Back
Abstract Session
Session: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes III: Genetic Factors (2221–2226)
2224: Genes Causative of Primary Immunodeficiency Are Risk Factors for and Over-expressed in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Monday, November 14, 2022
3:45 PM – 3:55 PM Eastern Time
Location: Terrace Ballroom IV
- AL
Adam Labonte, PhD
AMPEL BioSolutions
Charlottesville, VA, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Haley Davis1, Adam Labonte1, Katherine Owen2, Erika Hubbard1, Jessica Kain1, Brian Kegerreis1, Prathyusha Bachali3, Amrie Grammer4 and Peter Lipsky1, 1AMPEL BioSolutions, Charlottesville, VA, 2RILITE, Crozet, VA, 3AMPEL BioSolutions, Redmond, WA, 4AMPEL LLC, Charlottesville, VA
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a polygenic autoimmune disease whose specific causes are incompletely understood and for which there exists no single comprehensive diagnostic test. Primary immunodeficiency diseases (PID) are severe failures of the immune system caused by single-gene defects. Genes with impaired function in PID may represent a rich source of candidates for genes overexpressed in SLE. The goal of this study was to investigate whether these genes were overrepresented in SLE patient gene expression.
Methods: A comprehensive database of 453 PID genes was compiled based on previous reports published by the International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS) committee as well as review of published autoimmune disease literature. This database was analyzed for biological function enrichment using gene set variation analysis (GSVA) and compared to known SLE risk genes and SLE patient differential gene expression (DE). PID genes were grouped using protein-protein interaction network clustering, and the resulting clusters were tested by GSVA and machine learning to determine their efficacy as focused diagnostic gene lists.
Results: Genes included in the PID Database were highly enriched for functional ontologies and pathways involved in immune cell function and specific to immune cell populations. mCODE clustering produced 16 distinct cellular and functional groups which were differentially enriched in SLE patient subpopulations (Fig 1). PID genes also showed disproportionate overlap with SNP-predicted SLE risk genes, with 119 (26.2%) of the PID genes identified as lupus risk genes. The majority of PID genes were overexpressed in SLE patients and especially in those with active disease (SLEDAI >6) (Fig 2). Finally, functional groups of PID genes defined by mCODE were employed as features for machine learning and effectively classified patients as having lupus or not or having active or inactive SLE (Fig 3). Notably, different sets of clusters were effective in each classification.
Conclusion: PID genes overlap SLE risk genes, are over-expressed in SLE and can be used in machine learning models to classify SLE. PID genes, thereby, represent a key set of genes involved in lupus pathogenesis.
.jpg) Figure 1. PID mCODE clusters show unique expression patterns among immune cell populations. A. Schematic of protein-protein interaction network of PID gene mCODE clusters. Node size correlates to number of genes in each cluster and node color maps to number of intracluster connections. Edge weight thickness represents number of intercluster connections and edge color is mapped to mCODE combined edge score. Each node is labeled with the most highly represented BIG-C category for its member genes. B. DE data from sorted cell datasets overlayed on PID mCODE network. Each node represents one gene, with overexpressed genes shown in red and undexpressed genes shown in blue. Genes that were not significantly DE are shown in grey. Datasets used for each panel include GSE39088 (whole blood), GSE50772 (PBMC), GSE4588 (CD19 B cells), and GSE51997 (CD4 T cells, classical CD14+CD16- monocytes, and nonclassical CD14+CD16+ monocytes).
Figure 1. PID mCODE clusters show unique expression patterns among immune cell populations. A. Schematic of protein-protein interaction network of PID gene mCODE clusters. Node size correlates to number of genes in each cluster and node color maps to number of intracluster connections. Edge weight thickness represents number of intercluster connections and edge color is mapped to mCODE combined edge score. Each node is labeled with the most highly represented BIG-C category for its member genes. B. DE data from sorted cell datasets overlayed on PID mCODE network. Each node represents one gene, with overexpressed genes shown in red and undexpressed genes shown in blue. Genes that were not significantly DE are shown in grey. Datasets used for each panel include GSE39088 (whole blood), GSE50772 (PBMC), GSE4588 (CD19 B cells), and GSE51997 (CD4 T cells, classical CD14+CD16- monocytes, and nonclassical CD14+CD16+ monocytes).
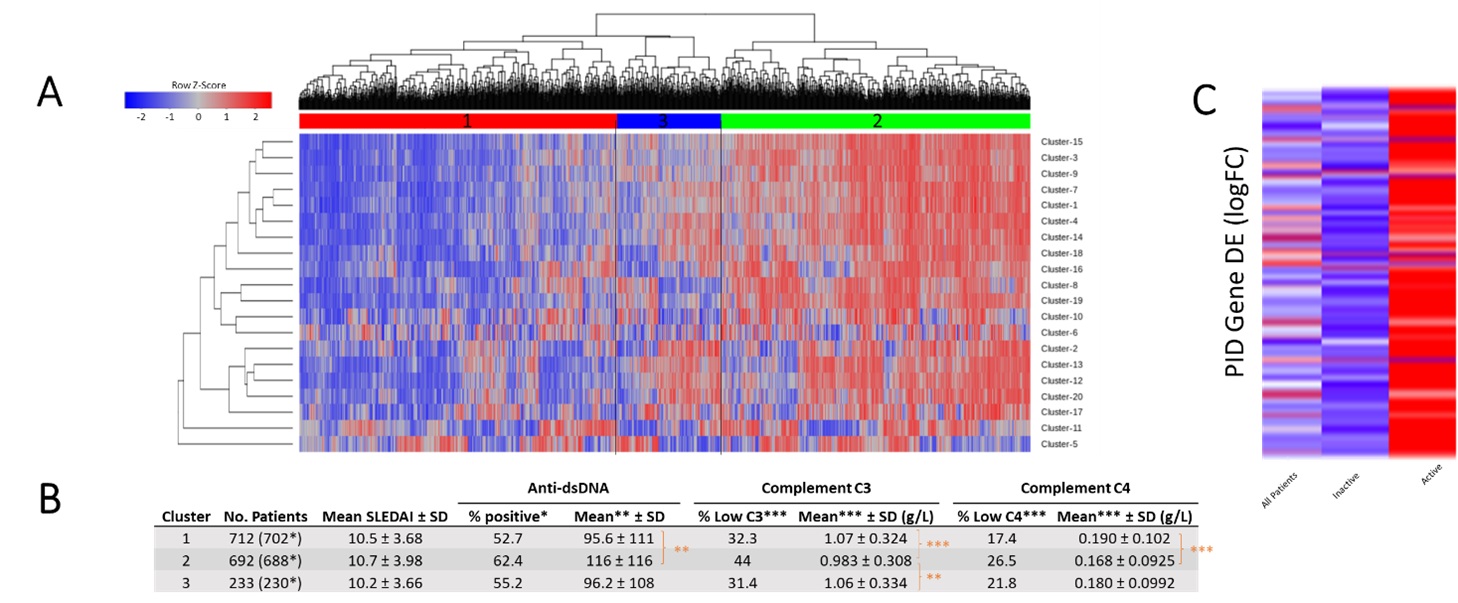 Figure 2. mCODE-derived PID gene clusters can identify clinically meaningful patient groups. A. GSVA of SLE patient DE gene data (GSE88884) using PID mCODE clusters as input gene sets. Output is shown following directed hierarchical clustering set to k=3 (clustering groups are shown as colored and numbered bars between heatmap and dendrogram). B. Clinical data summary and statistics of the three groups resulting from directed hierarchical clustering. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001. C. Total PID gene DE profile of patients within GSE88884, shown as logFC analysis for all patients combined, inactive (SLEDAI < 6) patients only, or active (SLEDAI ≥ 6) patients only.
Figure 2. mCODE-derived PID gene clusters can identify clinically meaningful patient groups. A. GSVA of SLE patient DE gene data (GSE88884) using PID mCODE clusters as input gene sets. Output is shown following directed hierarchical clustering set to k=3 (clustering groups are shown as colored and numbered bars between heatmap and dendrogram). B. Clinical data summary and statistics of the three groups resulting from directed hierarchical clustering. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001. C. Total PID gene DE profile of patients within GSE88884, shown as logFC analysis for all patients combined, inactive (SLEDAI < 6) patients only, or active (SLEDAI ≥ 6) patients only.
.jpg) Figure 3. PID gene clusters show utility as ML classifiers for SLE patient disease status. A, B. ROC curves (left) and individual classifier performance statistics (right) for 9 ML classifiers trained using PID mCODE clusters to correctly sort SLE patients from healthy controls (A) or active SLE patients from inactive SLE patients (B). C. Top feature clusters for ML identification of SLE vs control (left) or active SLE vs inactive SLE (right) across all classifiers. Overall feature importance data is mapped onto the PID mCODE schematic by node color, and clusters with positive feature importance values are annotated by defining BIG-C functional category.
Figure 3. PID gene clusters show utility as ML classifiers for SLE patient disease status. A, B. ROC curves (left) and individual classifier performance statistics (right) for 9 ML classifiers trained using PID mCODE clusters to correctly sort SLE patients from healthy controls (A) or active SLE patients from inactive SLE patients (B). C. Top feature clusters for ML identification of SLE vs control (left) or active SLE vs inactive SLE (right) across all classifiers. Overall feature importance data is mapped onto the PID mCODE schematic by node color, and clusters with positive feature importance values are annotated by defining BIG-C functional category.
Disclosures: H. Davis, None; A. Labonte, None; K. Owen, None; E. Hubbard, None; J. Kain, None; B. Kegerreis, None; P. Bachali, None; A. Grammer, None; P. Lipsky, None.
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a polygenic autoimmune disease whose specific causes are incompletely understood and for which there exists no single comprehensive diagnostic test. Primary immunodeficiency diseases (PID) are severe failures of the immune system caused by single-gene defects. Genes with impaired function in PID may represent a rich source of candidates for genes overexpressed in SLE. The goal of this study was to investigate whether these genes were overrepresented in SLE patient gene expression.
Methods: A comprehensive database of 453 PID genes was compiled based on previous reports published by the International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS) committee as well as review of published autoimmune disease literature. This database was analyzed for biological function enrichment using gene set variation analysis (GSVA) and compared to known SLE risk genes and SLE patient differential gene expression (DE). PID genes were grouped using protein-protein interaction network clustering, and the resulting clusters were tested by GSVA and machine learning to determine their efficacy as focused diagnostic gene lists.
Results: Genes included in the PID Database were highly enriched for functional ontologies and pathways involved in immune cell function and specific to immune cell populations. mCODE clustering produced 16 distinct cellular and functional groups which were differentially enriched in SLE patient subpopulations (Fig 1). PID genes also showed disproportionate overlap with SNP-predicted SLE risk genes, with 119 (26.2%) of the PID genes identified as lupus risk genes. The majority of PID genes were overexpressed in SLE patients and especially in those with active disease (SLEDAI >6) (Fig 2). Finally, functional groups of PID genes defined by mCODE were employed as features for machine learning and effectively classified patients as having lupus or not or having active or inactive SLE (Fig 3). Notably, different sets of clusters were effective in each classification.
Conclusion: PID genes overlap SLE risk genes, are over-expressed in SLE and can be used in machine learning models to classify SLE. PID genes, thereby, represent a key set of genes involved in lupus pathogenesis.
.jpg) Figure 1. PID mCODE clusters show unique expression patterns among immune cell populations. A. Schematic of protein-protein interaction network of PID gene mCODE clusters. Node size correlates to number of genes in each cluster and node color maps to number of intracluster connections. Edge weight thickness represents number of intercluster connections and edge color is mapped to mCODE combined edge score. Each node is labeled with the most highly represented BIG-C category for its member genes. B. DE data from sorted cell datasets overlayed on PID mCODE network. Each node represents one gene, with overexpressed genes shown in red and undexpressed genes shown in blue. Genes that were not significantly DE are shown in grey. Datasets used for each panel include GSE39088 (whole blood), GSE50772 (PBMC), GSE4588 (CD19 B cells), and GSE51997 (CD4 T cells, classical CD14+CD16- monocytes, and nonclassical CD14+CD16+ monocytes).
Figure 1. PID mCODE clusters show unique expression patterns among immune cell populations. A. Schematic of protein-protein interaction network of PID gene mCODE clusters. Node size correlates to number of genes in each cluster and node color maps to number of intracluster connections. Edge weight thickness represents number of intercluster connections and edge color is mapped to mCODE combined edge score. Each node is labeled with the most highly represented BIG-C category for its member genes. B. DE data from sorted cell datasets overlayed on PID mCODE network. Each node represents one gene, with overexpressed genes shown in red and undexpressed genes shown in blue. Genes that were not significantly DE are shown in grey. Datasets used for each panel include GSE39088 (whole blood), GSE50772 (PBMC), GSE4588 (CD19 B cells), and GSE51997 (CD4 T cells, classical CD14+CD16- monocytes, and nonclassical CD14+CD16+ monocytes).  Figure 2. mCODE-derived PID gene clusters can identify clinically meaningful patient groups. A. GSVA of SLE patient DE gene data (GSE88884) using PID mCODE clusters as input gene sets. Output is shown following directed hierarchical clustering set to k=3 (clustering groups are shown as colored and numbered bars between heatmap and dendrogram). B. Clinical data summary and statistics of the three groups resulting from directed hierarchical clustering. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001. C. Total PID gene DE profile of patients within GSE88884, shown as logFC analysis for all patients combined, inactive (SLEDAI < 6) patients only, or active (SLEDAI ≥ 6) patients only.
Figure 2. mCODE-derived PID gene clusters can identify clinically meaningful patient groups. A. GSVA of SLE patient DE gene data (GSE88884) using PID mCODE clusters as input gene sets. Output is shown following directed hierarchical clustering set to k=3 (clustering groups are shown as colored and numbered bars between heatmap and dendrogram). B. Clinical data summary and statistics of the three groups resulting from directed hierarchical clustering. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001. C. Total PID gene DE profile of patients within GSE88884, shown as logFC analysis for all patients combined, inactive (SLEDAI < 6) patients only, or active (SLEDAI ≥ 6) patients only. .jpg) Figure 3. PID gene clusters show utility as ML classifiers for SLE patient disease status. A, B. ROC curves (left) and individual classifier performance statistics (right) for 9 ML classifiers trained using PID mCODE clusters to correctly sort SLE patients from healthy controls (A) or active SLE patients from inactive SLE patients (B). C. Top feature clusters for ML identification of SLE vs control (left) or active SLE vs inactive SLE (right) across all classifiers. Overall feature importance data is mapped onto the PID mCODE schematic by node color, and clusters with positive feature importance values are annotated by defining BIG-C functional category.
Figure 3. PID gene clusters show utility as ML classifiers for SLE patient disease status. A, B. ROC curves (left) and individual classifier performance statistics (right) for 9 ML classifiers trained using PID mCODE clusters to correctly sort SLE patients from healthy controls (A) or active SLE patients from inactive SLE patients (B). C. Top feature clusters for ML identification of SLE vs control (left) or active SLE vs inactive SLE (right) across all classifiers. Overall feature importance data is mapped onto the PID mCODE schematic by node color, and clusters with positive feature importance values are annotated by defining BIG-C functional category.Disclosures: H. Davis, None; A. Labonte, None; K. Owen, None; E. Hubbard, None; J. Kain, None; B. Kegerreis, None; P. Bachali, None; A. Grammer, None; P. Lipsky, None.

