Back
Abstract Session
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes I: Diagnosis and Disease Activity (1609–1614)
1611: Putative Role of the Histidine and Tryptophan Biochemical Pathways in the Mode of Action of Upadacitinib in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
5:00 PM – 5:10 PM Eastern Time
Location: Room 113
- WM
Walter P. Maksymowych, MD
University of Alberta
Edmonton, AB, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Thierry Sornasse1, Liang Li2, Shuang Zhao2, Xiaohang Wang2, Fang Cai3, Yingtao Bi4, In-Ho Song5, Stephanie Wichuk6, Robert G. Lambert7 and Walter P Maksymowych8, 1AbbVie, South San Francisco, CA, 2The Metabolomics Innovation Centre and Department of Chemistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 3AbbVie, Redwood City, CA, 4AbbVie, Inc, Worcester, MA, 5AbbVie, Inc., North Chicago, IL, 6University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 7Department of Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 8Department of Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) 15 mg QD is efficacious in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) exhibiting inadequate responses to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs-IR).1 We determined the impact of UPA on the global metabolome in these patients.
Methods: Baseline (BL), weeks 4, and 14 serum samples were obtained from a subset of patients enrolled in SELECT-AXIS1 (PBO, n = 59 out of 94; UPA, n = 59 out of 93). Patients met the modified New York AS criteria and had active disease at BL. Samples were processed using dansyl-12C-labeling kits or DmPA-12C-labeling kits for each chemical-group channel and analyzed by LC-MS–based metabolomics. Data analysis was performed using IsoMS Pro 1.2.15 (NovaMT Inc.) and metabolite identification was done using NovaMT Metabolite Database v2.0.2 Tier 1 and 2 metabolites matched single compounds from a labeled metabolite library and a linked identity library, respectively. Tier 3 metabolites matched more than 1 compound. Differentially modulated metabolites (DMM) were identified using a mixed linear model measuring change from BL for each treatment group (selection criteria, absolute Log10 fold change ≥ 0.079, and false discovery rate ≤ 0.1). Pathway enrichment analyses were conducted using MetaboAnalyst 5.0.3 Relationships between metabolite level changes, and clinical changes were assessed by Pearson's correlation.
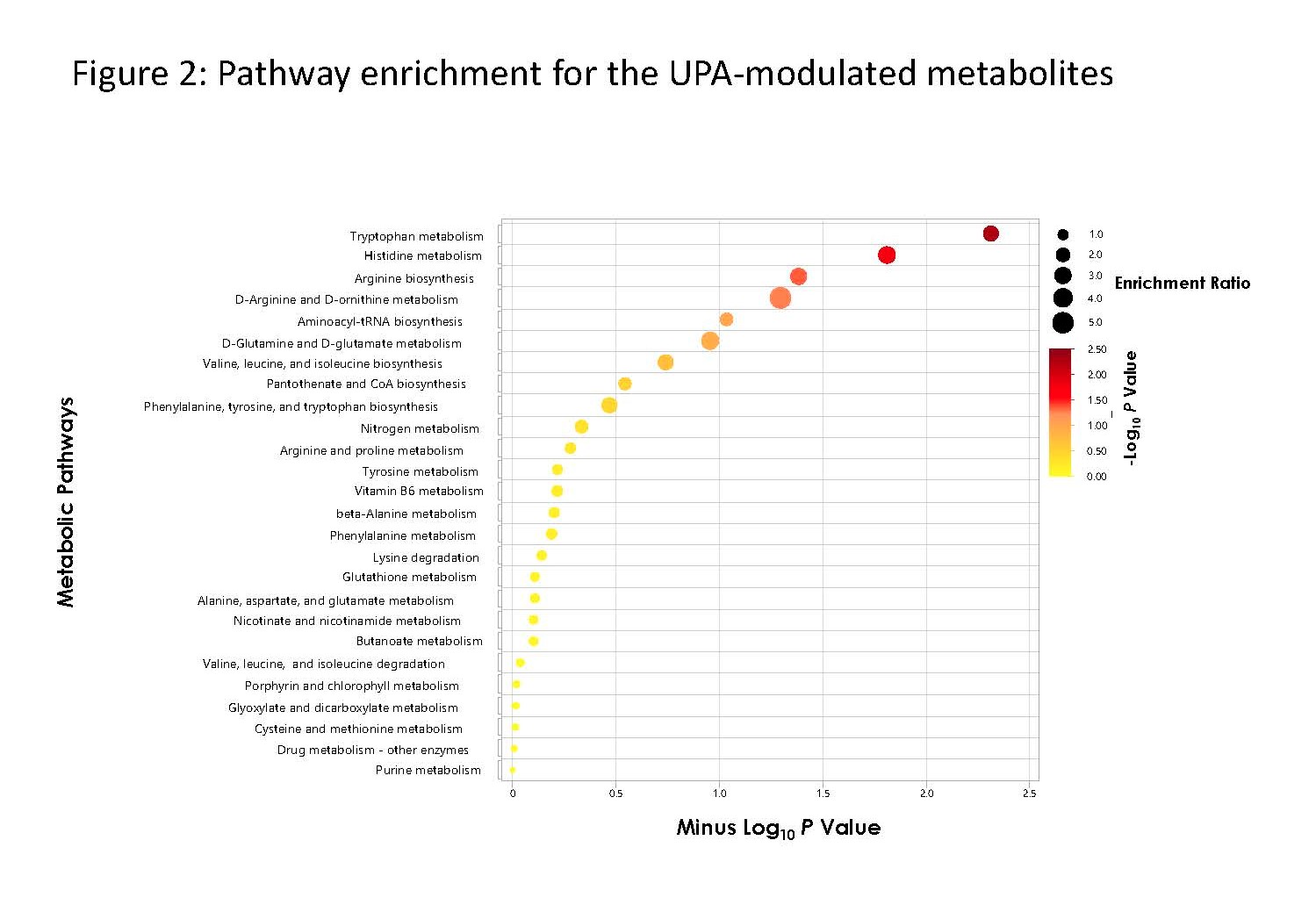
Results: We detected a total of 8020 distinct metabolites (ie, ≥ 80% detectability across timepoints within each treatment group) across the global metabolome. From these 8020 metabolites, we identified 289 and 221 DMM at weeks 4 and 14 in the UPA group vs 32 and 89 in the PBO group, respectively (Fig. 1). Most DMM in the UPA group (187 and 144 at weeks 4 and 14, respectively) belonged to the Tier 3 identification category, and 51 and 40 at weeks 4 and 14, respectively, belonged to the Tier 1 and 2 categories. Pathway enrichment suggests UPA affects the histidine and tryptophan biochemical pathways (Fig. 2), consistent with increases in metabolites observed in the UPA group. Increases in histidine and tryptophan levels were significantly associated with an improvement in CRP levels and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-CRP scores (P ≤ .05). Increases in histidine levels were also associated with the improvement in MRI Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Spine indices.
Conclusion: This is the first comprehensive metabolome analysis of serum samples collected from patients with AS treated with UPA. Data highlight the promise of advanced metabolomics to elucidate therapeutic agent's mode of action in AS. The putative effect of UPA on the tryptophan biochemical pathway is of particular interest because the tryptophan/kynurenine pathway is associated with chronic pain4 and is perturbed toward the degradation of tryptophan in patients with AS.5 We hypothesize that the increase in tryptophan and histidine may be related to the mode of action of UPA in NSAID-IR patients with AS.
References
1. van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet. 2019;394:2108
2. Blackmore D, et al. Metabolomics. 2020;16:10
3. Pang Z, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:W388
4. Jovanovic F, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6045
5. Eryavuz Onmaz D, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108018
.jpg)
Disclosures: T. Sornasse, AbbVie; L. Li, Nova Medical Testing Inc. (NovaMT), Meliomics Inc., NovaMT, Bruker; S. Zhao, None; X. Wang, None; F. Cai, AbbVie; Y. Bi, AbbVie; I. Song, AbbVie; S. Wichuk, None; R. Lambert, None; W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, CARE Arthritis Limited.
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) 15 mg QD is efficacious in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) exhibiting inadequate responses to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs-IR).1 We determined the impact of UPA on the global metabolome in these patients.
Methods: Baseline (BL), weeks 4, and 14 serum samples were obtained from a subset of patients enrolled in SELECT-AXIS1 (PBO, n = 59 out of 94; UPA, n = 59 out of 93). Patients met the modified New York AS criteria and had active disease at BL. Samples were processed using dansyl-12C-labeling kits or DmPA-12C-labeling kits for each chemical-group channel and analyzed by LC-MS–based metabolomics. Data analysis was performed using IsoMS Pro 1.2.15 (NovaMT Inc.) and metabolite identification was done using NovaMT Metabolite Database v2.0.2 Tier 1 and 2 metabolites matched single compounds from a labeled metabolite library and a linked identity library, respectively. Tier 3 metabolites matched more than 1 compound. Differentially modulated metabolites (DMM) were identified using a mixed linear model measuring change from BL for each treatment group (selection criteria, absolute Log10 fold change ≥ 0.079, and false discovery rate ≤ 0.1). Pathway enrichment analyses were conducted using MetaboAnalyst 5.0.3 Relationships between metabolite level changes, and clinical changes were assessed by Pearson's correlation.
Results: We detected a total of 8020 distinct metabolites (ie, ≥ 80% detectability across timepoints within each treatment group) across the global metabolome. From these 8020 metabolites, we identified 289 and 221 DMM at weeks 4 and 14 in the UPA group vs 32 and 89 in the PBO group, respectively (Fig. 1). Most DMM in the UPA group (187 and 144 at weeks 4 and 14, respectively) belonged to the Tier 3 identification category, and 51 and 40 at weeks 4 and 14, respectively, belonged to the Tier 1 and 2 categories. Pathway enrichment suggests UPA affects the histidine and tryptophan biochemical pathways (Fig. 2), consistent with increases in metabolites observed in the UPA group. Increases in histidine and tryptophan levels were significantly associated with an improvement in CRP levels and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-CRP scores (P ≤ .05). Increases in histidine levels were also associated with the improvement in MRI Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Spine indices.
Conclusion: This is the first comprehensive metabolome analysis of serum samples collected from patients with AS treated with UPA. Data highlight the promise of advanced metabolomics to elucidate therapeutic agent's mode of action in AS. The putative effect of UPA on the tryptophan biochemical pathway is of particular interest because the tryptophan/kynurenine pathway is associated with chronic pain4 and is perturbed toward the degradation of tryptophan in patients with AS.5 We hypothesize that the increase in tryptophan and histidine may be related to the mode of action of UPA in NSAID-IR patients with AS.
References
1. van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet. 2019;394:2108
2. Blackmore D, et al. Metabolomics. 2020;16:10
3. Pang Z, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:W388
4. Jovanovic F, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6045
5. Eryavuz Onmaz D, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108018
.jpg)

Disclosures: T. Sornasse, AbbVie; L. Li, Nova Medical Testing Inc. (NovaMT), Meliomics Inc., NovaMT, Bruker; S. Zhao, None; X. Wang, None; F. Cai, AbbVie; Y. Bi, AbbVie; I. Song, AbbVie; S. Wichuk, None; R. Lambert, None; W. Maksymowych, AbbVie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, CARE Arthritis Limited.

