Back
Poster Session B
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (1004–1034) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
1023: Are We Treating-to-target in Spondyloarthritis (SpA)? A Cross Sectional Analysis from the Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology (APLAR) SpA Registry
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- IC
Isaac Cheng, PhD
The Chinese University of Hong Kong
Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Isaac Cheng1, Ying Ying Leung2, Ho SO1, Praveena Chiowchanwisawakit3, Stanley Angkodjojo4, Muhammad Saeed5, Kichul Shin6, Han Joo Baek7, Mohit Goyal8, Muhammad Haroon9, Eman Satti10, Nallasivan Subramanian11, Fariz Yahya12, Soosan Soroosh13, ASAL ADNAN RIDHA14, Ho Yin Chung15, James Cheng-Chung WEI16, Kishimoto Mitsumasa17 and Lai-shan Tam1, 1The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2Rheumatology Department, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, Singapore, 3Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, 4Sengkang General Hospital / Singhealth, Singapore, Singapore, 5Central Park Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan, 6Seoul Metropolitan Government- Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 7Gachon University College of Medicine, Inchon, Republic of Korea, 8CARE Pain & Arthritis Centre, Udaipur, India, 9Doctor, Tralee, Ireland, 10Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Qatar, 11Velammal Medical College Hospital, Velammal, India, 12University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13Army University for Medical School, Tehran, Iran, 14Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Baghdad, Iraq, 15Chiron Medical, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 16Chung Shan Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan, 17Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
Background/Purpose: Data on the extent to which internationally agreed treat-to-target (T2T) recommendations were applied in clinical practice in patients with SpA across the Asia-Pacific region is lacking. The APLAR SpA Registry is a multi-centre study aiming to assess the utility of early diagnosis and intensive protocolized treatment to patients with SpA on the long-term outcome in order to improve management of the disease and inform health-care policy. This analysis aimed to provide a snapshot of the baseline characteristics of participants in this registry.
Methods: Patients fulfilled CASPAR 2006 classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and 2009 ASAS criteria for axial spondylitis (AxSpA) were recruited. The current analysis included the first 299 patients recruited across 9 Asia-Pacific regions (Hong Kong, Singapore, Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, India, Qatar and Pakistan)
Results: 123 patients with PsA (age: 50±14 years, 62 (52%) male, disease duration: 6.4±7.2 years) and 176 patients with AxSpA (age: 37±13 years, 138 (81%) male, disease duration 5.1±7.2 years) were included. Majority (95%) of them were Asian, 86% had education level above secondary school and 65% were employed. They had moderate inflammatory burden (mean DAPSA in PsA: 18.60±14.79, mean ASDAS in AxSpA: 2.37±1.16). The majority of patients with PsA received conventional synthetic disease-modifying drug (csDMARDs, 83%) with relatively low prevalence of biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) use (31%). Most patients with AxSpA used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs, 78%) while nearly half of them were using bDMARDs (46%). The demographics and clinical data are listed in table 1. The prevalence of bDMARDs use in our registry was lower than that from the USA (CorEvitas PsA Registry, 59%), Turkey and Canada (PsA International Database [PsArt-ID, 40%] and the Netherlands AxSpA registry (56%) (1-3). Regarding T2T, 32% and 40% of patient with PsA achieved minimal disease activity (MDA) and Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis low disease activity (DAPSA LDA) respectively. The proportion of patients achieving target in other cohorts were 46% for MDA in PsArt-ID and 46% for DAPSA-LDA in CorEvitas Registry (1, 2). Meanwhile, 36% and 68% of patient with AxSpA achieved Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)< 4 and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score low disease activity (ASDAS LDA). The proportion of patients achieving ASDAS LDA were comparable to the Netherlands registry for patients with ASDAS-LDA (Fig 1A)(3). Patient on bDMARDs were more likely to achieve target (PsA: MDA achieved in 35% bDMARDs users vs 30% in non bDMARDs users; DAPSA LDA achieved in 67% in bDMARDs users vs 40% in non bDMARDs users. In AxSpA, BASDAI< 4 was achieved in 78% in bDMARDs users vs 62% in non bDMARDs users; ASDAS LDA achieved in 56% in bDMARDs users vs 42% in non bDMARDs users) (Fig 1B). There was no significant difference between socio-economic status, age, gender and disease duration between biologic user and non user
Conclusion: SpA patients using bDMARDs were more likely to achieve treatment target. We expect that more patients will be able to achieve target when the T2T strategy is widely adopted in this APLAR cohort in the following years
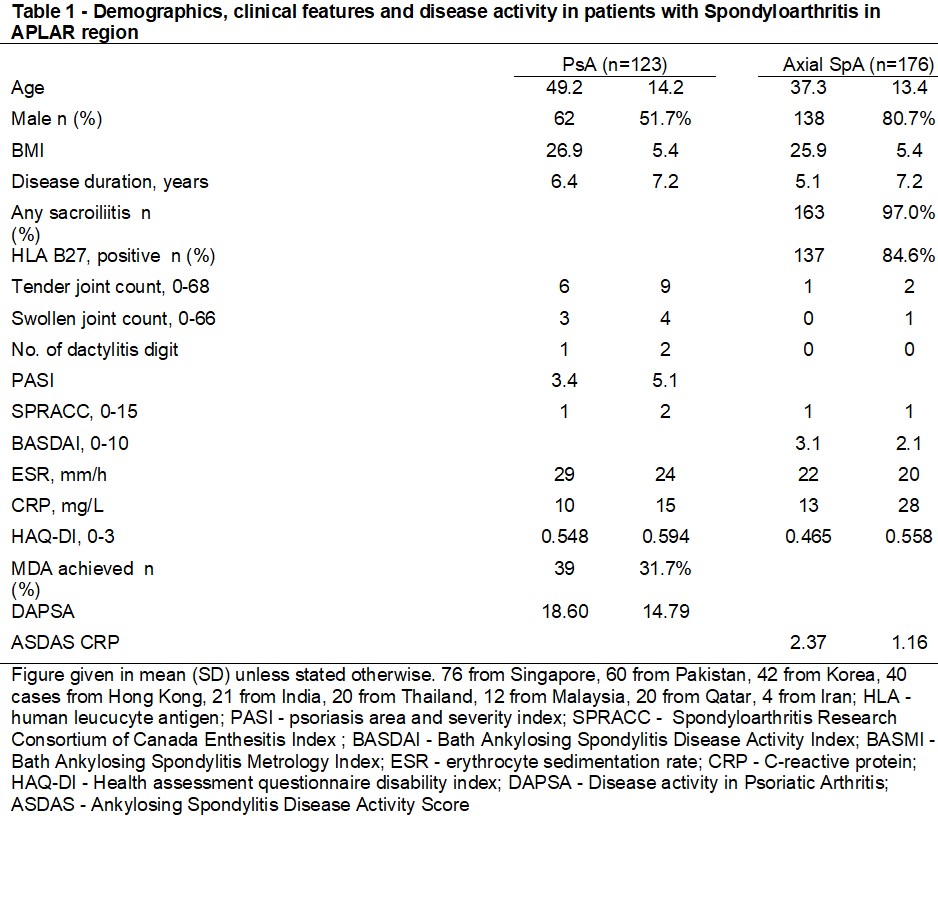 Table 1 - Demographics, clinical features and disease activity in patients with Spondyloarthritis in APLAR region
Table 1 - Demographics, clinical features and disease activity in patients with Spondyloarthritis in APLAR region
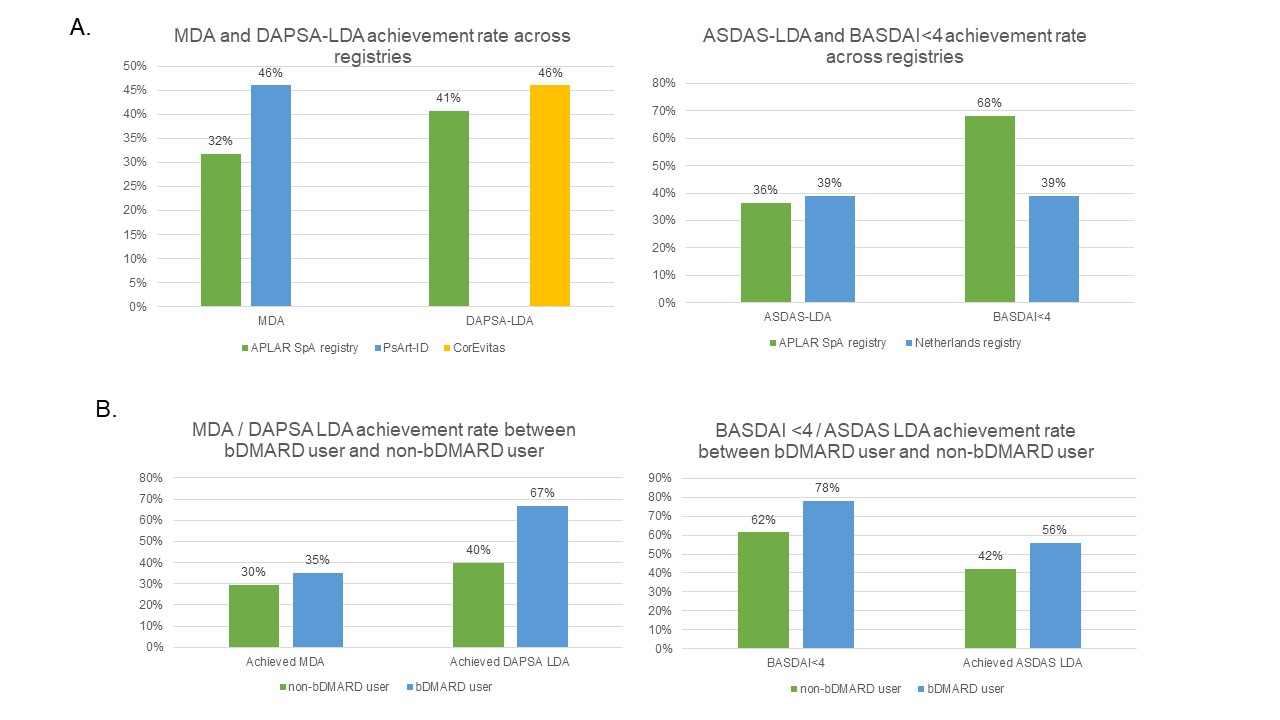 Figure 1 - (A) Achievement of low disease activity in APLAR SpA registry and other registry and (B) use of bDMARDs among patients in APLAR SpA registry with or without achieving low disease activity
Figure 1 - (A) Achievement of low disease activity in APLAR SpA registry and other registry and (B) use of bDMARDs among patients in APLAR SpA registry with or without achieving low disease activity
Disclosures: I. Cheng, None; Y. Leung, AbbVie/Abbott, Janssen, Pfizer, DKSH; H. SO, None; P. Chiowchanwisawakit, None; S. Angkodjojo, None; M. Saeed, None; K. Shin, None; H. Baek, None; M. Goyal, None; M. Haroon, None; E. Satti, None; N. Subramanian, None; F. Yahya, None; S. Soroosh, None; A. RIDHA, None; H. Chung, None; J. WEI, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi-Aventis, TSH Taiwan, UCB, JHL Taiwan; K. Mitsumasa, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen-Astellas BioPharma, Asahi-Kasei Pharma, Astellas, Ayumi Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis, Pfizer, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Teijin Pharma, UCB; L. Tam, AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, AstraZeneca.
Background/Purpose: Data on the extent to which internationally agreed treat-to-target (T2T) recommendations were applied in clinical practice in patients with SpA across the Asia-Pacific region is lacking. The APLAR SpA Registry is a multi-centre study aiming to assess the utility of early diagnosis and intensive protocolized treatment to patients with SpA on the long-term outcome in order to improve management of the disease and inform health-care policy. This analysis aimed to provide a snapshot of the baseline characteristics of participants in this registry.
Methods: Patients fulfilled CASPAR 2006 classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and 2009 ASAS criteria for axial spondylitis (AxSpA) were recruited. The current analysis included the first 299 patients recruited across 9 Asia-Pacific regions (Hong Kong, Singapore, Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, India, Qatar and Pakistan)
Results: 123 patients with PsA (age: 50±14 years, 62 (52%) male, disease duration: 6.4±7.2 years) and 176 patients with AxSpA (age: 37±13 years, 138 (81%) male, disease duration 5.1±7.2 years) were included. Majority (95%) of them were Asian, 86% had education level above secondary school and 65% were employed. They had moderate inflammatory burden (mean DAPSA in PsA: 18.60±14.79, mean ASDAS in AxSpA: 2.37±1.16). The majority of patients with PsA received conventional synthetic disease-modifying drug (csDMARDs, 83%) with relatively low prevalence of biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) use (31%). Most patients with AxSpA used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs, 78%) while nearly half of them were using bDMARDs (46%). The demographics and clinical data are listed in table 1. The prevalence of bDMARDs use in our registry was lower than that from the USA (CorEvitas PsA Registry, 59%), Turkey and Canada (PsA International Database [PsArt-ID, 40%] and the Netherlands AxSpA registry (56%) (1-3). Regarding T2T, 32% and 40% of patient with PsA achieved minimal disease activity (MDA) and Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis low disease activity (DAPSA LDA) respectively. The proportion of patients achieving target in other cohorts were 46% for MDA in PsArt-ID and 46% for DAPSA-LDA in CorEvitas Registry (1, 2). Meanwhile, 36% and 68% of patient with AxSpA achieved Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI)< 4 and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score low disease activity (ASDAS LDA). The proportion of patients achieving ASDAS LDA were comparable to the Netherlands registry for patients with ASDAS-LDA (Fig 1A)(3). Patient on bDMARDs were more likely to achieve target (PsA: MDA achieved in 35% bDMARDs users vs 30% in non bDMARDs users; DAPSA LDA achieved in 67% in bDMARDs users vs 40% in non bDMARDs users. In AxSpA, BASDAI< 4 was achieved in 78% in bDMARDs users vs 62% in non bDMARDs users; ASDAS LDA achieved in 56% in bDMARDs users vs 42% in non bDMARDs users) (Fig 1B). There was no significant difference between socio-economic status, age, gender and disease duration between biologic user and non user
Conclusion: SpA patients using bDMARDs were more likely to achieve treatment target. We expect that more patients will be able to achieve target when the T2T strategy is widely adopted in this APLAR cohort in the following years
 Table 1 - Demographics, clinical features and disease activity in patients with Spondyloarthritis in APLAR region
Table 1 - Demographics, clinical features and disease activity in patients with Spondyloarthritis in APLAR region Figure 1 - (A) Achievement of low disease activity in APLAR SpA registry and other registry and (B) use of bDMARDs among patients in APLAR SpA registry with or without achieving low disease activity
Figure 1 - (A) Achievement of low disease activity in APLAR SpA registry and other registry and (B) use of bDMARDs among patients in APLAR SpA registry with or without achieving low disease activityDisclosures: I. Cheng, None; Y. Leung, AbbVie/Abbott, Janssen, Pfizer, DKSH; H. SO, None; P. Chiowchanwisawakit, None; S. Angkodjojo, None; M. Saeed, None; K. Shin, None; H. Baek, None; M. Goyal, None; M. Haroon, None; E. Satti, None; N. Subramanian, None; F. Yahya, None; S. Soroosh, None; A. RIDHA, None; H. Chung, None; J. WEI, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen, Celgene, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi-Aventis, TSH Taiwan, UCB, JHL Taiwan; K. Mitsumasa, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen-Astellas BioPharma, Asahi-Kasei Pharma, Astellas, Ayumi Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis, Pfizer, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Teijin Pharma, UCB; L. Tam, AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, AstraZeneca.

