Back
Abstract Session
Immunobiology
Session: Abstracts: B Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disease (1629–1632)
1629: AUR200: An Improved BAFF/APRIL Inhibitor with Increased Potency and Safety for the Treatment of B Cell-Mediated Diseases
Monday, November 14, 2022
9:00 AM – 9:10 AM Eastern Time
Location: Room 114 Nutter Theatre
- SM
Shawn Morales
Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Temecula, CA, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Shawn Morales, Jennifer Cross and Robert Huizinga, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Victoria, BC, Canada
Background/Purpose: AUR200 targets both B cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), which are key mediators in the pathogenesis of B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Dual blockade of BAFF and APRIL is proposed to be more effective than targeting either molecule alone. AUR200 is a potent recombinant IgG4 Fc fusion protein containing a modified B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) extracellular domain for enhanced binding to BAFF and APRIL. AUR200 is under development as a next generation therapeutic for B cell-mediated diseases.
Methods: The binding affinity (KD) and half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL were determined by surface plasmon resonance (Carterra LSA, HC30M sensor chip) and competitive ELISA, respectively. Proliferation was measured with human primary B cells or mouse splenocytes stimulated with BAFF, APRIL or BAFF-60mer. In a therapeutic systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) study, NZBxNZW F1 mice, randomized by body weight and proteinuria scores, were treated by weekly subcutaneous (SC) injections of AUR200 (1, 3 or 10 mg/kg) from 28 to 34 weeks of age. Urine protein (Albustix® strips) was scored weekly. At week 34, serum antibodies and cytokines were measured by ELISA. Kidneys were formalin-fixed, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and scored by a board-certified veterinary pathologist. In another study, nonhuman primates (cynomolgus monkeys) received either a single dose (1 mg/kg, SC) or weekly doses (5, 20 or 80 mg/kg, SC) of AUR200 for 4 weeks. Serum immunoglobulins and PBMC B cells were measured. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test (GraphPad Prism v9.2).
Results: AUR200 binds human BAFF and APRIL with high affinity and reduces BAFF and APRIL-costimulated proliferation of human primary B cells and mouse splenocytes. AUR200 is more potent than transmembrane activator and calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI)-Fc fusion proteins with similar mechanisms of action (Figure 1). When administered therapeutically in a SLE mouse model, AUR200 significantly improved survival at all doses tested and reduced both proteinuria and histological markers of renal damage. At all doses tested, AUR200 significantly decreased IFNγ and IL-17A, both T cell cytokines, and dose-dependently reduced anti-dsDNA autoantibodies. A single subcutaneous dose of AUR200 in cynomolgus monkeys suppressed peripheral B cells while weekly dosing over 4 weeks resulted in sustained reductions in all serum immunoglobins. Over the month of dosing, AUR200 remained well-tolerated with no adverse findings at any of the doses tested.
Conclusion: AUR200 is a BCMA-IgG4 Fc fusion protein currently in preclinical development. AUR200 demonstrates best in class binding affinity to both BAFF and APRIL due to the engineered modifications to the BCMA binding pocket. In a mouse model of SLE, AUR200 dosed therapeutically reduced several markers of disease activity and improved overall survival. AUR200 was well-tolerated, in both mouse and cynomolgus monkeys, with no adverse effects. These data highlight the potential utility for AUR200 in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
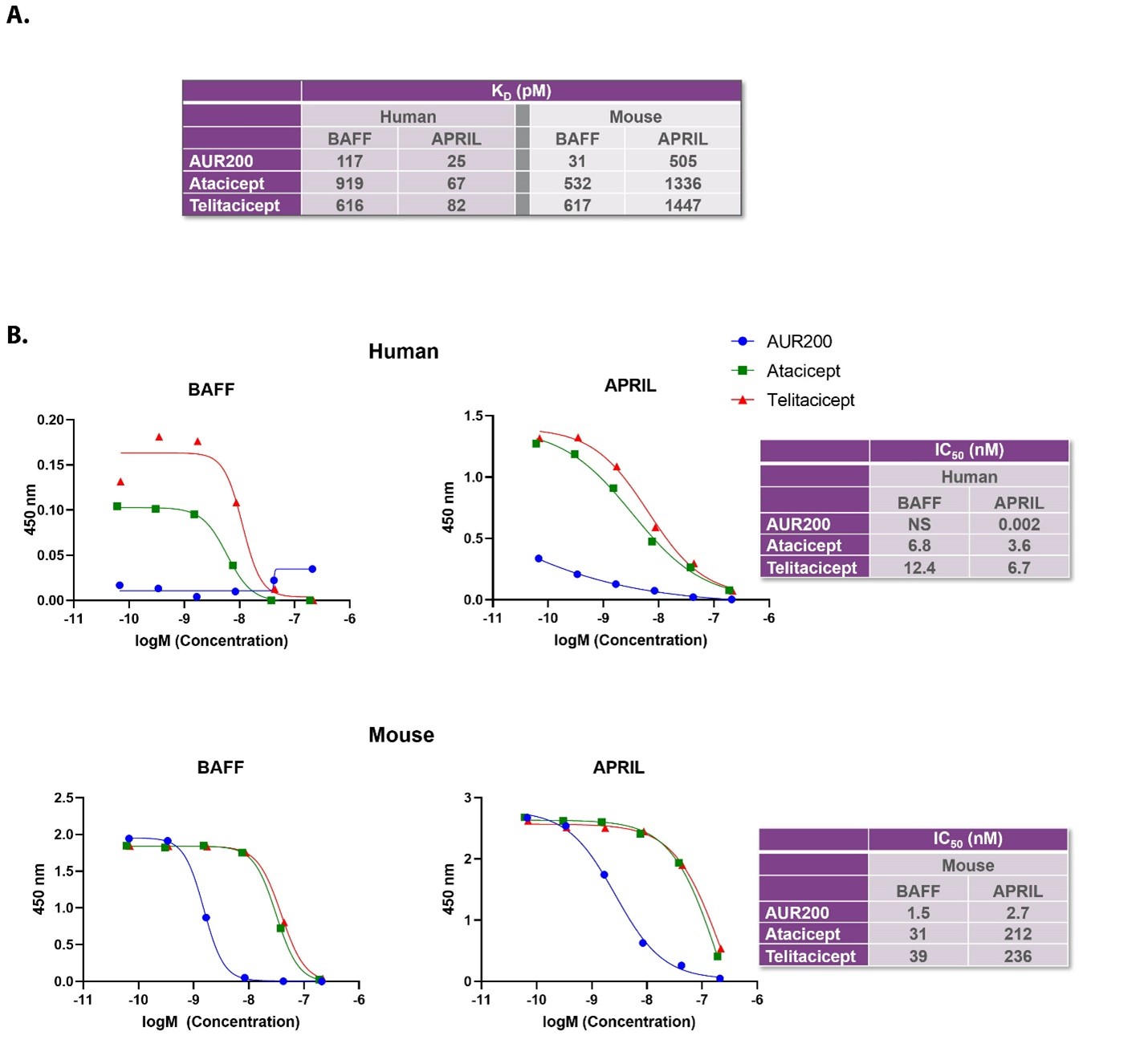 Figure 1. AUR200 potently neutralizes BAFF and APRIL. The binding affinity (KD) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by surface plasmon resonance (A). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by competitive ELISA (B). NS, no signal.
Figure 1. AUR200 potently neutralizes BAFF and APRIL. The binding affinity (KD) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by surface plasmon resonance (A). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by competitive ELISA (B). NS, no signal.
Disclosures: S. Morales, Aurinia; J. Cross, aurinia pharmaceuticals; R. Huizinga, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Background/Purpose: AUR200 targets both B cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), which are key mediators in the pathogenesis of B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Dual blockade of BAFF and APRIL is proposed to be more effective than targeting either molecule alone. AUR200 is a potent recombinant IgG4 Fc fusion protein containing a modified B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) extracellular domain for enhanced binding to BAFF and APRIL. AUR200 is under development as a next generation therapeutic for B cell-mediated diseases.
Methods: The binding affinity (KD) and half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL were determined by surface plasmon resonance (Carterra LSA, HC30M sensor chip) and competitive ELISA, respectively. Proliferation was measured with human primary B cells or mouse splenocytes stimulated with BAFF, APRIL or BAFF-60mer. In a therapeutic systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) study, NZBxNZW F1 mice, randomized by body weight and proteinuria scores, were treated by weekly subcutaneous (SC) injections of AUR200 (1, 3 or 10 mg/kg) from 28 to 34 weeks of age. Urine protein (Albustix® strips) was scored weekly. At week 34, serum antibodies and cytokines were measured by ELISA. Kidneys were formalin-fixed, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and scored by a board-certified veterinary pathologist. In another study, nonhuman primates (cynomolgus monkeys) received either a single dose (1 mg/kg, SC) or weekly doses (5, 20 or 80 mg/kg, SC) of AUR200 for 4 weeks. Serum immunoglobulins and PBMC B cells were measured. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test (GraphPad Prism v9.2).
Results: AUR200 binds human BAFF and APRIL with high affinity and reduces BAFF and APRIL-costimulated proliferation of human primary B cells and mouse splenocytes. AUR200 is more potent than transmembrane activator and calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI)-Fc fusion proteins with similar mechanisms of action (Figure 1). When administered therapeutically in a SLE mouse model, AUR200 significantly improved survival at all doses tested and reduced both proteinuria and histological markers of renal damage. At all doses tested, AUR200 significantly decreased IFNγ and IL-17A, both T cell cytokines, and dose-dependently reduced anti-dsDNA autoantibodies. A single subcutaneous dose of AUR200 in cynomolgus monkeys suppressed peripheral B cells while weekly dosing over 4 weeks resulted in sustained reductions in all serum immunoglobins. Over the month of dosing, AUR200 remained well-tolerated with no adverse findings at any of the doses tested.
Conclusion: AUR200 is a BCMA-IgG4 Fc fusion protein currently in preclinical development. AUR200 demonstrates best in class binding affinity to both BAFF and APRIL due to the engineered modifications to the BCMA binding pocket. In a mouse model of SLE, AUR200 dosed therapeutically reduced several markers of disease activity and improved overall survival. AUR200 was well-tolerated, in both mouse and cynomolgus monkeys, with no adverse effects. These data highlight the potential utility for AUR200 in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
 Figure 1. AUR200 potently neutralizes BAFF and APRIL. The binding affinity (KD) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by surface plasmon resonance (A). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by competitive ELISA (B). NS, no signal.
Figure 1. AUR200 potently neutralizes BAFF and APRIL. The binding affinity (KD) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by surface plasmon resonance (A). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of AUR200 against human or murine BAFF and APRIL, determined by competitive ELISA (B). NS, no signal.Disclosures: S. Morales, Aurinia; J. Cross, aurinia pharmaceuticals; R. Huizinga, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.

