Back
Poster Session B
Fibrosing rheumatic diseases (scleroderma, MCTD, IgG4-related disease, scleroderma mimics)
Session: (1046–1070) Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I
1064: Test-retest Reliability for the Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire for the Measurement of Calcinosis Burden in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AV
Antonia Valenzuela, MD, MS
Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile
Santiago, Chile
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Antonia Valenzuela1, Anne-Marie Russell2, Lorinda Chung3, Kelly Jensen4 and Lesley Ann Saketkoo5, 1Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 2University of Exeter, Exeter, United Kingdom, 3Stanford University, Stanford, CA, 4University of Colorado, Bellevue, WA, 5University Medical Center - Comprehensive Pulmonary Hypertension Center and ILD Clinic Programs // New Orleans Scleroderma and Sarcoidosis Patient Care & Research Centeris, New Orleans, LA
Background/Purpose: Calcinosis cutis is a debilitating manifestation in systemic sclerosis (SSc) responsible for a high burden of disability and hand dysfunction, contributing as much as arthritis to patient physical limitations. The Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire is a novel patient reported outcome measure (PROM) developed to assess the severity and impact of SSc-related calcinosis in clinical studies/clinical practice. It contains 6 items of quantification, a test question of interpretation and 3 domains: Pain/sensation (5 items); Physical Function (4 items) and Psychological Impact (6 items). We aimed to assess the test–retest reliability of this PROM in SSc patients with calcinosis.
Methods: Items for the PROM were generated from patient's experiences of SSc-calcinosis to quantify the impact of calcinosis. Items are rated no limitation (0) to worst limitation possible (10). Items are grouped by domain and total scores. Test-retest reliability was assessed using mean absolute change and mean absolute difference and examined through paired T-tests. A global rate of change score (GCRS) was calculated at time point 2 (TP2) using a 0-10 scale. Internal reliability was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The ICC was calculated for total scores and domains using a two-way random effects model, selecting absolute agreement.
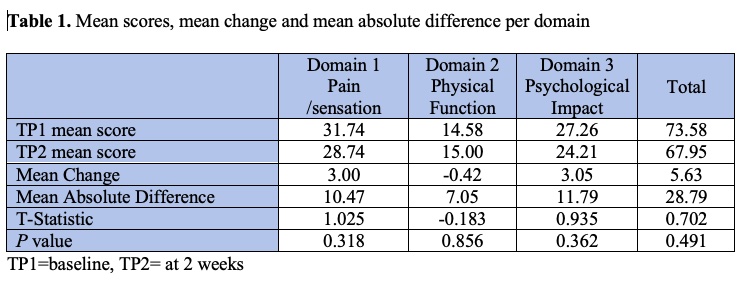
Results: All 19 respondents were SSc female patients, 5 from the United Kingdom and 14 from the United States. Mean days between completion was 16.8 days (range 14-24). In quantification of calcinosis, 9 participants scored zero at TP1 increasing to 11 at TP2 for at least one item. Median score of feeling certain lesion is calcinosis at TP1 =5 (range 0-80) and TP2=5 (range 0-100). The mean, mean scores, mean change, mean absolute difference for domains and total scores at TP1 and TP2 are presented in table 1. All p values associated with the T- test were >0.05 indicating that there were no significant differences between scores at TP1 and TP2 (good stability). The mean GRCS was 2 (range 1-3) indicating no significant change on calcinosis burden within 2 weeks. ICC values were > 0.5 suggesting moderate reliability in this small cohort.
Conclusion: The Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire demonstrated a good stability. The test-retest reliability was moderate. This may be due to the heterogeneity in this small group of SSc patients with calcinosis. Recruitment is continuing. Next steps are to perform factor analysis to evaluate how items fit the domains, and correlations with Raynaud phenomenon, digital ulcers, and how well this correlated with other PROMs, such as the Cochin Hand Function Scale, SHAQ and SF-36.
Disclosures: A. Valenzuela, None; A. Russell, None; L. Chung, Kyverna, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Eicos, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Jasper, Genentech; K. Jensen, None; L. Saketkoo, None.
Background/Purpose: Calcinosis cutis is a debilitating manifestation in systemic sclerosis (SSc) responsible for a high burden of disability and hand dysfunction, contributing as much as arthritis to patient physical limitations. The Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire is a novel patient reported outcome measure (PROM) developed to assess the severity and impact of SSc-related calcinosis in clinical studies/clinical practice. It contains 6 items of quantification, a test question of interpretation and 3 domains: Pain/sensation (5 items); Physical Function (4 items) and Psychological Impact (6 items). We aimed to assess the test–retest reliability of this PROM in SSc patients with calcinosis.
Methods: Items for the PROM were generated from patient's experiences of SSc-calcinosis to quantify the impact of calcinosis. Items are rated no limitation (0) to worst limitation possible (10). Items are grouped by domain and total scores. Test-retest reliability was assessed using mean absolute change and mean absolute difference and examined through paired T-tests. A global rate of change score (GCRS) was calculated at time point 2 (TP2) using a 0-10 scale. Internal reliability was assessed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The ICC was calculated for total scores and domains using a two-way random effects model, selecting absolute agreement.
Results: All 19 respondents were SSc female patients, 5 from the United Kingdom and 14 from the United States. Mean days between completion was 16.8 days (range 14-24). In quantification of calcinosis, 9 participants scored zero at TP1 increasing to 11 at TP2 for at least one item. Median score of feeling certain lesion is calcinosis at TP1 =5 (range 0-80) and TP2=5 (range 0-100). The mean, mean scores, mean change, mean absolute difference for domains and total scores at TP1 and TP2 are presented in table 1. All p values associated with the T- test were >0.05 indicating that there were no significant differences between scores at TP1 and TP2 (good stability). The mean GRCS was 2 (range 1-3) indicating no significant change on calcinosis burden within 2 weeks. ICC values were > 0.5 suggesting moderate reliability in this small cohort.
Conclusion: The Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire demonstrated a good stability. The test-retest reliability was moderate. This may be due to the heterogeneity in this small group of SSc patients with calcinosis. Recruitment is continuing. Next steps are to perform factor analysis to evaluate how items fit the domains, and correlations with Raynaud phenomenon, digital ulcers, and how well this correlated with other PROMs, such as the Cochin Hand Function Scale, SHAQ and SF-36.

Disclosures: A. Valenzuela, None; A. Russell, None; L. Chung, Kyverna, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Eicos, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Jasper, Genentech; K. Jensen, None; L. Saketkoo, None.

