Back
Abstract Session
Session: Abstracts: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases (2204–2208)
2206: Understanding Inter-rater Variability in Scoring of Entheseal Lesions: Results from the Diagnostic Ultrasound Enthesitis Tool (DUET) Study
Monday, November 14, 2022
3:30 PM – 3:40 PM Eastern Time
Location: Room 126

Lihi Eder, MD, PhD
University of Toronto
Toronto, ON, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Lihi Eder1, Fangya Ma2, Josefina Marin3, Minna Kohler4, Janeth Yinh5, Ari Polachek6, Marcos Rosemffet7, Ernesto Rodriguez8, Ilaria Tinnazzi9, Amir Haddad10, Philippe Carron11, Mariana Alves Ferreira Martins12, Catherine Bakewell13, Fahmeen J. Afgani14, Richard Cook2, Sibel Aydin15 and Gurjit S. Kaeley16, 1Women’s College Research Institute, Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 3Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 4Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 5Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 6Tel Aviv Medical Center, Tel Aviv, Israel, 7Rheumatology Unit, Instituto de Rehabilitación Psicofísica, Capital Federal, Argentina, 8Florida Medical Clinic, Tampa, FL, 9Ospedale Sacro Cuore-Don Calabria, Negrar, Italy, 10Carmel Medical Centre, Haifa, Israel, 11Ghent University Hospital, Ghent, Belgium, 12São José Do Rio Preto Medical School, São José do Rio Preto, Brazil, 13Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, UT, 14Women's College Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15University of Ottawa, Rheumatology, Ottawa, Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 16UF COM-J, Ponte Vedra Beach, FL
Background/Purpose: Variability in scoring of sonographic entheseal lesions may be influenced by patient characteristics and sonographer expertise. We aimed to assess inter-rater agreement in scoring elementary lesions of enthesitis between central and local readers and factors influencing variability in scoring.
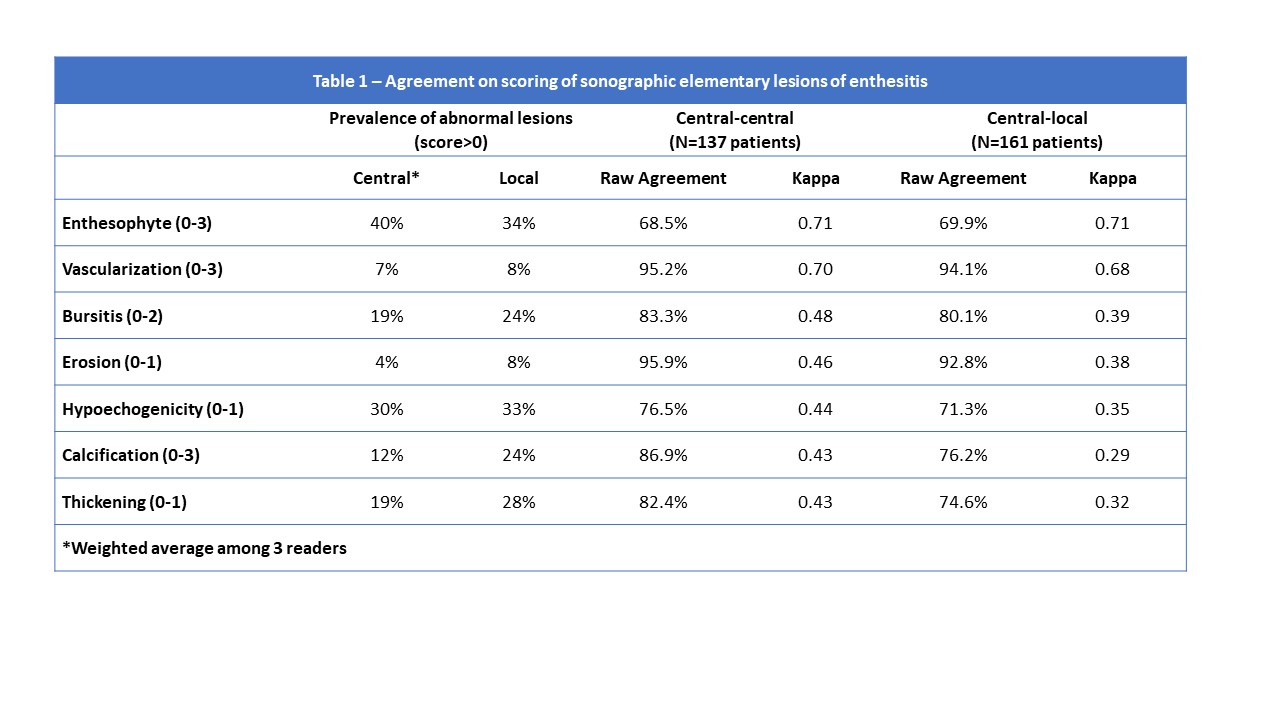
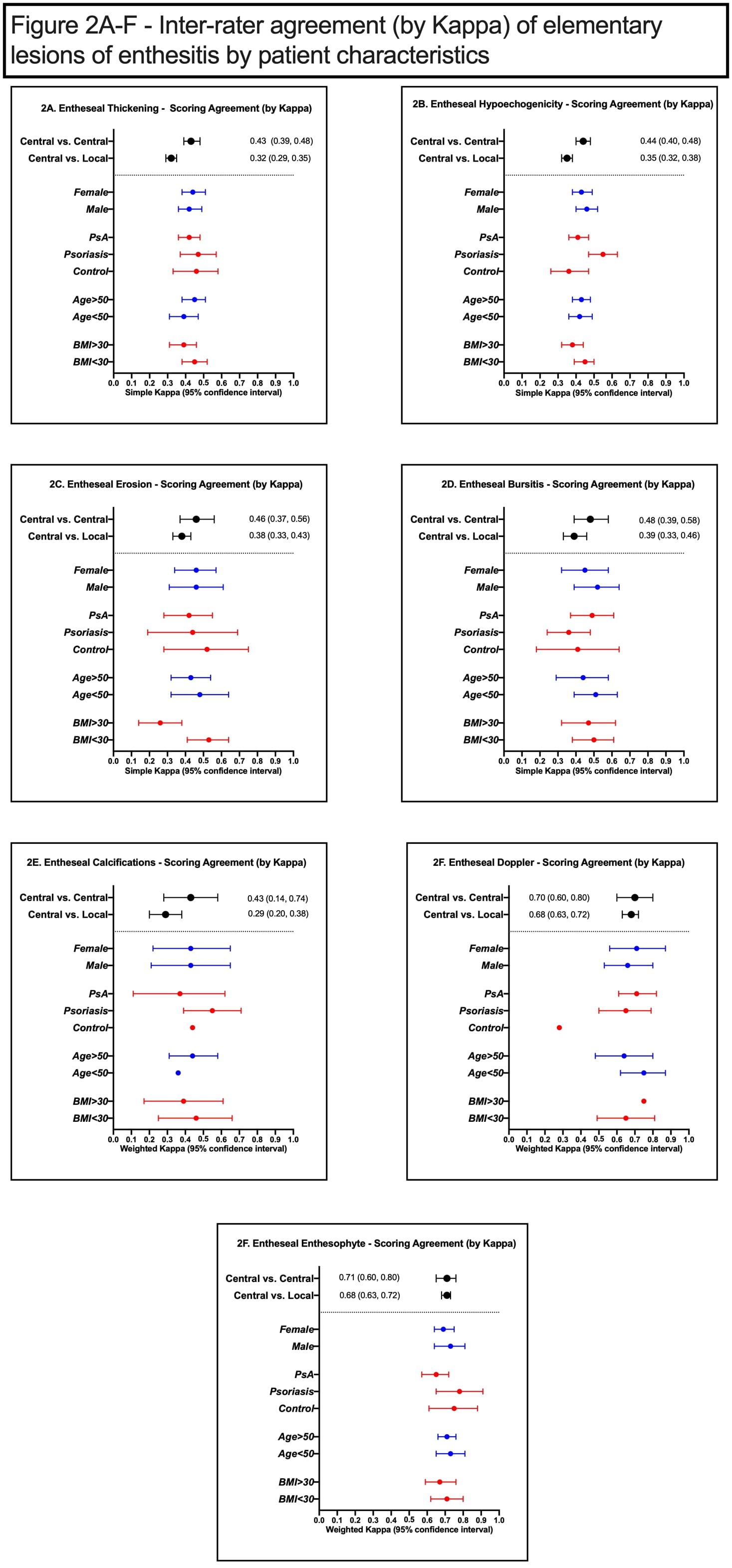
Methods: DUET is an international multicenter study that aims to develop a novel sonographic scoring system for enthesitis to assist with diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Patients with PsA, psoriasis alone and non-psoriatic controls underwent an ultrasound assessment of 16 entheseal sites in the upper and lower extremities by local sonographers. Each set of scans was stored as short DICOM clips, scored locally and then sent for central scoring by two out of three central sonographers. The local and central sonographers participated in pre-study training to ensure standard acquisition and scoring of elementary lesions of enthesitis following accepted definitions (Figure 1). The following lesions were scored on a semi-quantitative scale: hypoechogenicity (0-1), thickening (0-1), calcification (0-3), enthesophyte (0-3), erosion (0-1), vascularization (0-3) and bursitis (0-2). We assessed the raw agreement (%) and Kappa statistics between the central readers and between central and local readers for the different elementary lesions. The effect of age, sex, obesity and disease category on agreement was assessed by performing series of subgroup analyses.
Results: A total of 161 patients (2,576 entheses) were analyzed (88 PsA, 41 psoriasis, 32 controls). 47.8% were above the age of 50, 52.8% females and 47.8% were obese. Hypoechogenicity and enthesophytes were the most common elementary lesions while erosions and vascularization were the least common (Table 1). Highest raw agreement was found for erosion (92.8%-95.9%) and vascularization (94.1%-95.2%). Among central readers, inter-rater agreement (by Kappa) ranged from moderate to substantial for all elementary lesions being highest for enthesophytes (0.71) and vascularization (0.70) and lowest for thickening (0.43) and calcifications (0.43) (Table 1). Inter-rater agreement was numerically lower for central vs. local readers for most lesions. Most patient characteristics did not have a substantial influence on inter-rater agreement among central readers for entheseal elementary lesions (Figure 1). Kappa scores tended to be numerically lower in obese patients for most elementary lesions.
Conclusion: Moderate to substantial inter-rater agreement was achieved for most sonographic elementary lesions especially among central readers. Inter-rater agreement is not influenced by most patient characteristics apart from obesity which may increase variability in scoring.
.jpg)
Disclosures: L. Eder, AbbVie, Lilly, Novartis, UCB, Pfizer; F. Ma, None; J. Marin, AbbVie/Abbott, UCB, Janssen, Novartis; M. Kohler, Setpoint Medical, Springer; J. Yinh, None; A. Polachek, None; M. Rosemffet, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, Sandoz, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Pfizer, Raffo; E. Rodriguez, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Horizon, Sanofi; I. Tinnazzi, None; A. Haddad, None; P. Carron, Biogen, AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB; M. Alves Ferreira Martins, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Pfizer; C. Bakewell, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Janssen, UCB; F. Afgani, None; R. Cook, None; S. Aydin, None; G. Kaeley, None.
Background/Purpose: Variability in scoring of sonographic entheseal lesions may be influenced by patient characteristics and sonographer expertise. We aimed to assess inter-rater agreement in scoring elementary lesions of enthesitis between central and local readers and factors influencing variability in scoring.
Methods: DUET is an international multicenter study that aims to develop a novel sonographic scoring system for enthesitis to assist with diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Patients with PsA, psoriasis alone and non-psoriatic controls underwent an ultrasound assessment of 16 entheseal sites in the upper and lower extremities by local sonographers. Each set of scans was stored as short DICOM clips, scored locally and then sent for central scoring by two out of three central sonographers. The local and central sonographers participated in pre-study training to ensure standard acquisition and scoring of elementary lesions of enthesitis following accepted definitions (Figure 1). The following lesions were scored on a semi-quantitative scale: hypoechogenicity (0-1), thickening (0-1), calcification (0-3), enthesophyte (0-3), erosion (0-1), vascularization (0-3) and bursitis (0-2). We assessed the raw agreement (%) and Kappa statistics between the central readers and between central and local readers for the different elementary lesions. The effect of age, sex, obesity and disease category on agreement was assessed by performing series of subgroup analyses.
Results: A total of 161 patients (2,576 entheses) were analyzed (88 PsA, 41 psoriasis, 32 controls). 47.8% were above the age of 50, 52.8% females and 47.8% were obese. Hypoechogenicity and enthesophytes were the most common elementary lesions while erosions and vascularization were the least common (Table 1). Highest raw agreement was found for erosion (92.8%-95.9%) and vascularization (94.1%-95.2%). Among central readers, inter-rater agreement (by Kappa) ranged from moderate to substantial for all elementary lesions being highest for enthesophytes (0.71) and vascularization (0.70) and lowest for thickening (0.43) and calcifications (0.43) (Table 1). Inter-rater agreement was numerically lower for central vs. local readers for most lesions. Most patient characteristics did not have a substantial influence on inter-rater agreement among central readers for entheseal elementary lesions (Figure 1). Kappa scores tended to be numerically lower in obese patients for most elementary lesions.
Conclusion: Moderate to substantial inter-rater agreement was achieved for most sonographic elementary lesions especially among central readers. Inter-rater agreement is not influenced by most patient characteristics apart from obesity which may increase variability in scoring.
.jpg)


Disclosures: L. Eder, AbbVie, Lilly, Novartis, UCB, Pfizer; F. Ma, None; J. Marin, AbbVie/Abbott, UCB, Janssen, Novartis; M. Kohler, Setpoint Medical, Springer; J. Yinh, None; A. Polachek, None; M. Rosemffet, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, Sandoz, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Pfizer, Raffo; E. Rodriguez, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Horizon, Sanofi; I. Tinnazzi, None; A. Haddad, None; P. Carron, Biogen, AbbVie/Abbott, Eli Lilly, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB; M. Alves Ferreira Martins, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Pfizer; C. Bakewell, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Janssen, UCB; F. Afgani, None; R. Cook, None; S. Aydin, None; G. Kaeley, None.

