Back
Poster Session A
Session: (0123–0149) Miscellaneous Rheumatic and Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
0126: Should Arthrocentesis Be Attempted in the Symptomatic but Non-Effusive Knee?
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- RP
Rosemina Patel, MD
University of New Mexico School of Medicine
Albuquerque, NM, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Rosemina Patel1, Angie Ariza-hutchinson1, Ahsan Iqbal1, Matthew McElwee1, N. Suzanne Emil1, Sharon Nunez1, maheshwari muruganandam1, frank O'Sullivan1, Roderick Fields1, Yvonne Waters2 and Wilmer Sibbitt1, 1University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, 2University of New Mexico Hospital, Corrales, NM
Background/Purpose: Arthrocentesis of the painful but non-effusive knee is usually not undertaken due to a high arthrocentesis failure rate. We hypothesized that compression-assisted arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee would permit synovial fluid analysis and provide useful diagnostic information.
Methods: The absence of a knee effusion was determined by physical examination and ultrasound visualization. Conventional arthrocentesis first with and then without pneumatic compression was performed in 114 consecutive painful, non-effusive knees and synovial fluid was collected and analyzed for total nucleated cell (TNC) counts, TNC differential, crystals, Gram stain, and bacterial cultures.
Results: Arthrocentesis success (≥ 0.5 ml) in the symptomatic non-effusive knee was 23.7% (27/114) without compression and 57.0% (65/114) with compression. OR: 0.22 (OR: 0.23 (0.13, 0.41); p=0.0001). The volume of aspirated synovial fluid increased from 0.43±0.95 ml to 1.8±2.5; p< 0.0001) when compression was used. Fluid from the non-effusive knee demonstrated: I) Normal fluid (TNC< 200) in 41.5% (27/65) (mean TNC 56.3±37.8), II) Non-inflammatory fluid (TNC 200-2000) in 41.5% (27/65) (mean TNC 556±3304), III) Inflammatory (TNC >2000) in 6.2% (4/65) (mean TNC 30,108±26,102); and V) Crystal-induced in 10.8% (7/65) (mean TNC 7115±1625). Amongst the crystal-induced fluid, two had sodium urate crystals both with normal or non-inflammatory fluid and five had calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) only one of which was inflammatory.
Conclusion: Compression-assisted arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee is successful in most cases and detects non-effusive inter-critical gout, other crystal-induced diseases, and inflammatory arthritis. Diagnostic arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee should be particularly considered in cases where there has been no prior synovial fluid analysis.
 Characteristics of synovial fluid in painful non-effusive joint
Characteristics of synovial fluid in painful non-effusive joint
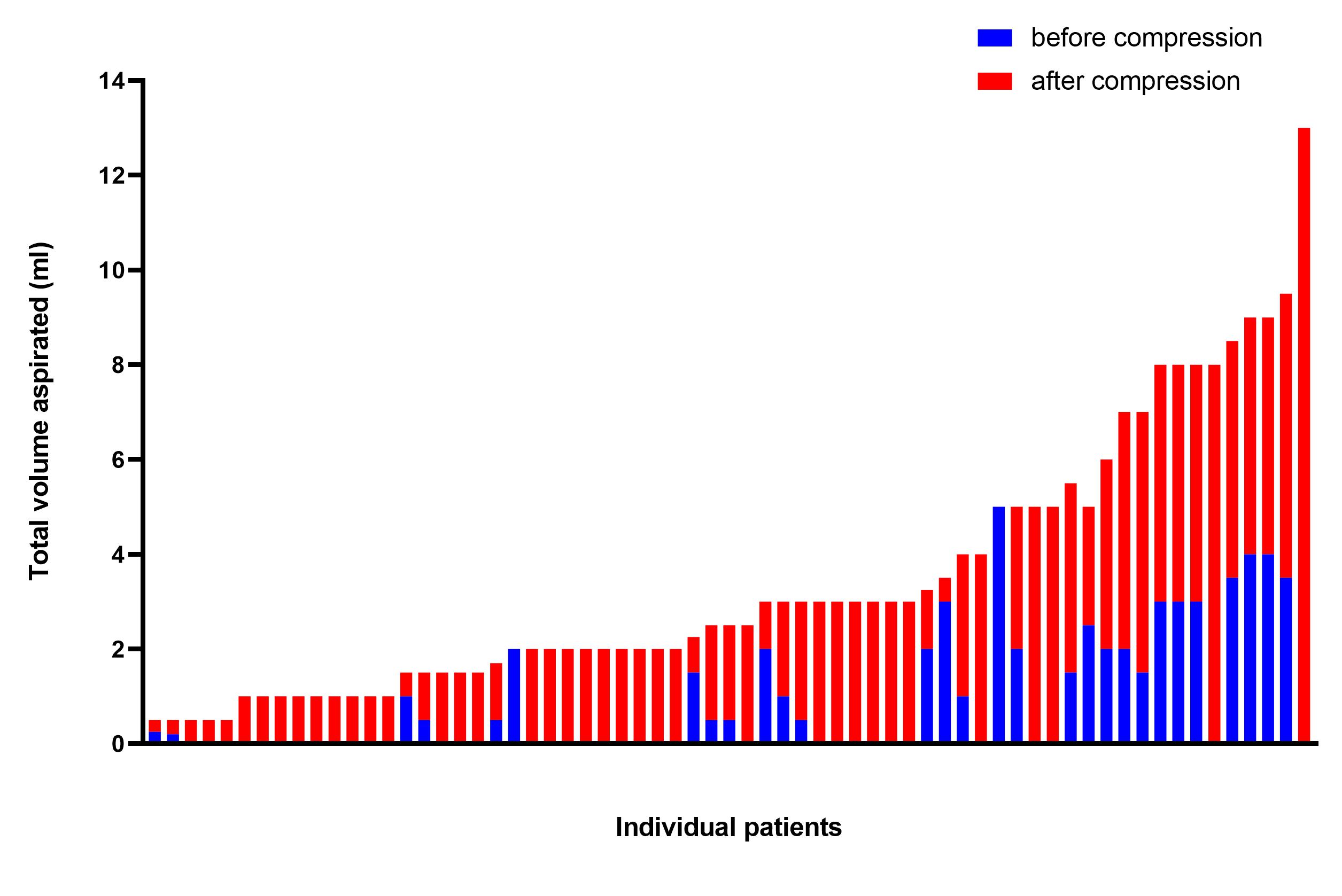 Volume of arthrocentesis in non-effusive knees with and without pneumatic compression
Volume of arthrocentesis in non-effusive knees with and without pneumatic compression
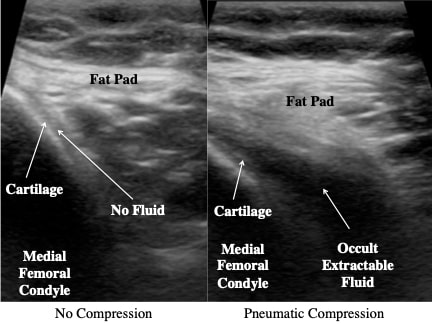 Ultrasound Image of Non-Effusive Knee with and without Pneumatic Compression (medial knee). The figure on the left is the flexed non-effusive knee, where the needle cannot access the synovial fluid because the fat pad (Fat Pad) forces fluid from the surface of the cartilage to the superior knee. The figure on the right is a non-effusive knee with the pneumatic compression that compresses the suprapatellar bursa and induces collapse driving the occult synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid) inferiorly where the fluid collects over the cartilage surfaces (Cartilage) of the medial femoral condyle (Medial Femoral Condyle) displacing the fat pad (Fat Pad). The needle can then access the synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid).
Ultrasound Image of Non-Effusive Knee with and without Pneumatic Compression (medial knee). The figure on the left is the flexed non-effusive knee, where the needle cannot access the synovial fluid because the fat pad (Fat Pad) forces fluid from the surface of the cartilage to the superior knee. The figure on the right is a non-effusive knee with the pneumatic compression that compresses the suprapatellar bursa and induces collapse driving the occult synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid) inferiorly where the fluid collects over the cartilage surfaces (Cartilage) of the medial femoral condyle (Medial Femoral Condyle) displacing the fat pad (Fat Pad). The needle can then access the synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid).
Disclosures: R. Patel, None; A. Ariza-hutchinson, None; A. Iqbal, None; M. McElwee, None; N. Emil, None; S. Nunez, None; m. muruganandam, None; f. O'Sullivan, None; R. Fields, None; Y. Waters, None; W. Sibbitt, None.
Background/Purpose: Arthrocentesis of the painful but non-effusive knee is usually not undertaken due to a high arthrocentesis failure rate. We hypothesized that compression-assisted arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee would permit synovial fluid analysis and provide useful diagnostic information.
Methods: The absence of a knee effusion was determined by physical examination and ultrasound visualization. Conventional arthrocentesis first with and then without pneumatic compression was performed in 114 consecutive painful, non-effusive knees and synovial fluid was collected and analyzed for total nucleated cell (TNC) counts, TNC differential, crystals, Gram stain, and bacterial cultures.
Results: Arthrocentesis success (≥ 0.5 ml) in the symptomatic non-effusive knee was 23.7% (27/114) without compression and 57.0% (65/114) with compression. OR: 0.22 (OR: 0.23 (0.13, 0.41); p=0.0001). The volume of aspirated synovial fluid increased from 0.43±0.95 ml to 1.8±2.5; p< 0.0001) when compression was used. Fluid from the non-effusive knee demonstrated: I) Normal fluid (TNC< 200) in 41.5% (27/65) (mean TNC 56.3±37.8), II) Non-inflammatory fluid (TNC 200-2000) in 41.5% (27/65) (mean TNC 556±3304), III) Inflammatory (TNC >2000) in 6.2% (4/65) (mean TNC 30,108±26,102); and V) Crystal-induced in 10.8% (7/65) (mean TNC 7115±1625). Amongst the crystal-induced fluid, two had sodium urate crystals both with normal or non-inflammatory fluid and five had calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) only one of which was inflammatory.
Conclusion: Compression-assisted arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee is successful in most cases and detects non-effusive inter-critical gout, other crystal-induced diseases, and inflammatory arthritis. Diagnostic arthrocentesis of the symptomatic non-effusive knee should be particularly considered in cases where there has been no prior synovial fluid analysis.
 Characteristics of synovial fluid in painful non-effusive joint
Characteristics of synovial fluid in painful non-effusive joint Volume of arthrocentesis in non-effusive knees with and without pneumatic compression
Volume of arthrocentesis in non-effusive knees with and without pneumatic compression Ultrasound Image of Non-Effusive Knee with and without Pneumatic Compression (medial knee). The figure on the left is the flexed non-effusive knee, where the needle cannot access the synovial fluid because the fat pad (Fat Pad) forces fluid from the surface of the cartilage to the superior knee. The figure on the right is a non-effusive knee with the pneumatic compression that compresses the suprapatellar bursa and induces collapse driving the occult synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid) inferiorly where the fluid collects over the cartilage surfaces (Cartilage) of the medial femoral condyle (Medial Femoral Condyle) displacing the fat pad (Fat Pad). The needle can then access the synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid).
Ultrasound Image of Non-Effusive Knee with and without Pneumatic Compression (medial knee). The figure on the left is the flexed non-effusive knee, where the needle cannot access the synovial fluid because the fat pad (Fat Pad) forces fluid from the surface of the cartilage to the superior knee. The figure on the right is a non-effusive knee with the pneumatic compression that compresses the suprapatellar bursa and induces collapse driving the occult synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid) inferiorly where the fluid collects over the cartilage surfaces (Cartilage) of the medial femoral condyle (Medial Femoral Condyle) displacing the fat pad (Fat Pad). The needle can then access the synovial fluid (Occult Extractable Fluid).Disclosures: R. Patel, None; A. Ariza-hutchinson, None; A. Iqbal, None; M. McElwee, None; N. Emil, None; S. Nunez, None; m. muruganandam, None; f. O'Sullivan, None; R. Fields, None; Y. Waters, None; W. Sibbitt, None.

