Back
Poster Session C
Imaging
Session: (1228–1266) Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster
1231: [68Ga]- CPCR4 Trifluoroacetate PET/CT Imaging of Chemokine Receptor CXCR4- Expression in Systemic Sclerosis Related Interstitial Lung Disease
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- CK
Chirag Rajkumar Kopp, MD, MBBS, DM
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research
Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Chirag Rajkumar Kopp1, Shefali Sharma2, Venkata Subramanian Krishnaraju3, Chandra Bhushan Prasad3, Jagdeep Singh3, Shashi Anand3, Ranjana Minz3, Ashwani Sood3, Anindita Sinha3, Rajender Kumar Basher3, Sahajal Dhooria3, Varun Dhir4 and sanjay jain3, 1Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India, 2PGIMER< Chandigarh, Chandigarh, India, 3Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India, 4PGIMER, CHD, INDIA, Chandigarh, India
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) in Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a major contributor of morbidity and mortality. CXCR4/CXCL12 axis has been implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. In this pilot study, we characterize the CXCR4 expression in lung parenchyma using 68Ga-Lympholeucin (CPCR4 trifluoroacetate) and peripheral white blood cells using PET/CT and flow cytometry.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, we included SSc patients having active (n=14) and stable(n=3) ILD based on the duration, clinical and radiological progression, and FVC decline. 68Ga-Lympholeucin uptake in lung parenchyma was quantified in these 17 SSc-ILD patients and compared to the diseased controls without lung parenchymal involvement. Lung parenchyma was divided into 22 regions of interest (ROI) on PET/CT, drawn in the dorsobasal, middle and apical regions of the lung and individual areas were quantified for CXCR4 expression using SUVmean and compared to the controls. Flow cytometry was performed in 16 patients to quantify CXCR4 expression on CD4+ T cell, CD8+ T cell, CD14+ monocytes and CD19+ B cells, and compared with healthy controls.
Results: SSc-ILD patients underwent 68Ga-Lympholeucin PET/CT imaging showed significant SUVmean uptake in the lung parenchyma compared to controls. Most significant areas of uptake were noted in the dorsobasal regions of lung. Also, significantly higher CXCR4 uptake in the areas of ground glass (P< 0.001), reticulation (P< 0.001) and reticulation with architectural distortion (P< 0.001) opacities as compared to normal regions. Higher proportion of CD4 (83.83±7.99 vs 60.28±12.20; P< 0.001) and CD8 (67.67±14.4 vs 43.67±12.59; P=0.003) cells in SSc-ILD patients showed CXCR4 expression as compared to controls.
Conclusion: 68Ga-Lympholeucin PET/CT is a good imaging modality to quantify CXCR4 expression in lung parenchyma of SSc-ILD patients. Increased CXCR4 expression in the lung parenchyma using PET/CT and peripheral T cells could be used as a biomarker of disease activity and assessment of response to therapy.
.jpg)
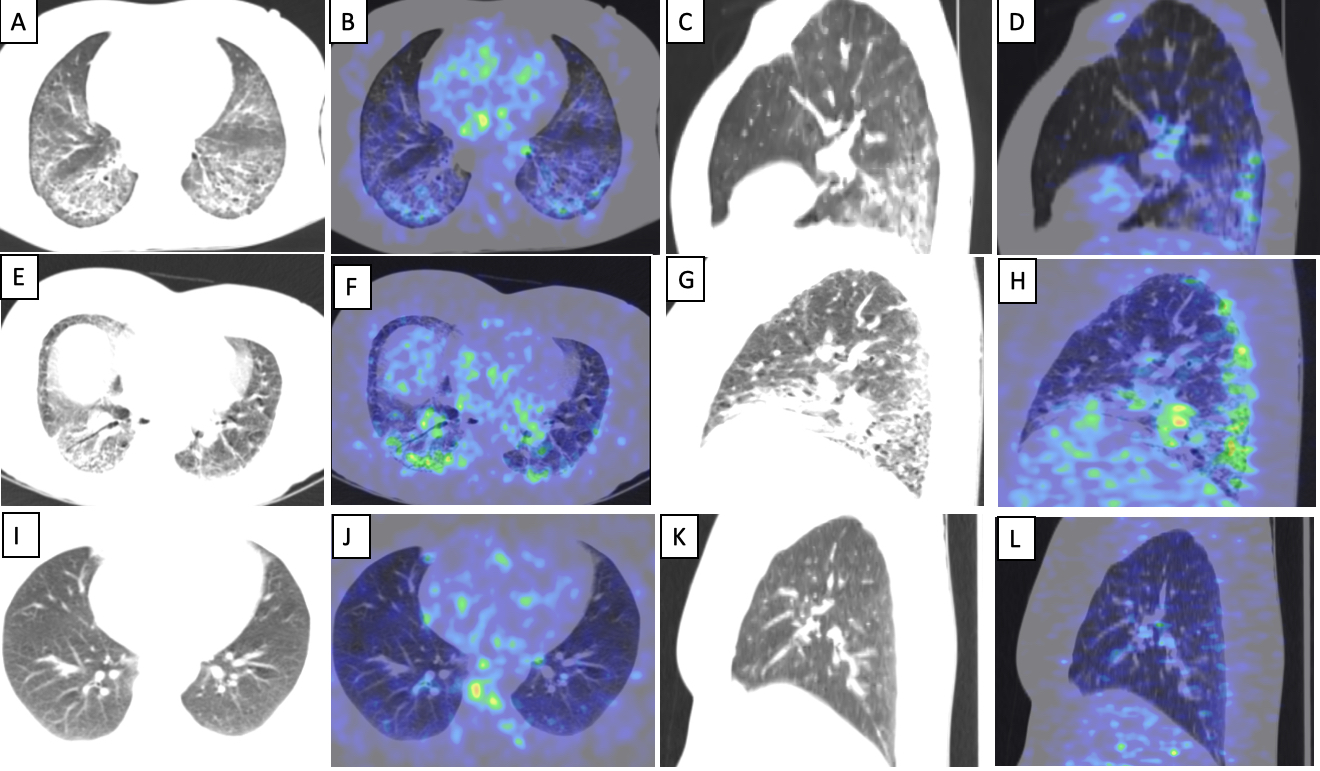 In patient with stable disease, transaxial CT images (A) showing reticular opacities with subpleural sparing and areas of architectural distortion with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (B). Reformatted sagittal CT (C) and fused PET/CT (D) images showing the changes confined predominantly to the basal zones with relative sparing of the upper lobes. In patient with active disease, (E) showing reticular opacities and areas of patchy consolidation and ground glassing with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (F). Reformatted sagittal CT (G) and fused PET/CT (H) images showing similar changes predominantly in the posterior lung fields with focal areas of architectural distortion
In patient with stable disease, transaxial CT images (A) showing reticular opacities with subpleural sparing and areas of architectural distortion with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (B). Reformatted sagittal CT (C) and fused PET/CT (D) images showing the changes confined predominantly to the basal zones with relative sparing of the upper lobes. In patient with active disease, (E) showing reticular opacities and areas of patchy consolidation and ground glassing with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (F). Reformatted sagittal CT (G) and fused PET/CT (H) images showing similar changes predominantly in the posterior lung fields with focal areas of architectural distortion
In control patient, transaxial (I) and reformatted sagittal CT images (J) showing no abnormality on the bilateral lung fields with no abnormal tracer uptake in the lung fields on the fused PET/CT images (K,L).
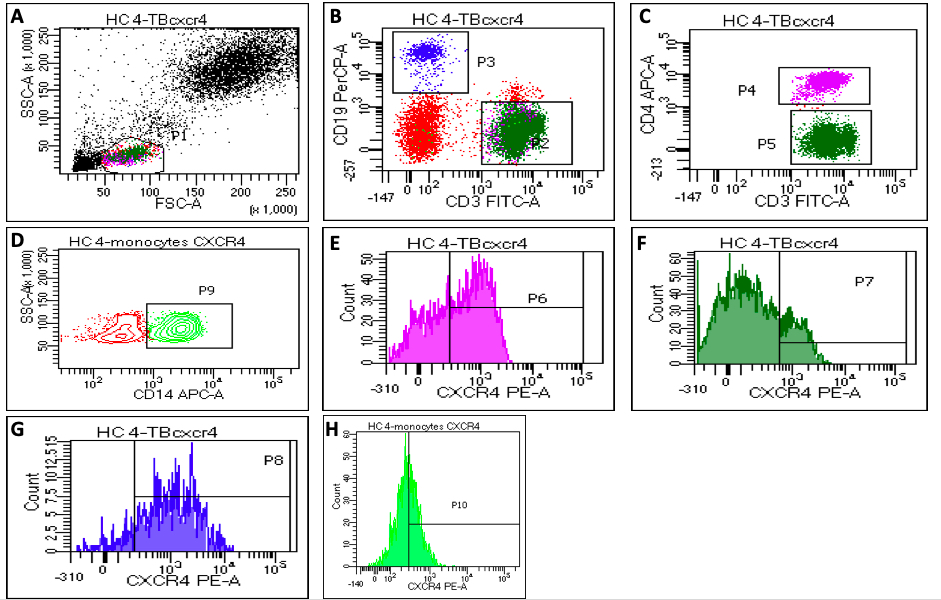 Representative flow diagrams showing gating strategy for CXCR4 expression: a) Gating of lymphocytes on FSC and SSC dot plot and monocytes were gated on cluster present between lymphocytes and granulocytes , b) showing CD3+ T cells as P2, CD19+ B cells as P3, c) showing CD4+ T cells as P4 and CD4- CD3+ (CD8 T cells) as P5 d) Showing CD14+ monocytes as P9, (e,f,g,h) showing CXCR4 expression on CD4+ T cells as p6, CD8+ T cells as p7, CD19+ B cells as p8 and CD14+ monocytes as p 10, respectively.
Representative flow diagrams showing gating strategy for CXCR4 expression: a) Gating of lymphocytes on FSC and SSC dot plot and monocytes were gated on cluster present between lymphocytes and granulocytes , b) showing CD3+ T cells as P2, CD19+ B cells as P3, c) showing CD4+ T cells as P4 and CD4- CD3+ (CD8 T cells) as P5 d) Showing CD14+ monocytes as P9, (e,f,g,h) showing CXCR4 expression on CD4+ T cells as p6, CD8+ T cells as p7, CD19+ B cells as p8 and CD14+ monocytes as p 10, respectively.
Disclosures: C. Kopp, None; S. Sharma, None; V. Krishnaraju, None; C. Prasad, None; J. Singh, None; S. Anand, None; R. Minz, None; A. Sood, None; A. Sinha, None; R. Basher, None; S. Dhooria, None; V. Dhir, None; s. jain, None.
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) in Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a major contributor of morbidity and mortality. CXCR4/CXCL12 axis has been implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. In this pilot study, we characterize the CXCR4 expression in lung parenchyma using 68Ga-Lympholeucin (CPCR4 trifluoroacetate) and peripheral white blood cells using PET/CT and flow cytometry.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, we included SSc patients having active (n=14) and stable(n=3) ILD based on the duration, clinical and radiological progression, and FVC decline. 68Ga-Lympholeucin uptake in lung parenchyma was quantified in these 17 SSc-ILD patients and compared to the diseased controls without lung parenchymal involvement. Lung parenchyma was divided into 22 regions of interest (ROI) on PET/CT, drawn in the dorsobasal, middle and apical regions of the lung and individual areas were quantified for CXCR4 expression using SUVmean and compared to the controls. Flow cytometry was performed in 16 patients to quantify CXCR4 expression on CD4+ T cell, CD8+ T cell, CD14+ monocytes and CD19+ B cells, and compared with healthy controls.
Results: SSc-ILD patients underwent 68Ga-Lympholeucin PET/CT imaging showed significant SUVmean uptake in the lung parenchyma compared to controls. Most significant areas of uptake were noted in the dorsobasal regions of lung. Also, significantly higher CXCR4 uptake in the areas of ground glass (P< 0.001), reticulation (P< 0.001) and reticulation with architectural distortion (P< 0.001) opacities as compared to normal regions. Higher proportion of CD4 (83.83±7.99 vs 60.28±12.20; P< 0.001) and CD8 (67.67±14.4 vs 43.67±12.59; P=0.003) cells in SSc-ILD patients showed CXCR4 expression as compared to controls.
Conclusion: 68Ga-Lympholeucin PET/CT is a good imaging modality to quantify CXCR4 expression in lung parenchyma of SSc-ILD patients. Increased CXCR4 expression in the lung parenchyma using PET/CT and peripheral T cells could be used as a biomarker of disease activity and assessment of response to therapy.
.jpg)
 In patient with stable disease, transaxial CT images (A) showing reticular opacities with subpleural sparing and areas of architectural distortion with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (B). Reformatted sagittal CT (C) and fused PET/CT (D) images showing the changes confined predominantly to the basal zones with relative sparing of the upper lobes. In patient with active disease, (E) showing reticular opacities and areas of patchy consolidation and ground glassing with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (F). Reformatted sagittal CT (G) and fused PET/CT (H) images showing similar changes predominantly in the posterior lung fields with focal areas of architectural distortion
In patient with stable disease, transaxial CT images (A) showing reticular opacities with subpleural sparing and areas of architectural distortion with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (B). Reformatted sagittal CT (C) and fused PET/CT (D) images showing the changes confined predominantly to the basal zones with relative sparing of the upper lobes. In patient with active disease, (E) showing reticular opacities and areas of patchy consolidation and ground glassing with increased tracer uptake on the fused PET/CT images (F). Reformatted sagittal CT (G) and fused PET/CT (H) images showing similar changes predominantly in the posterior lung fields with focal areas of architectural distortionIn control patient, transaxial (I) and reformatted sagittal CT images (J) showing no abnormality on the bilateral lung fields with no abnormal tracer uptake in the lung fields on the fused PET/CT images (K,L).
 Representative flow diagrams showing gating strategy for CXCR4 expression: a) Gating of lymphocytes on FSC and SSC dot plot and monocytes were gated on cluster present between lymphocytes and granulocytes , b) showing CD3+ T cells as P2, CD19+ B cells as P3, c) showing CD4+ T cells as P4 and CD4- CD3+ (CD8 T cells) as P5 d) Showing CD14+ monocytes as P9, (e,f,g,h) showing CXCR4 expression on CD4+ T cells as p6, CD8+ T cells as p7, CD19+ B cells as p8 and CD14+ monocytes as p 10, respectively.
Representative flow diagrams showing gating strategy for CXCR4 expression: a) Gating of lymphocytes on FSC and SSC dot plot and monocytes were gated on cluster present between lymphocytes and granulocytes , b) showing CD3+ T cells as P2, CD19+ B cells as P3, c) showing CD4+ T cells as P4 and CD4- CD3+ (CD8 T cells) as P5 d) Showing CD14+ monocytes as P9, (e,f,g,h) showing CXCR4 expression on CD4+ T cells as p6, CD8+ T cells as p7, CD19+ B cells as p8 and CD14+ monocytes as p 10, respectively.Disclosures: C. Kopp, None; S. Sharma, None; V. Krishnaraju, None; C. Prasad, None; J. Singh, None; S. Anand, None; R. Minz, None; A. Sood, None; A. Sinha, None; R. Basher, None; S. Dhooria, None; V. Dhir, None; s. jain, None.

