovant Therapeutics, Inc., Lilly, JK Market Research; P. Deepak, None; W. Kim, None; M. Yang, None; V. Chandrasekaran, None; G. Oliva Escudero, None; K. Huang, None; Z. Liu, None; L. McMorrow, None; M. Thapa, None; M. Ciorba, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Theravance, Incyte, Janssen; M. Matloubian, None; L. Gensler, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Moonlake; M. Nakamura, Moderna; S. Whelan, Vir Biotechnology, AbbVie/Abbott, SAb Therapeutics; W. Buchser, None; A. Ellebedy, AbbVie/Abbott, Emergent BioSolutions; A. Kim, GlaxoSmithKline, Kypha Inc., Foghorn Therapeutics, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Exagen Diagnostics, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AstraZeneca.
Background/Purpose: Most immunosuppressed patients with chronic inflammatory diseases (CID) mount total anti-Spike (S) IgG responses following vaccination with mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Less is known, however, about cross-variant neutralization potential, an immune correlate of protection that highly associates with efficacy of vaccination. Here, we describe how an additional dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination influences both total anti-S IgG and neutralizing titers to variants of concern.
Methods: The COVID-19 Vaccine Responses in Patients with Autoimmune Disease (COVaRiPAD) study is a prospective assessment of mRNA-based vaccine immunogenicity and reactogenicity in patients with CID. A total of 340 adults with CIDs were enrolled, with 81 participants having samples available at both 5 months after completion of the initial series and 4 weeks after the third dose. Serum anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) IgG+ binding and neutralizing antibody titers to vesicular stomatitis virus pseudotyped with S protein from D614G (common), (Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta), B.1.617.2 (Delta), P.1 (Gamma), and B.1.1.519 subvariant (Omicron) were quantified.
Results: When examining the effect of a third dose of vaccine, total anti-S IgG titers increased >100-fold for most classes with exception of those on B cell depleting therapies. The additional dose did increase neutralization titers to all variants tested in most immunosuppressive classes with n ≥ 4 (Table 2), including 3- to 9-fold increases in neutralization against Omicron.
Conclusion: Reassuringly, immunosuppressed patients with CID mounted improved total anti-S IgG and neutralizing antibody titers to variants of concern broadly across various immunosuppressive classes. This highlights the necessity to provide additional doses beyond the initial series, which likely will extend to doses beyond the third dose.
 Table 1. Exponential fold change of total anti-S IgG titers between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
Table 1. Exponential fold change of total anti-S IgG titers between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination Table 2. Exponential fold change of neutralizing titers to variants of concern (VOC) between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination
Table 2. Exponential fold change of neutralizing titers to variants of concern (VOC) between pre- and post-3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinationDisclosures: M. Paley, AbbVie/Abbott, Priovant Therapeutics, Inc., Lilly, JK Market Research; P. Deepak, None; W. Kim, None; M. Yang, None; V. Chandrasekaran, None; G. Oliva Escudero, None; K. Huang, None; Z. Liu, None; L. McMorrow, None; M. Thapa, None; M. Ciorba, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Theravance, Incyte, Janssen; M. Matloubian, None; L. Gensler, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Gilead, Moonlake; M. Nakamura, Moderna; S. Whelan, Vir Biotechnology, AbbVie/Abbott, SAb Therapeutics; W. Buchser, None; A. Ellebedy, AbbVie/Abbott, Emergent BioSolutions; A. Kim, GlaxoSmithKline, Kypha Inc., Foghorn Therapeutics, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Exagen Diagnostics, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, AstraZeneca.

