Back
Poster Session A
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0272–0316) RA – Treatment Poster I
0279: Effect of Filgotinib on Body Weight and BMI and Effect of Baseline BMI on the Efficacy and Safety of Filgotinib in RA
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- AB
Alejandro Balsa, MD
Hospital Universitario La Paz
Madrid, Spain
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Alejandro Balsa1, Siegfried Wassenberg2, Anne Tournadre3, Hans-Dieter Orzechowski4, Katrien Van Beneden5, Vijay Rajendran6, Udo Lendl4, Pieter-Jan Stiers5, Christopher Watson7, Roberto Felice Caporali8 and Patrick Verschueren9, 1Hospital La Paz Institute for Health Research, Madrid, Spain, 2Rheumazentrum Ratingen, Ratingen, Germany, 3University Hospital of Clermont Ferrand, Rheumatology, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 4Galapagos Biopharma Deutschland GmbH, Munich, Germany, 5Galapagos NV, Mechelen, Belgium, 6Galapagos NV, Gent, Belgium, 7Galapagos Biotech Ltd, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 8University of Milan, Milano, Italy, 9University Hospital Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL) is a Janus kinase (JAK) 1 preferential inhibitor approved for the treatment (tx) of moderate to severe RA. Weight gain has been reported with other JAK inhibitors1–3; it is important to describe the effect of FIL on body weight (BW)/BMI for physicians to correctly inform and appropriately treat patients. Our primary aim was to assess the effect of FIL on BW/BMI using data from the FINCH 1–3 studies. Secondary aims were to assess the efficacy and safety of FIL according to baseline BMI.
Methods: FINCH 1–3 (NCT02889796, NCT02873936, NCT02886728) were phase 3, randomized, double-blind, active/placebo (PBO)-controlled studies of FIL 100/200 mg (FIL100/FIL200) ± MTX in patients with active RA who had an inadequate response to MTX (FINCH 1) or biologic DMARD (FINCH 2), or were MTX naïve (FINCH 3). We assessed changes from baseline (CFB) in BW and BMI by tx group and baseline BMI, and the efficacy and safety of FIL by baseline BMI (< 25, 25–< 30, or ≥30 kg/m2). Efficacy measures included ACR20/50/70 response, Disease Activity Score 28 with CRP (DAS28-CRP), and HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Safety data were from 7 RA clinical trials (FINCH 1–4, DARWIN 1–3).4
Results: In FINCH 1–3, baseline disease characteristics such as HAQ-DI, DAS28-CRP, and Clinical Disease Activity Index were similar across BMI subgroups for each tx group. There were no clinically relevant CFB in median BW or BMI in any tx group or differences between tx groups. Mean CFB in BMI (kg/m2) were 0.4 with FIL200 and FIL100, and 0.3 with adalimumab (ADA) at Week 52 in FINCH 1; 0.2, 0.6, and −0.1 with FIL200, FIL100, and PBO, respectively, at Week 24 in FINCH 2; and 0.5, 0.6, 1.1, and 0.3 with FIL200+MTX, FIL100+MTX, FIL200, and MTX, respectively, at Week 52 in FINCH 3. CFB in BMI did not appear dependent on baseline BMI.
FIL200±MTX was efficacious vs controls regardless of baseline BMI for most measures at each timepoint. In FINCH 1, in the < 25, 25–< 30, and ≥30 kg/m2 BMI subgroups, DAS28-CRP < 2.6 was achieved by 38%, 29%, and 33% in the FIL200 group; 29%, 19%, and 21% in the ADA group; and 7%, 10%, and 11% in the PBO group at Week 12, respectively. The Figure shows ACR20 responders by baseline BMI in FINCH 1–3. Integrated safety data across baseline BMI subgroups are summarized in the Table. The rate for venous thromboembolism was numerically higher with FIL200 in the ≥30 than 25–< 30 or < 25 kg/m2 BMI subgroups; serious infection rate was numerically higher with FIL100 in the < 25 mg/m2 vs other BMI subgroups.
Conclusion: FIL did not substantially affect CFB in BW or BMI. FIL200±MTX was generally more efficacious vs controls regardless of baseline BMI, and the overall rate of treatment-emergent adverse events was similar across baseline BMI subgroups.
References:
1. Tofacitinib SmPC
2. Baricitinib SmPC
3. Upadacitinib SmPC
4. Winthrop K, et al. ACR 2021. Abstract 1698
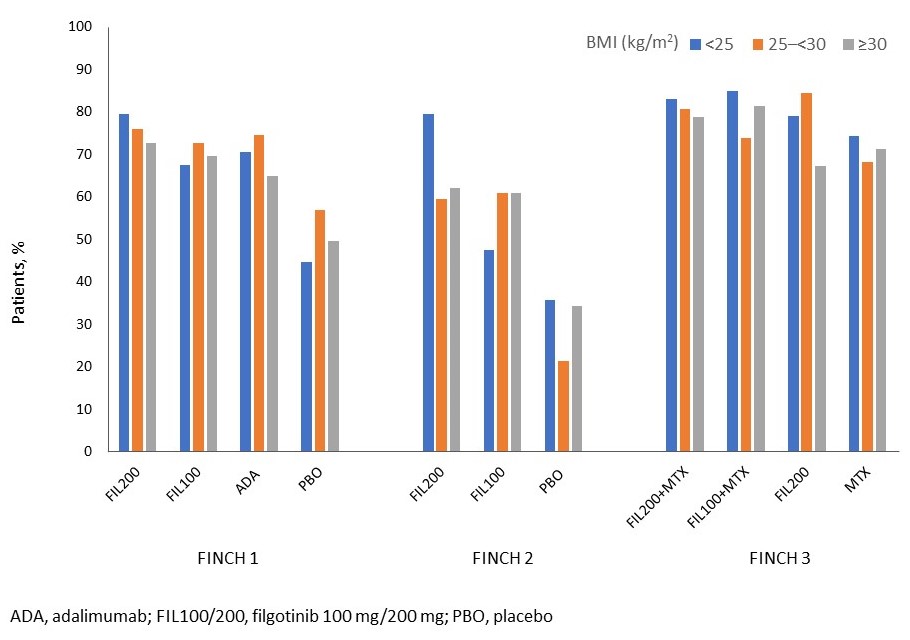 Figure. Proportion of patients to achieve ACR response at Week 12 (FINCH 1 and 2) or Week 24 (FINCH 3)
Figure. Proportion of patients to achieve ACR response at Week 12 (FINCH 1 and 2) or Week 24 (FINCH 3)
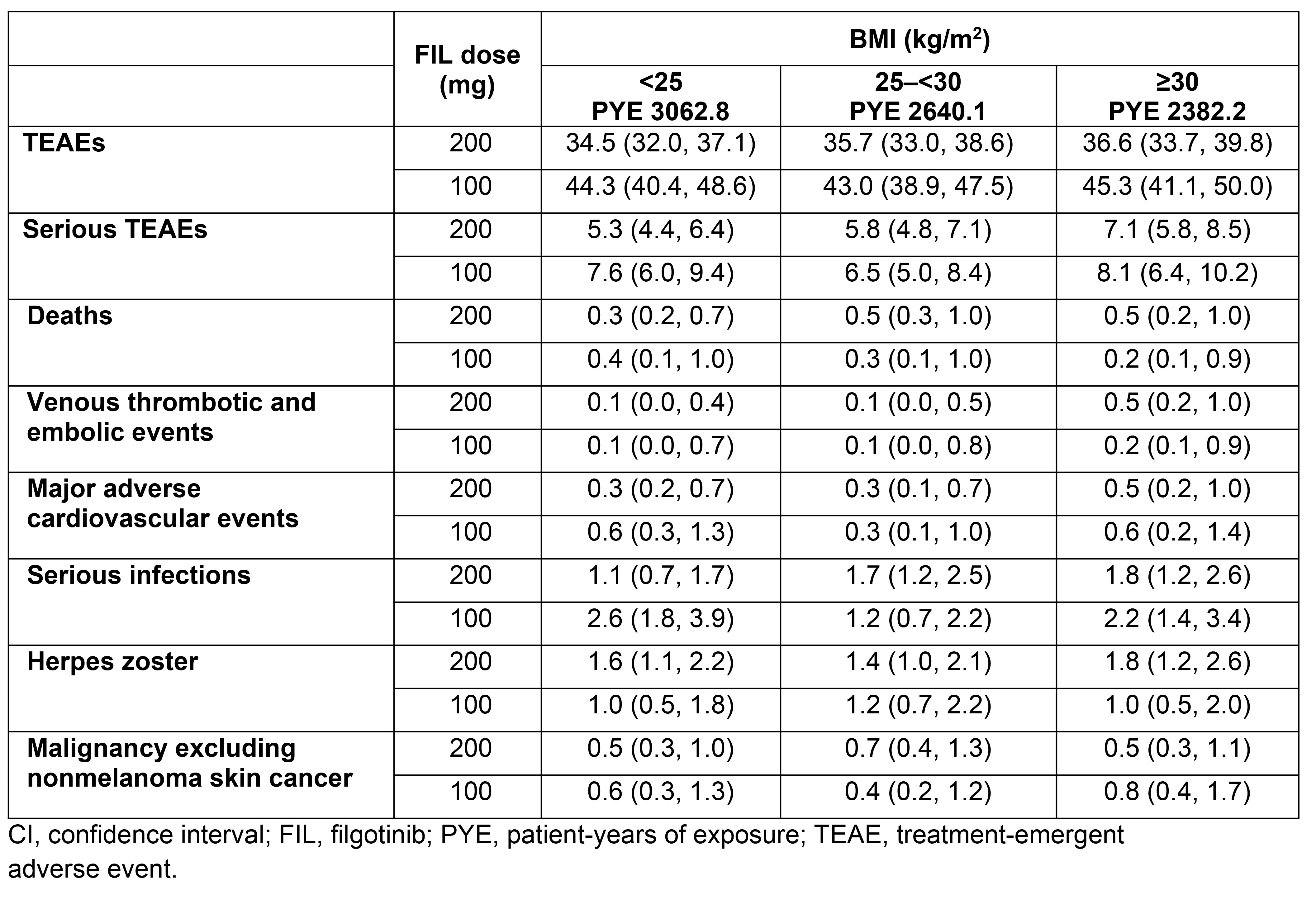 Table. Exposure-adjusted incidence rate (95% CI) of adverse events per 100 PYE by baseline BMI
Table. Exposure-adjusted incidence rate (95% CI) of adverse events per 100 PYE by baseline BMI
Disclosures: A. Balsa, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Gebro-Pharma, Novartis, Roche, UCB, Pfizer, AbbVie/Abbott, Galapagos, Gilead, Sandoz, Lilly, Nordic; S. Wassenberg, AbbVie, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, UCB, Galapagos, Gilead, Nichi-Iko, Sanofi; A. Tournadre, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Fresenius-Kabi, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB; H. Orzechowski, Galapagos; K. Van Beneden, Galapagos; V. Rajendran, Galapagos; U. Lendl, Galapagos; P. Stiers, Galapagos; C. Watson, Galapagos; R. Caporali, AbbVie, Celltrion, Fresenius-Kabi, Galapagos, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Sanofi; P. Verschueren, AbbVie, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roularta, Sidekick Health.
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL) is a Janus kinase (JAK) 1 preferential inhibitor approved for the treatment (tx) of moderate to severe RA. Weight gain has been reported with other JAK inhibitors1–3; it is important to describe the effect of FIL on body weight (BW)/BMI for physicians to correctly inform and appropriately treat patients. Our primary aim was to assess the effect of FIL on BW/BMI using data from the FINCH 1–3 studies. Secondary aims were to assess the efficacy and safety of FIL according to baseline BMI.
Methods: FINCH 1–3 (NCT02889796, NCT02873936, NCT02886728) were phase 3, randomized, double-blind, active/placebo (PBO)-controlled studies of FIL 100/200 mg (FIL100/FIL200) ± MTX in patients with active RA who had an inadequate response to MTX (FINCH 1) or biologic DMARD (FINCH 2), or were MTX naïve (FINCH 3). We assessed changes from baseline (CFB) in BW and BMI by tx group and baseline BMI, and the efficacy and safety of FIL by baseline BMI (< 25, 25–< 30, or ≥30 kg/m2). Efficacy measures included ACR20/50/70 response, Disease Activity Score 28 with CRP (DAS28-CRP), and HAQ-Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Safety data were from 7 RA clinical trials (FINCH 1–4, DARWIN 1–3).4
Results: In FINCH 1–3, baseline disease characteristics such as HAQ-DI, DAS28-CRP, and Clinical Disease Activity Index were similar across BMI subgroups for each tx group. There were no clinically relevant CFB in median BW or BMI in any tx group or differences between tx groups. Mean CFB in BMI (kg/m2) were 0.4 with FIL200 and FIL100, and 0.3 with adalimumab (ADA) at Week 52 in FINCH 1; 0.2, 0.6, and −0.1 with FIL200, FIL100, and PBO, respectively, at Week 24 in FINCH 2; and 0.5, 0.6, 1.1, and 0.3 with FIL200+MTX, FIL100+MTX, FIL200, and MTX, respectively, at Week 52 in FINCH 3. CFB in BMI did not appear dependent on baseline BMI.
FIL200±MTX was efficacious vs controls regardless of baseline BMI for most measures at each timepoint. In FINCH 1, in the < 25, 25–< 30, and ≥30 kg/m2 BMI subgroups, DAS28-CRP < 2.6 was achieved by 38%, 29%, and 33% in the FIL200 group; 29%, 19%, and 21% in the ADA group; and 7%, 10%, and 11% in the PBO group at Week 12, respectively. The Figure shows ACR20 responders by baseline BMI in FINCH 1–3. Integrated safety data across baseline BMI subgroups are summarized in the Table. The rate for venous thromboembolism was numerically higher with FIL200 in the ≥30 than 25–< 30 or < 25 kg/m2 BMI subgroups; serious infection rate was numerically higher with FIL100 in the < 25 mg/m2 vs other BMI subgroups.
Conclusion: FIL did not substantially affect CFB in BW or BMI. FIL200±MTX was generally more efficacious vs controls regardless of baseline BMI, and the overall rate of treatment-emergent adverse events was similar across baseline BMI subgroups.
References:
1. Tofacitinib SmPC
2. Baricitinib SmPC
3. Upadacitinib SmPC
4. Winthrop K, et al. ACR 2021. Abstract 1698
 Figure. Proportion of patients to achieve ACR response at Week 12 (FINCH 1 and 2) or Week 24 (FINCH 3)
Figure. Proportion of patients to achieve ACR response at Week 12 (FINCH 1 and 2) or Week 24 (FINCH 3) Table. Exposure-adjusted incidence rate (95% CI) of adverse events per 100 PYE by baseline BMI
Table. Exposure-adjusted incidence rate (95% CI) of adverse events per 100 PYE by baseline BMIDisclosures: A. Balsa, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Gebro-Pharma, Novartis, Roche, UCB, Pfizer, AbbVie/Abbott, Galapagos, Gilead, Sandoz, Lilly, Nordic; S. Wassenberg, AbbVie, Lilly, MSD, Pfizer, UCB, Galapagos, Gilead, Nichi-Iko, Sanofi; A. Tournadre, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Fresenius-Kabi, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB; H. Orzechowski, Galapagos; K. Van Beneden, Galapagos; V. Rajendran, Galapagos; U. Lendl, Galapagos; P. Stiers, Galapagos; C. Watson, Galapagos; R. Caporali, AbbVie, Celltrion, Fresenius-Kabi, Galapagos, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Sanofi; P. Verschueren, AbbVie, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Nordic Pharma, Pfizer, Roularta, Sidekick Health.

