Back
Poster Session B
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0913–0938) RA – Treatment Poster II
0913: Impact of Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs on Immunogenicity to COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- KJ
Karam Jabri, MD
SUNY Downstate Medical Center
Brooklyn, NY, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Karam Jabri1, Linda Burns2 and Joseph Grisanti3, 1University at Buffalo/Catholic Health, Depew, NY, 2Buffalo Rheumatology, Lancaster, NY, 3Buffalo Rheumatology & Medicine, Orchard Park, NY
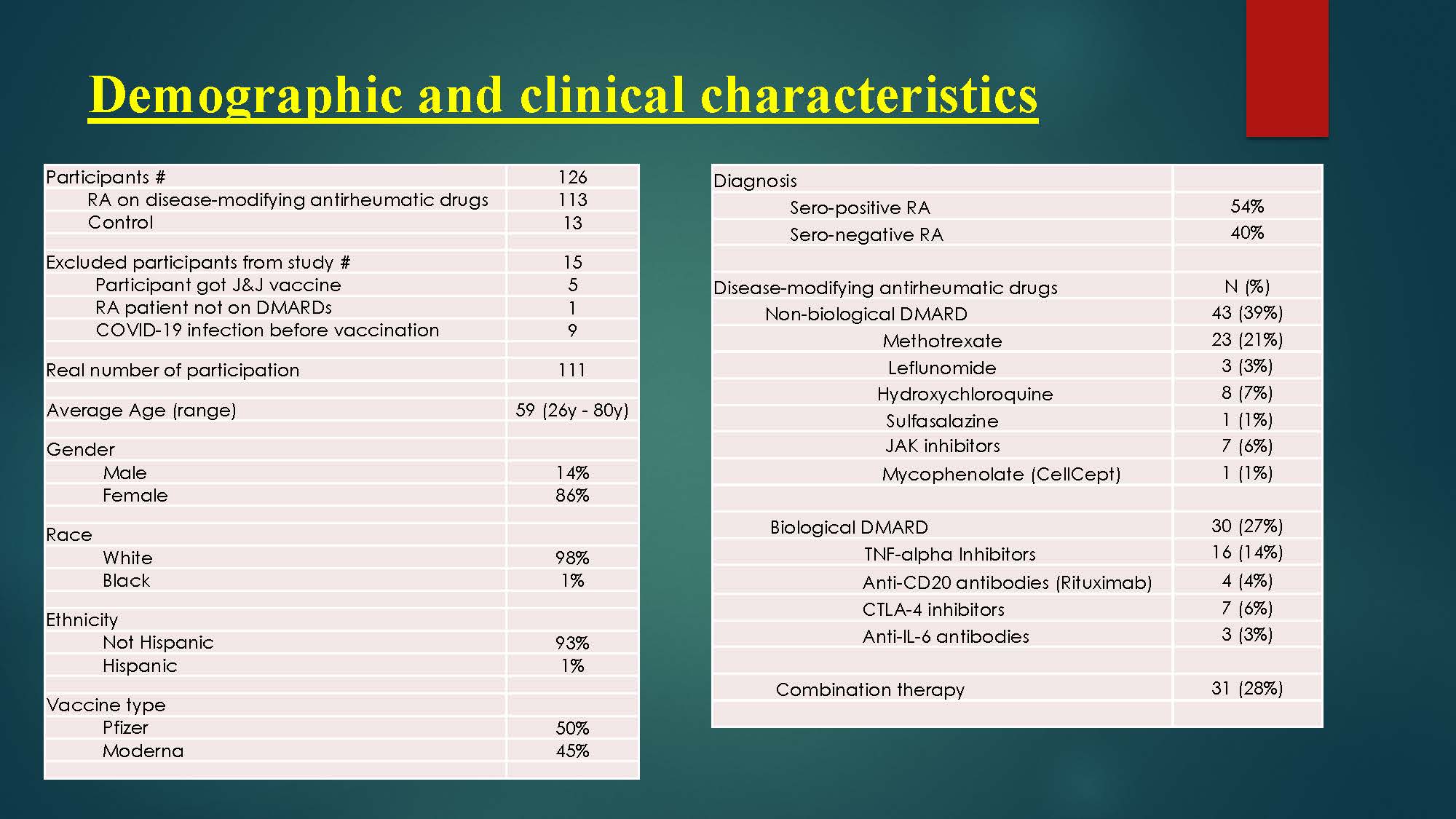
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at an increased risk of infection compared to healthy subjects (1). This is because of a multifactorial complex interaction between inherent immune dysfunction, comorbidity, disease activity, and immunosuppression (2). Methotrexate (MTX) is first line treatment for RA, either alone or in combination with biological therapy (3); however, MTX has significantly decreased vaccine response to pneumococcal and seasonal influenza vaccines (4-7). The effects of holding MTX for 2 weeks after vaccination were investigated in prospective, multicenter studies and it has significantly increased immunogenicity of influenza vaccine in patients with RA (8, 9). Furthermore, biologic therapy has an additional effect on vaccine immunogenicity with Rituximab has the most substantial impact (10-12),and TNFi drugs has a minimal effect (10); however, the infection risk associated with these drugs is a concern for clinicians and patients.
The purpose of this research study is to evaluate the impact of Immunosuppressive drugs commonly used in Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccine.
Methods: This is a prospective cohort study to check serum immunogenicity to COVID-19 vaccine. The efficacy of vaccination can be assessed by seroprotection rates (positive antibody) measured within 6 months post immunization. Study participants has undergone a screening process to determine eligibility. Serum samples for IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is the target of many candidate vaccines have been checked within 6 months post immunization to two-dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines to determine the immunity response to vaccine.
Results: Results of spike protein antibody range from undetectable level < 0.4 up to >2500 U/mL with positive result is >/= 0.80 U/mL, and negative result is < 0.80 U/mL for anti-SARS CoV-2S. 95% of RA patients on immunosuppressive therapy have positive antibodies titers to COVID-19 vaccine, and only 5% have negative or undetectable antibodies titers. Among negative responders, most were on regimens containing rituximab or mycophenolate.
As we held methotrexate for 1 week after each vaccine dose, there is a significant reduction in humoral immunity to COVID-19 vaccine between methotrexate group and non-methotrexate group (P-value is 0.005), as patients with MTX group have a higher antibodies titer than non-MTX group.
Conclusion: In this study of humoral response to two-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients with RA, the vast majority of participants developed antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is encouraging our patients to continue their treatment plans for RA.
Among negative responders, most were on regimens containing rituximab or mycophenolate.
Holding MTX for 1 week after each vaccine dose has significantly improved vaccine immunogenicity.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Disclosures: K. Jabri, None; L. Burns, None; J. Grisanti, None.
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at an increased risk of infection compared to healthy subjects (1). This is because of a multifactorial complex interaction between inherent immune dysfunction, comorbidity, disease activity, and immunosuppression (2). Methotrexate (MTX) is first line treatment for RA, either alone or in combination with biological therapy (3); however, MTX has significantly decreased vaccine response to pneumococcal and seasonal influenza vaccines (4-7). The effects of holding MTX for 2 weeks after vaccination were investigated in prospective, multicenter studies and it has significantly increased immunogenicity of influenza vaccine in patients with RA (8, 9). Furthermore, biologic therapy has an additional effect on vaccine immunogenicity with Rituximab has the most substantial impact (10-12),and TNFi drugs has a minimal effect (10); however, the infection risk associated with these drugs is a concern for clinicians and patients.
The purpose of this research study is to evaluate the impact of Immunosuppressive drugs commonly used in Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on humoral immune responses to COVID-19 vaccine.
Methods: This is a prospective cohort study to check serum immunogenicity to COVID-19 vaccine. The efficacy of vaccination can be assessed by seroprotection rates (positive antibody) measured within 6 months post immunization. Study participants has undergone a screening process to determine eligibility. Serum samples for IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is the target of many candidate vaccines have been checked within 6 months post immunization to two-dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines to determine the immunity response to vaccine.
Results: Results of spike protein antibody range from undetectable level < 0.4 up to >2500 U/mL with positive result is >/= 0.80 U/mL, and negative result is < 0.80 U/mL for anti-SARS CoV-2S. 95% of RA patients on immunosuppressive therapy have positive antibodies titers to COVID-19 vaccine, and only 5% have negative or undetectable antibodies titers. Among negative responders, most were on regimens containing rituximab or mycophenolate.
As we held methotrexate for 1 week after each vaccine dose, there is a significant reduction in humoral immunity to COVID-19 vaccine between methotrexate group and non-methotrexate group (P-value is 0.005), as patients with MTX group have a higher antibodies titer than non-MTX group.
Conclusion: In this study of humoral response to two-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients with RA, the vast majority of participants developed antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is encouraging our patients to continue their treatment plans for RA.
Among negative responders, most were on regimens containing rituximab or mycophenolate.
Holding MTX for 1 week after each vaccine dose has significantly improved vaccine immunogenicity.

.jpg)
.jpg)
Disclosures: K. Jabri, None; L. Burns, None; J. Grisanti, None.

