Back
Poster Session A
Session: (0123–0149) Miscellaneous Rheumatic and Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
0127: The Adult SAPHO and Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis Observational Study (The SAPHO-CNO Study) Supports Multidimensional Disease Symptomatology with High Levels of Pain and Fatigue, and Low Levels of Function
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AL
Aleksander Lenert, MD, MS, FRCPC
University of Iowa
Iowa City, IA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Aleksander Lenert1, Robyn Domsic2, Karmela Kim Chan3, Melissa Oliver4, Jisna Paul5, Courtney Kremer6, Emma Leisinger1, Svjetlana Dolovcak7, Sandy D. Hong8, Aruni Jayatilleke9, Petar Lenert7, T. Shawn Sato1, Samir Shah10, Shima Yasin11, Yongdong (Dan) Zhao12, Daniel Solomon13, Jonathan Templin1 and Polly Ferguson11, 1University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, 2University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, 3Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, 4Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, 5Ohio State University Hospital, Dublin, OH, 6University of Iowa Stead Family Children's Hospital, Solna, IA, 7University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City, IA, 8University of Iowa Stead Family Children's Hospital, Iowa City, IA, 9Temple University, PHILADELPHIA, PA, 10Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA, 11University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, Iowa City, IA, 12University of Washington, Redmond, WA, 13Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Background/Purpose: Quality of life (QOL) and disease impact are important to adults with SAPHO syndrome and chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) but remain poorly described. Patient-reported outcomes (PRO) represent key perspectives of patients living with a chronic rheumatic disease and are important considerations in overall disease activity assessment. Due to the rarity of SAPHO-CNO and paucity of prospective studies, PROs and QOL remain understudied. We identified key QOL domains through PRO measures (PROMs) in the SAPHO-CNO Study.
Methods: Adults (≥18 years of age) with SAPHO-CNO were enrolled in the SAPHO-CNO Study (SCS), a prospective longitudinal observational study with accompanying biospecimen collection. In the SCS, subjects complete serial questionnaires and undergo clinician disease activity assessments. Subjects have a confirmed diagnosis of SAPHO-CNO and meet Benhamou/Modified Kahn diagnostic criteria. Baseline questionnaires include demographics, clinical presentation, symptoms, disease activity, clinical outcomes and PROM instruments related to key QOL domains. We collected validated legacy PROM scales and instruments including patient global assessments for SAPHO-CNO disease activity, pain, function and fatigue (0-10 numeric rating scale, NRS), modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ, 0-3 scale) and 36-item Short Form survey (SF-36, 8 domains, 0-100). Several Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) short form (SF) instruments were collected. Descriptive statistics with measures of central tendency based on variable distribution curves were used to summarize the findings.
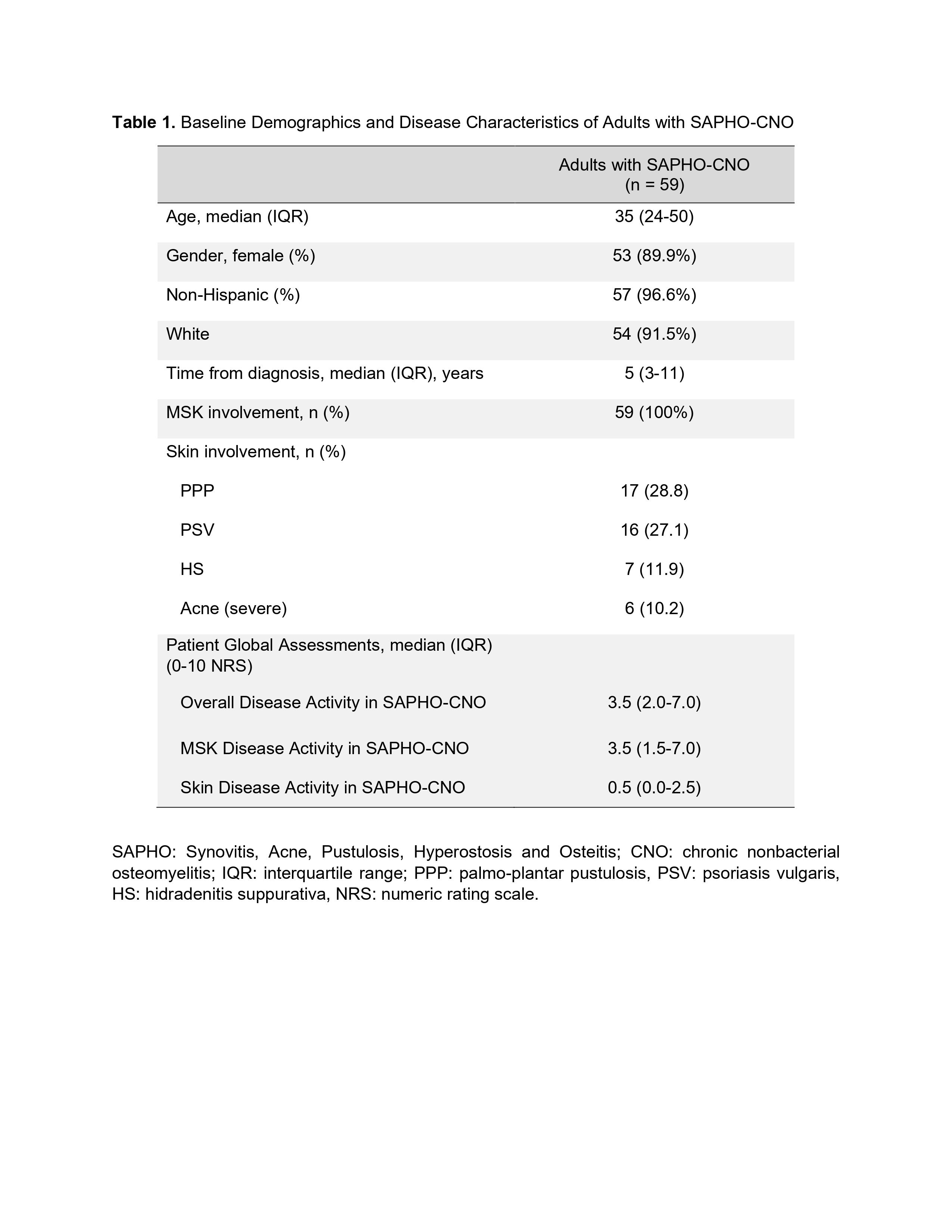
Results: Fifty-nine enrolled subjects completed their baseline study visit and were included in this cross-sectional analysis. The findings are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Adults with SAPHO-CNO were predominantly female non-Hispanic Caucasians, with a reported median time from diagnosis of 5 years with an interquartile range (IQR) of 3-11 years. All subjects had MSK involvement (bone and/or joint symptoms), with the most common cutaneous manifestations of palmo-plantar pustulosis (PPP) and psoriasis vulgaris (PSV), followed by hidradenitis suppurative (HS) and severe acne (Table 1).
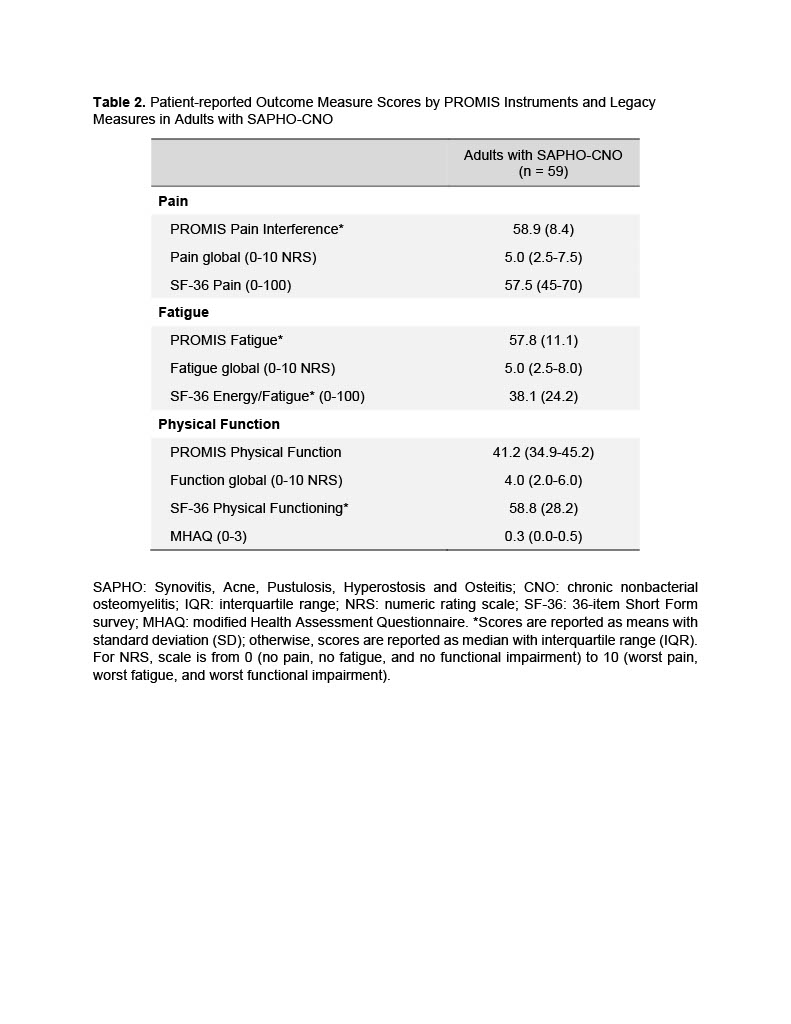
Adults with SAPHO-CNO reported high scores, 0.8 or greater standard deviations (SD), for both PROMIS pain interference and fatigue domains compared with standardized scores for the general population (mean T-score 50, SD 10) (Table 2). For pain interference and fatigue PROMIS domains, 69.5% and 64.4% of subjects had a T-score >55 respectively. Additionally, subjects reported lower scores, ~ 0.9 SDs, for PROMIS physical function; 72.9% of subjects had a T-score < 45. Similar to PROMIS scores, legacy PROM instruments showed corollary scores in pain, fatigue and function (Table 2). Median (IQR) patient-reported global scores were 5.0 (2.5-7.5) for pain, 5.0 (2.5-8.0) for fatigue, and 4.0 (2.0-6.0) for function.
Conclusion: Adult SAPHO-CNO patients, with a median of 5 years since diagnosis, demonstrate multidimensional symptomatology with high pain and fatigue, and low function as reported by PROMIS and legacy instruments.
Disclosures: A. Lenert, None; R. Domsic, None; K. Chan, None; M. Oliver, None; J. Paul, None; C. Kremer, None; E. Leisinger, None; S. Dolovcak, None; S. Hong, None; A. Jayatilleke, None; P. Lenert, None; T. Sato, None; S. Shah, None; S. Yasin, None; Y. Zhao, None; D. Solomon, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, moderna, CorEvitas; J. Templin, None; P. Ferguson, None.
Background/Purpose: Quality of life (QOL) and disease impact are important to adults with SAPHO syndrome and chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis (CNO) but remain poorly described. Patient-reported outcomes (PRO) represent key perspectives of patients living with a chronic rheumatic disease and are important considerations in overall disease activity assessment. Due to the rarity of SAPHO-CNO and paucity of prospective studies, PROs and QOL remain understudied. We identified key QOL domains through PRO measures (PROMs) in the SAPHO-CNO Study.
Methods: Adults (≥18 years of age) with SAPHO-CNO were enrolled in the SAPHO-CNO Study (SCS), a prospective longitudinal observational study with accompanying biospecimen collection. In the SCS, subjects complete serial questionnaires and undergo clinician disease activity assessments. Subjects have a confirmed diagnosis of SAPHO-CNO and meet Benhamou/Modified Kahn diagnostic criteria. Baseline questionnaires include demographics, clinical presentation, symptoms, disease activity, clinical outcomes and PROM instruments related to key QOL domains. We collected validated legacy PROM scales and instruments including patient global assessments for SAPHO-CNO disease activity, pain, function and fatigue (0-10 numeric rating scale, NRS), modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ, 0-3 scale) and 36-item Short Form survey (SF-36, 8 domains, 0-100). Several Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) short form (SF) instruments were collected. Descriptive statistics with measures of central tendency based on variable distribution curves were used to summarize the findings.
Results: Fifty-nine enrolled subjects completed their baseline study visit and were included in this cross-sectional analysis. The findings are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Adults with SAPHO-CNO were predominantly female non-Hispanic Caucasians, with a reported median time from diagnosis of 5 years with an interquartile range (IQR) of 3-11 years. All subjects had MSK involvement (bone and/or joint symptoms), with the most common cutaneous manifestations of palmo-plantar pustulosis (PPP) and psoriasis vulgaris (PSV), followed by hidradenitis suppurative (HS) and severe acne (Table 1).
Adults with SAPHO-CNO reported high scores, 0.8 or greater standard deviations (SD), for both PROMIS pain interference and fatigue domains compared with standardized scores for the general population (mean T-score 50, SD 10) (Table 2). For pain interference and fatigue PROMIS domains, 69.5% and 64.4% of subjects had a T-score >55 respectively. Additionally, subjects reported lower scores, ~ 0.9 SDs, for PROMIS physical function; 72.9% of subjects had a T-score < 45. Similar to PROMIS scores, legacy PROM instruments showed corollary scores in pain, fatigue and function (Table 2). Median (IQR) patient-reported global scores were 5.0 (2.5-7.5) for pain, 5.0 (2.5-8.0) for fatigue, and 4.0 (2.0-6.0) for function.
Conclusion: Adult SAPHO-CNO patients, with a median of 5 years since diagnosis, demonstrate multidimensional symptomatology with high pain and fatigue, and low function as reported by PROMIS and legacy instruments.


Disclosures: A. Lenert, None; R. Domsic, None; K. Chan, None; M. Oliver, None; J. Paul, None; C. Kremer, None; E. Leisinger, None; S. Dolovcak, None; S. Hong, None; A. Jayatilleke, None; P. Lenert, None; T. Sato, None; S. Shah, None; S. Yasin, None; Y. Zhao, None; D. Solomon, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, moderna, CorEvitas; J. Templin, None; P. Ferguson, None.

