Back
Abstract Session
Session: Abstracts: T Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disease (2183–2186)
2183: mTORC2 Contributes to Murine Systemic Autoimmunity
Monday, November 14, 2022
3:00 PM – 3:10 PM Eastern Time
Location: Room 114 Nutter Theatre
- HZ
Hu Zeng, PhD
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Xian Zhou1, Haiyu Qi1, Meilu Li1, Yanfeng Li1, Xingxing Zhu2, Anne Davidson3 and Hu Zeng1, 1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 2Mayo Clinic, Rochester, 3Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, NY
Background/Purpose: The development of many systemic autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, is associated with overactivation of the type I interferon (IFN) pathway, lymphopenia, and imbalance between follicular helper T (Tfh) cell and regulatory T cells (Treg). However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these immunological perturbations remain incompletely understood. Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) shares the mTOR kinase with mTORC1, but differs from mTORC1 with its scaffold protein and defining subunit Rictor. Previous investigations show that mTORC2 is critically required for Tfh differentiation, but not for other effector T cell lineages. It exerts a negative regulation on Treg generation and suppressive function. This study aims to experimentally test the hypothesis that genetic targeting mTORC2 may benefit systemic autoimmunity. We explored the molecular, cellular, and metabolic mechanisms through which mTORC2 may contribute to murine systemic autoimmunity.
Methods: We generated B6.Lpr mice with T cell specific deletion of Rictor, or Treg specific deletion of Rictor. Immune cell homeostasis was analyzed by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. Antibody and inflammatory cytokine production were measured by ELISA or beads-based immunoassays. T cell metabolic activity was measured by Seahorse XFe96 bioanalyzer. Signaling events following TCR and/or type I IFN stimulation were measured by immunoblot or phosflow assays.
Results: Using genetic mouse models, we show that the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) promotes Tfh differentiation and disrupts Treg homeostasis. Inactivation of mTORC2 in total T cells, but not in Tregs, greatly ameliorated the immunopathology in a systemic autoimmunity mouse model. This was associated with reduced Tfh differentiation, B cell activation, and reduced T cell glucose metabolism. Finally, we show that type I IFN can synergize with TCR ligation to activate mTORC2 in T cells, which partially contributes to T cell lymphopenia. T cell specific deletion of Rictor partially restores the T cell lymphopenia phenotype in a lupus-prone mouse model.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that mTORC2 may act as downstream of type I IFN, TCR, and costimulatory receptor ICOS, to promote glucose metabolism, Tfh differentiation, and T cell lymphopenia, but not to suppress Treg function in systemic autoimmunity. Our results suggest that mTORC2 might be a rational target for systemic autoimmunity treatment.
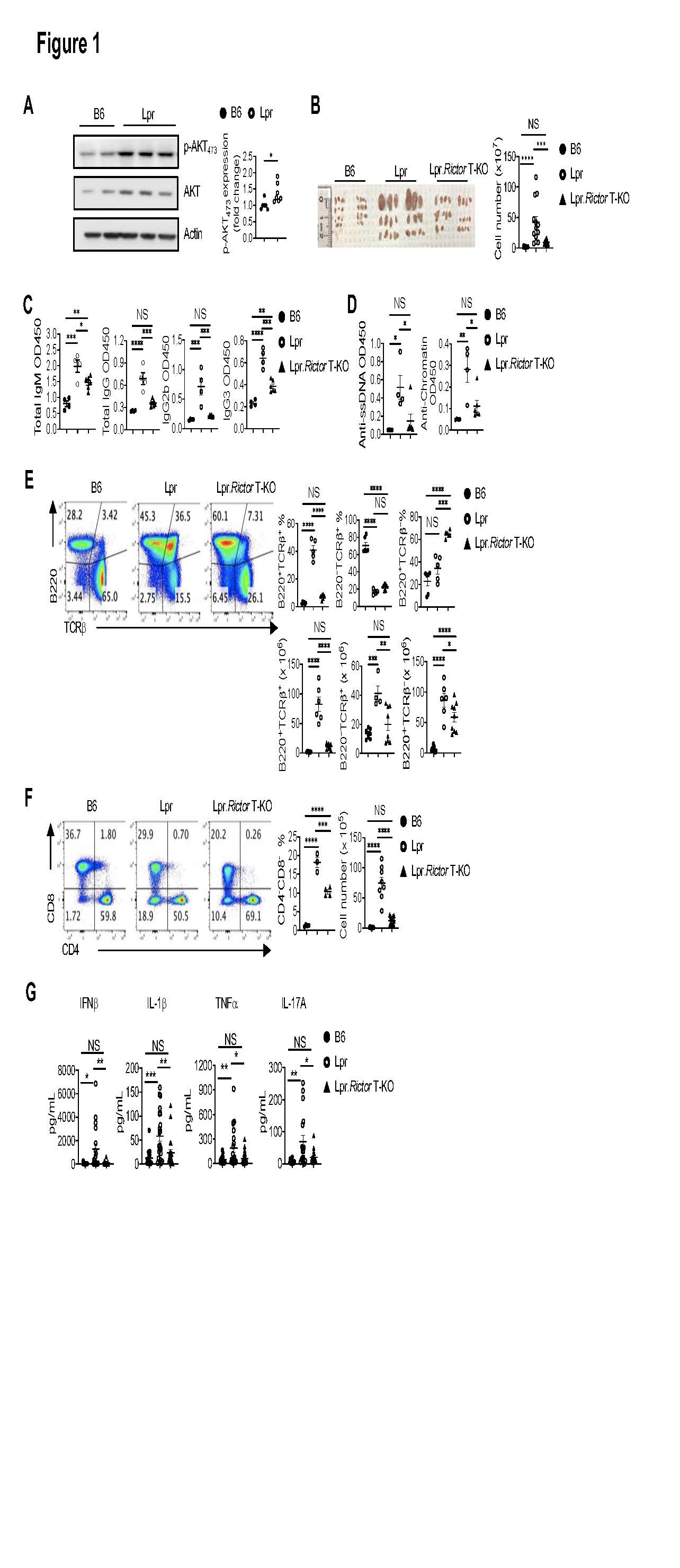 Figure 1. Rictor deletion in T cells rectifies immunopathology in Lpr mice. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473 in B6 and Lpr CD4+ T cells isolated from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN). Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells). (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Titers of total immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG, IgG2b and IgG3 were measured by ELISA. (D) Titers of anti-ssDNA (left) and anti-chromatin (right) were measured by ELISA. Samples were from 9 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (E) Expression of B220 and TCRon lymphocytes. Right, the frequencies (upper panels) and absolute numbers (lower panels) of B220+TCR+, B220–TCR+, B220+TCR– cells. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cells among B220–TCR+ cells. Right, the frequency (left) and absolute number (right) of CD4–CD8– T cell population. (E) and (F) Cells were from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN) of 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (G) The inflammatory cytokine levels in mouse sera samples collected from 5-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. p values were calculated with one-way ANOVA. Results were presentative of 3 (A) independent experiment and pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Figure 1. Rictor deletion in T cells rectifies immunopathology in Lpr mice. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473 in B6 and Lpr CD4+ T cells isolated from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN). Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells). (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Titers of total immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG, IgG2b and IgG3 were measured by ELISA. (D) Titers of anti-ssDNA (left) and anti-chromatin (right) were measured by ELISA. Samples were from 9 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (E) Expression of B220 and TCRon lymphocytes. Right, the frequencies (upper panels) and absolute numbers (lower panels) of B220+TCR+, B220–TCR+, B220+TCR– cells. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cells among B220–TCR+ cells. Right, the frequency (left) and absolute number (right) of CD4–CD8– T cell population. (E) and (F) Cells were from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN) of 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (G) The inflammatory cytokine levels in mouse sera samples collected from 5-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. p values were calculated with one-way ANOVA. Results were presentative of 3 (A) independent experiment and pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
 Figure 2. Rictor deletion in Treg is unable to restore immune dysregulation in Lpr mice. (A) Frequency of FOXP3+ Treg cells in splenic CD4+ T cells. (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Frequency of B220+TCR+ cells in pLN among B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. (D) Frequencies of pre-Tfh (BCL6 –CXCR5+) and Tfh (BCL6 +CXCR5+) cells in pLN. (E) Frequency of GC B cells. (F) The ratio between Tfh and Treg frequency in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO mice. (G) Serum concentrations of immunoglobulin IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b were measured by LEGENDplex. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Results were pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Figure 2. Rictor deletion in Treg is unable to restore immune dysregulation in Lpr mice. (A) Frequency of FOXP3+ Treg cells in splenic CD4+ T cells. (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Frequency of B220+TCR+ cells in pLN among B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. (D) Frequencies of pre-Tfh (BCL6 –CXCR5+) and Tfh (BCL6 +CXCR5+) cells in pLN. (E) Frequency of GC B cells. (F) The ratio between Tfh and Treg frequency in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO mice. (G) Serum concentrations of immunoglobulin IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b were measured by LEGENDplex. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Results were pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
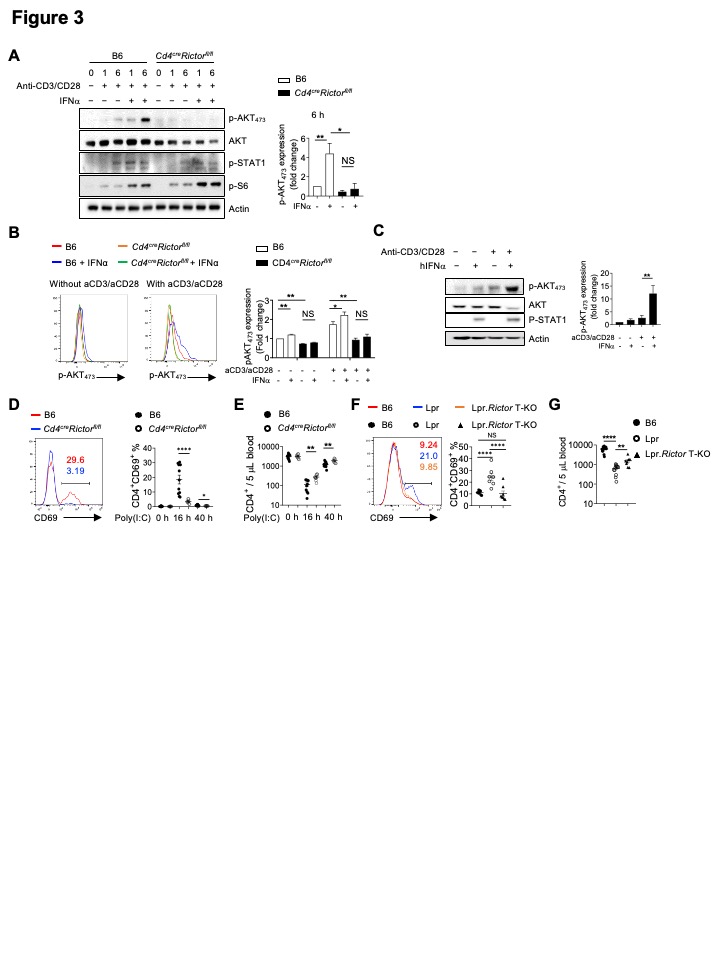 Figure 3. Type I IFN synergizes with TCR to promote CD69 expression and suppress T cell egress. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), p-STAT1 and p-S6 in CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice stimulated with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of IFNα for 1 and 6 hours. Right, summaries of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline B6 CD4+ T cells) stimulated for 6 hours. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of p-AKT473 expression in CD4+ T cells treated with IFNα alone, or in combination with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 overnight. Right, summary of the relative pAKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells without any stimulation). (C) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), and p-STAT1 in human CD4+ T cells with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 activation in presence or absence of human IFN for 3 hours. Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline. (D) and (E) B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice were administered with poly(I:C) intraperitoneally. (D) Expression of CD69 in blood CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice after poly(I:C) administration. Numbers indicate the percentages of CD69+CD4+ T cells. Right, summary of CD69+ percentage in CD4+ T cells at baseline or treated with poly(I:C) for 16 h and 40 h. (E) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined before and after poly(I:C) treatment. (F) Expression of CD69 in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of CD69+ percentages among pLN CD4+ T cells. (G) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined in 4-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (A, B, D and E, unpaired Student’s t test, C, F and G, one-way ANOVA). Results were presentative of 4 (A, C), or pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Figure 3. Type I IFN synergizes with TCR to promote CD69 expression and suppress T cell egress. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), p-STAT1 and p-S6 in CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice stimulated with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of IFNα for 1 and 6 hours. Right, summaries of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline B6 CD4+ T cells) stimulated for 6 hours. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of p-AKT473 expression in CD4+ T cells treated with IFNα alone, or in combination with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 overnight. Right, summary of the relative pAKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells without any stimulation). (C) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), and p-STAT1 in human CD4+ T cells with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 activation in presence or absence of human IFN for 3 hours. Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline. (D) and (E) B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice were administered with poly(I:C) intraperitoneally. (D) Expression of CD69 in blood CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice after poly(I:C) administration. Numbers indicate the percentages of CD69+CD4+ T cells. Right, summary of CD69+ percentage in CD4+ T cells at baseline or treated with poly(I:C) for 16 h and 40 h. (E) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined before and after poly(I:C) treatment. (F) Expression of CD69 in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of CD69+ percentages among pLN CD4+ T cells. (G) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined in 4-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (A, B, D and E, unpaired Student’s t test, C, F and G, one-way ANOVA). Results were presentative of 4 (A, C), or pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Disclosures: X. Zhou, None; H. Qi, None; M. Li, None; Y. Li, None; X. Zhu, None; A. Davidson, None; H. Zeng, None.
Background/Purpose: The development of many systemic autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, is associated with overactivation of the type I interferon (IFN) pathway, lymphopenia, and imbalance between follicular helper T (Tfh) cell and regulatory T cells (Treg). However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying these immunological perturbations remain incompletely understood. Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) shares the mTOR kinase with mTORC1, but differs from mTORC1 with its scaffold protein and defining subunit Rictor. Previous investigations show that mTORC2 is critically required for Tfh differentiation, but not for other effector T cell lineages. It exerts a negative regulation on Treg generation and suppressive function. This study aims to experimentally test the hypothesis that genetic targeting mTORC2 may benefit systemic autoimmunity. We explored the molecular, cellular, and metabolic mechanisms through which mTORC2 may contribute to murine systemic autoimmunity.
Methods: We generated B6.Lpr mice with T cell specific deletion of Rictor, or Treg specific deletion of Rictor. Immune cell homeostasis was analyzed by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. Antibody and inflammatory cytokine production were measured by ELISA or beads-based immunoassays. T cell metabolic activity was measured by Seahorse XFe96 bioanalyzer. Signaling events following TCR and/or type I IFN stimulation were measured by immunoblot or phosflow assays.
Results: Using genetic mouse models, we show that the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) promotes Tfh differentiation and disrupts Treg homeostasis. Inactivation of mTORC2 in total T cells, but not in Tregs, greatly ameliorated the immunopathology in a systemic autoimmunity mouse model. This was associated with reduced Tfh differentiation, B cell activation, and reduced T cell glucose metabolism. Finally, we show that type I IFN can synergize with TCR ligation to activate mTORC2 in T cells, which partially contributes to T cell lymphopenia. T cell specific deletion of Rictor partially restores the T cell lymphopenia phenotype in a lupus-prone mouse model.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that mTORC2 may act as downstream of type I IFN, TCR, and costimulatory receptor ICOS, to promote glucose metabolism, Tfh differentiation, and T cell lymphopenia, but not to suppress Treg function in systemic autoimmunity. Our results suggest that mTORC2 might be a rational target for systemic autoimmunity treatment.
 Figure 1. Rictor deletion in T cells rectifies immunopathology in Lpr mice. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473 in B6 and Lpr CD4+ T cells isolated from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN). Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells). (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Titers of total immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG, IgG2b and IgG3 were measured by ELISA. (D) Titers of anti-ssDNA (left) and anti-chromatin (right) were measured by ELISA. Samples were from 9 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (E) Expression of B220 and TCRon lymphocytes. Right, the frequencies (upper panels) and absolute numbers (lower panels) of B220+TCR+, B220–TCR+, B220+TCR– cells. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cells among B220–TCR+ cells. Right, the frequency (left) and absolute number (right) of CD4–CD8– T cell population. (E) and (F) Cells were from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN) of 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (G) The inflammatory cytokine levels in mouse sera samples collected from 5-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. p values were calculated with one-way ANOVA. Results were presentative of 3 (A) independent experiment and pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Figure 1. Rictor deletion in T cells rectifies immunopathology in Lpr mice. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473 in B6 and Lpr CD4+ T cells isolated from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN). Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells). (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Titers of total immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG, IgG2b and IgG3 were measured by ELISA. (D) Titers of anti-ssDNA (left) and anti-chromatin (right) were measured by ELISA. Samples were from 9 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (E) Expression of B220 and TCRon lymphocytes. Right, the frequencies (upper panels) and absolute numbers (lower panels) of B220+TCR+, B220–TCR+, B220+TCR– cells. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of CD4 and CD8 T cells among B220–TCR+ cells. Right, the frequency (left) and absolute number (right) of CD4–CD8– T cell population. (E) and (F) Cells were from peripheral lymph nodes (pLN) of 6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. (G) The inflammatory cytokine levels in mouse sera samples collected from 5-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001. p values were calculated with one-way ANOVA. Results were presentative of 3 (A) independent experiment and pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM. Figure 2. Rictor deletion in Treg is unable to restore immune dysregulation in Lpr mice. (A) Frequency of FOXP3+ Treg cells in splenic CD4+ T cells. (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Frequency of B220+TCR+ cells in pLN among B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. (D) Frequencies of pre-Tfh (BCL6 –CXCR5+) and Tfh (BCL6 +CXCR5+) cells in pLN. (E) Frequency of GC B cells. (F) The ratio between Tfh and Treg frequency in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO mice. (G) Serum concentrations of immunoglobulin IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b were measured by LEGENDplex. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Results were pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Figure 2. Rictor deletion in Treg is unable to restore immune dysregulation in Lpr mice. (A) Frequency of FOXP3+ Treg cells in splenic CD4+ T cells. (B) Image of peripheral lymph nodes taken from 6 months old B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. Right, summary of total cellularity of lymph nodes. (C) Frequency of B220+TCR+ cells in pLN among B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO. (D) Frequencies of pre-Tfh (BCL6 –CXCR5+) and Tfh (BCL6 +CXCR5+) cells in pLN. (E) Frequency of GC B cells. (F) The ratio between Tfh and Treg frequency in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr, Lpr.Rictor T-KO and Lpr.Rictor Treg-KO mice. (G) Serum concentrations of immunoglobulin IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b were measured by LEGENDplex. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (one-way ANOVA). Results were pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM. Figure 3. Type I IFN synergizes with TCR to promote CD69 expression and suppress T cell egress. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), p-STAT1 and p-S6 in CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice stimulated with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of IFNα for 1 and 6 hours. Right, summaries of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline B6 CD4+ T cells) stimulated for 6 hours. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of p-AKT473 expression in CD4+ T cells treated with IFNα alone, or in combination with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 overnight. Right, summary of the relative pAKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells without any stimulation). (C) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), and p-STAT1 in human CD4+ T cells with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 activation in presence or absence of human IFN for 3 hours. Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline. (D) and (E) B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice were administered with poly(I:C) intraperitoneally. (D) Expression of CD69 in blood CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice after poly(I:C) administration. Numbers indicate the percentages of CD69+CD4+ T cells. Right, summary of CD69+ percentage in CD4+ T cells at baseline or treated with poly(I:C) for 16 h and 40 h. (E) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined before and after poly(I:C) treatment. (F) Expression of CD69 in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of CD69+ percentages among pLN CD4+ T cells. (G) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined in 4-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (A, B, D and E, unpaired Student’s t test, C, F and G, one-way ANOVA). Results were presentative of 4 (A, C), or pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.
Figure 3. Type I IFN synergizes with TCR to promote CD69 expression and suppress T cell egress. (A) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), p-STAT1 and p-S6 in CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice stimulated with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of IFNα for 1 and 6 hours. Right, summaries of the relative p-AKT473 expression (normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline B6 CD4+ T cells) stimulated for 6 hours. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of p-AKT473 expression in CD4+ T cells treated with IFNα alone, or in combination with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 overnight. Right, summary of the relative pAKT473 expression (normalized to that in B6 CD4+ T cells without any stimulation). (C) Immunoblot analysis of p-AKT473, AKT (pan), and p-STAT1 in human CD4+ T cells with or without anti-CD3/anti-CD28 activation in presence or absence of human IFN for 3 hours. Right, summary of the relative p-AKT473 expression normalized to total AKT and then compared with baseline. (D) and (E) B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice were administered with poly(I:C) intraperitoneally. (D) Expression of CD69 in blood CD4+ T cells from B6 and Cd4creRictorfl/fl mice after poly(I:C) administration. Numbers indicate the percentages of CD69+CD4+ T cells. Right, summary of CD69+ percentage in CD4+ T cells at baseline or treated with poly(I:C) for 16 h and 40 h. (E) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined before and after poly(I:C) treatment. (F) Expression of CD69 in CD4+ T cells from B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. Right, summary of CD69+ percentages among pLN CD4+ T cells. (G) Blood CD4+ T cell counts were determined in 4-6 months old B6, Lpr and Lpr.Rictor T-KO mice. NS, not significant; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 (A, B, D and E, unpaired Student’s t test, C, F and G, one-way ANOVA). Results were presentative of 4 (A, C), or pooled from at least 3 (A-G) independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.Disclosures: X. Zhou, None; H. Qi, None; M. Li, None; Y. Li, None; X. Zhu, None; A. Davidson, None; H. Zeng, None.

