Back
Abstract Session
Session: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies (2237–2242)
2237: Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of Subcutaneous Abatacept in Adults with Active Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy: Results of the 24-Week Double-Blind and 28-Week Open-Label Periods
Monday, November 14, 2022
4:30 PM – 4:40 PM Eastern Time
Location: Room 201

Rohit Aggarwal, MD, MS
University of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh, PA, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Rohit Aggarwal1, Ingrid Lundberg2, Yeong-Wook Song3, Aziz Shaibani4, Victoria Werth5 and Michael Maldonado6, 1Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, 2Karolinska Universitetssjukhuset, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, 3Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 4Nerve and Muscle Center of Texas, Houston, TX, 5Philadelphia VAMC, Philadelphia, PA, USA and Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, 6Bristol Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ
Background/Purpose: A 52-week (wk), randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled phase 3 trial of subcutaneous (SC) abatacept (ABA) and standard of care (SOC) was performed in patients (pts) with active, treatment-refractory idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM; NCT02971683). The 24-wk double-blind (DB) period results from the intention-to-treat population were previously reported.1 This study aims to describe the efficacy and safety of continued therapy with SC ABA + SOC through 52 wks, and of therapy initiation with SC ABA + SOC after switching from PBO during the 28-wk open-label (OL) period, in pts with IIM.
Methods: Adults with active, treatment-refractory IIM received SC ABA (125 mg wkly) + SOC or PBO + SOC in the DB period (wks 0–24). In the OL period (wks 24–52), all pts in the PBO arm were switched to SC ABA + SOC. Primary endpoint: proportion of pts meeting International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies definition of improvement (IMACS DOI). Secondary endpoints: change from baseline in myositis Functional Index-2 (FI-2), HAQ-disability index (DI), Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Tool, 2016 ACR/EULAR Myositis Response Criteria (MRC, with Total Improvement Score [TIS]), and Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI). Safety and tolerability were assessed. Post hoc analyses were performed based on IIM disease subtypes, dermatomyositis (DM) and non-DM (including polymyositis [PM] and autoimmune necrotizing myopathy [ANM]).
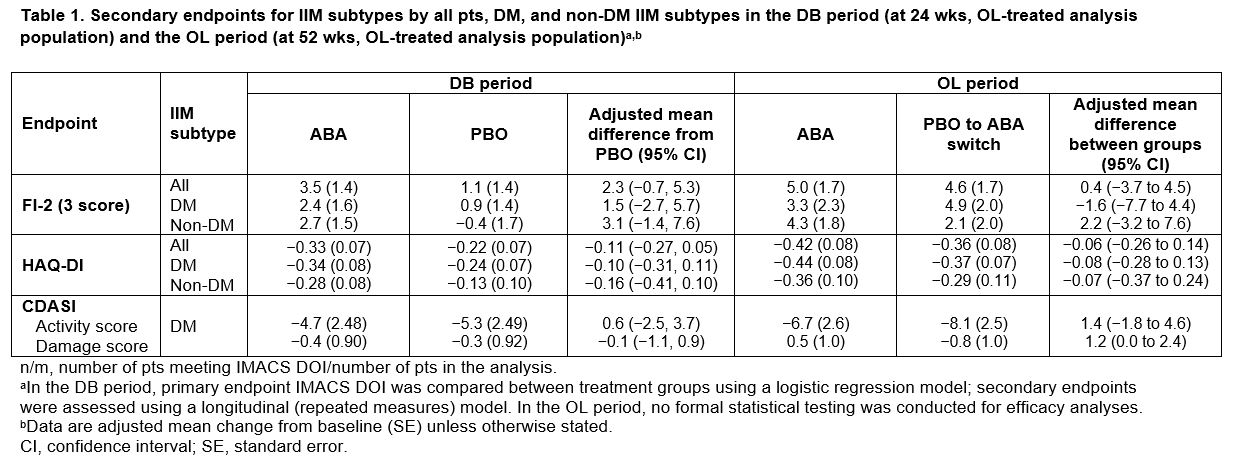
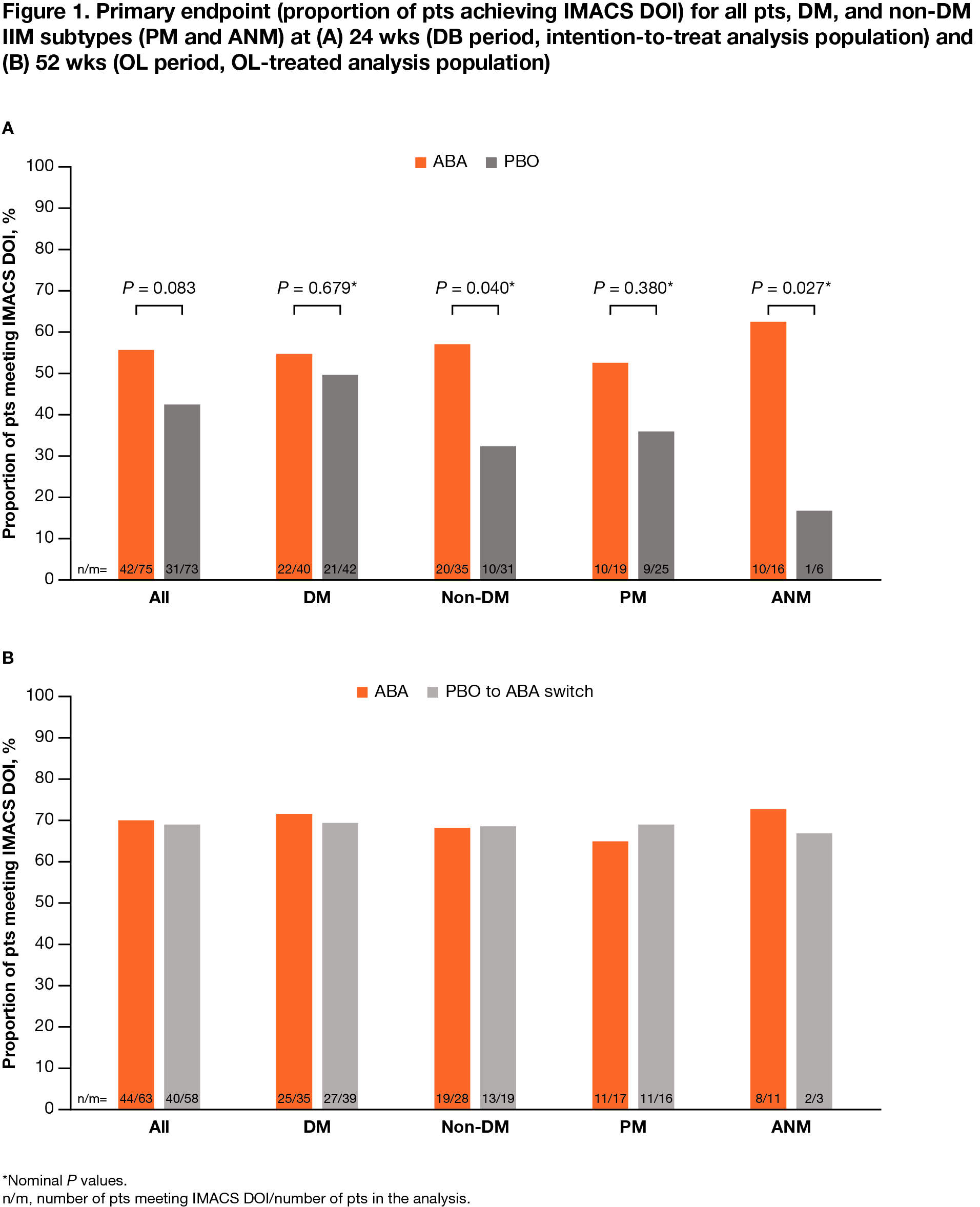
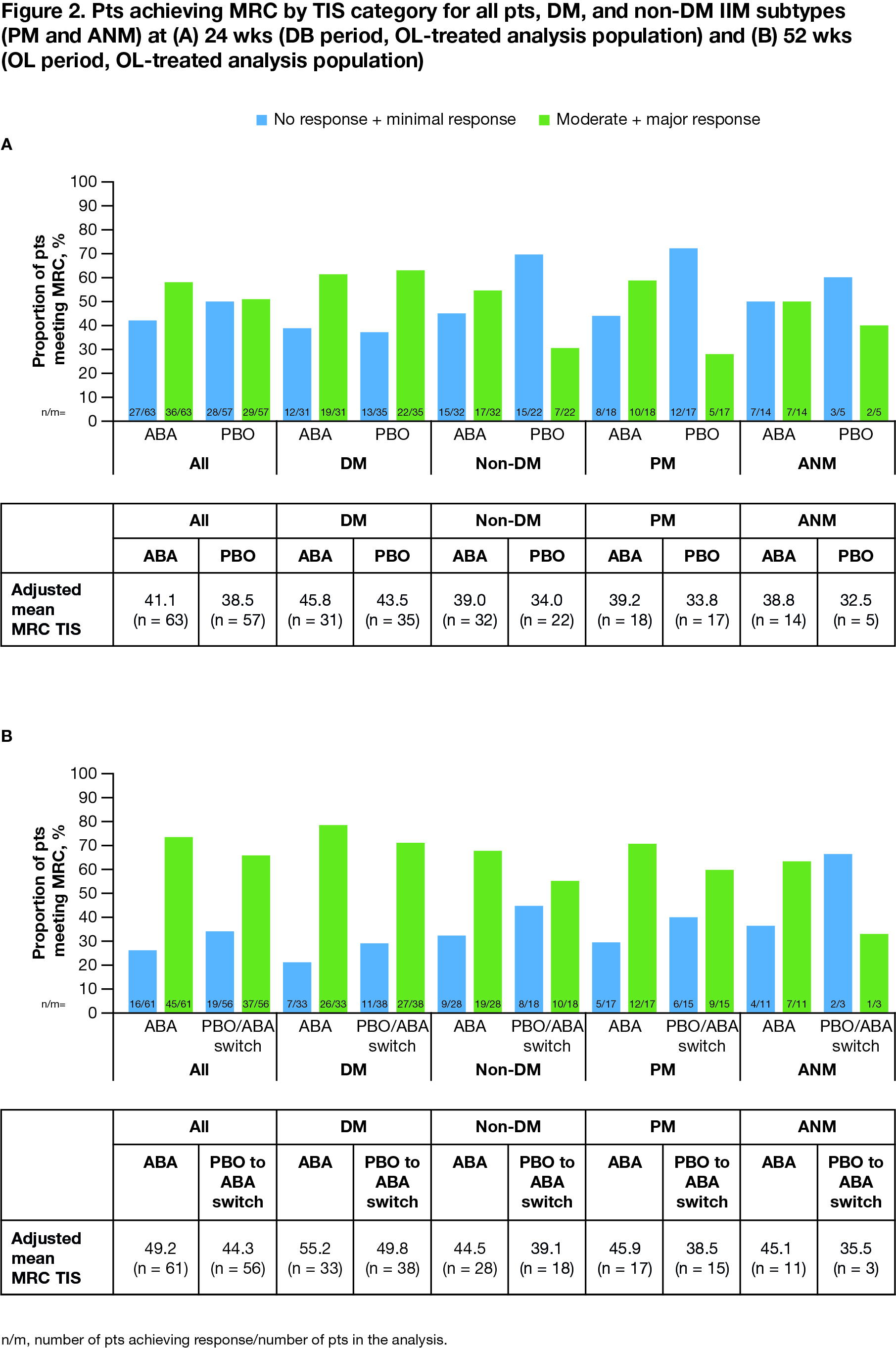
Results: All pts who completed the DB period (90.5%; total n = 134/148 [ABA, n = 69/75; PBO, n = 65/73]) entered the OL period, where 133 pts were treated (DM, n = 75; PM, n = 39; ANM, n = 19). Proportion of pts achieving IMACS DOI at wk 52 demonstrated a sustained benefit in continuing ABA (ABA group) and an improvement on switching from PBO to ABA (PBO/ABA switch group) in the OL period, particularly in non-DM subtypes (Figure 1). In all patients and the DM/non-DM subtypes, FI-2, HAQ-DI, and CDASI improved when continuing on ABA and switching to ABA (Table 1). Adjusted mean TIS continued to improve by wk 52 vs 24 in the overall ABA group (49.2 vs 41.1), showing continued benefit with long-term treatment (Figure 2). Overall, for ABA, the proportion of pts with MRC moderate/major responses increased from 57.1% to 73.8% between wks 24 and 52. In the PBO/ABA switch group, the adjusted mean TIS increased as did the proportion of pts with MRC moderate/major responses, which increased from 50.9% at wk 24 to 66.1% at wk 52, showing disease improvement when switching to ABA (Figure 2). The DM and non-DM subgroups showed TIS improvements from wk 24 to 52, with greater improvement in the ABA groups (Figure 2). Proportion of pts with MRC moderate/major responses generally increased in both ABA and PBO/ABA switch groups for DM and non-DM IIM subtypes. The safety profile of ABA in the OL was consistent with that seen in the DB.
Conclusion: In the OL period, post hoc analyses suggest a continued benefit for pts in the ABA arm and new improvement for pts switching from PBO to ABA. ABA use through 52 wks of therapy was well tolerated by pts with IIM.
1Aggarwal R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:711.
Medical writing: Candice Judith Dcosta (Caudex), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
Study was executed by Sandra Overfield and Robin Scully.
Disclosures: R. Aggarwal, Mallinckrodt, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Pfizer, Octapharma, CSL Behring, Q32, Kezar, AstraZeneca, Alexion, Argenx, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, Janssen, Kyverna, Roivant, AbbVie, Jubilant, Orphazyme, Genentech; I. Lundberg, Argenx, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Corbus, EMD Serono, Roche, Pfizer, Orphazyme, Octapharma, Kezar, Janssen; Y. Song, None; A. Shaibani, None; V. Werth, GlaxoSmithKline, CLASI; M. Maldonado, Bristol Myers Squibb.
Background/Purpose: A 52-week (wk), randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled phase 3 trial of subcutaneous (SC) abatacept (ABA) and standard of care (SOC) was performed in patients (pts) with active, treatment-refractory idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM; NCT02971683). The 24-wk double-blind (DB) period results from the intention-to-treat population were previously reported.1 This study aims to describe the efficacy and safety of continued therapy with SC ABA + SOC through 52 wks, and of therapy initiation with SC ABA + SOC after switching from PBO during the 28-wk open-label (OL) period, in pts with IIM.
Methods: Adults with active, treatment-refractory IIM received SC ABA (125 mg wkly) + SOC or PBO + SOC in the DB period (wks 0–24). In the OL period (wks 24–52), all pts in the PBO arm were switched to SC ABA + SOC. Primary endpoint: proportion of pts meeting International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies definition of improvement (IMACS DOI). Secondary endpoints: change from baseline in myositis Functional Index-2 (FI-2), HAQ-disability index (DI), Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Tool, 2016 ACR/EULAR Myositis Response Criteria (MRC, with Total Improvement Score [TIS]), and Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI). Safety and tolerability were assessed. Post hoc analyses were performed based on IIM disease subtypes, dermatomyositis (DM) and non-DM (including polymyositis [PM] and autoimmune necrotizing myopathy [ANM]).
Results: All pts who completed the DB period (90.5%; total n = 134/148 [ABA, n = 69/75; PBO, n = 65/73]) entered the OL period, where 133 pts were treated (DM, n = 75; PM, n = 39; ANM, n = 19). Proportion of pts achieving IMACS DOI at wk 52 demonstrated a sustained benefit in continuing ABA (ABA group) and an improvement on switching from PBO to ABA (PBO/ABA switch group) in the OL period, particularly in non-DM subtypes (Figure 1). In all patients and the DM/non-DM subtypes, FI-2, HAQ-DI, and CDASI improved when continuing on ABA and switching to ABA (Table 1). Adjusted mean TIS continued to improve by wk 52 vs 24 in the overall ABA group (49.2 vs 41.1), showing continued benefit with long-term treatment (Figure 2). Overall, for ABA, the proportion of pts with MRC moderate/major responses increased from 57.1% to 73.8% between wks 24 and 52. In the PBO/ABA switch group, the adjusted mean TIS increased as did the proportion of pts with MRC moderate/major responses, which increased from 50.9% at wk 24 to 66.1% at wk 52, showing disease improvement when switching to ABA (Figure 2). The DM and non-DM subgroups showed TIS improvements from wk 24 to 52, with greater improvement in the ABA groups (Figure 2). Proportion of pts with MRC moderate/major responses generally increased in both ABA and PBO/ABA switch groups for DM and non-DM IIM subtypes. The safety profile of ABA in the OL was consistent with that seen in the DB.
Conclusion: In the OL period, post hoc analyses suggest a continued benefit for pts in the ABA arm and new improvement for pts switching from PBO to ABA. ABA use through 52 wks of therapy was well tolerated by pts with IIM.
1Aggarwal R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:711.
Medical writing: Candice Judith Dcosta (Caudex), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
Study was executed by Sandra Overfield and Robin Scully.



Disclosures: R. Aggarwal, Mallinckrodt, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Pfizer, Octapharma, CSL Behring, Q32, Kezar, AstraZeneca, Alexion, Argenx, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corbus, Janssen, Kyverna, Roivant, AbbVie, Jubilant, Orphazyme, Genentech; I. Lundberg, Argenx, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Corbus, EMD Serono, Roche, Pfizer, Orphazyme, Octapharma, Kezar, Janssen; Y. Song, None; A. Shaibani, None; V. Werth, GlaxoSmithKline, CLASI; M. Maldonado, Bristol Myers Squibb.

