Back
Poster Session C
Imaging
Session: (1228–1266) Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster
1230: Diabetes Mellitus Nailfold Capillaroscopy Pattern: DM Pattern
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- GM
Genessis Maldonado, MD, MACR
Loyola MacNeal Hospital
Oak Park, IL, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Genessis Maldonado1, Amala Chacko1, Diana Franco1, Lydia Robles1, Deyger Navarrete1, Madalina Ionescu1 and Zineb Aouhab2, 1Loyola MacNeal Hospital, Berwyn, IL, 2Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, IL
Background/Purpose: Recent data has shown the presence of nailfold architecture abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), the changes has been associated with uncontrolled disease. The purpose was to identify by nailfold capillaroscopy the microvascular changes in patients with T2DM.
Methods: Observational, descriptive and prospective study which included patients with T2DM. Capillaroscopy was performed with DinoLite capillaroscope in the 4th and 5th digit of the non-dominant hand. Data analysis was performed in SPSS v22.
Results: The study included 100 patients with T2DM. Female in 51% [51] and male 49% [49] with a mean age of 60.13±16.51 [22-92]. Race/ethnicity was reported as Hispanic 59% [59], white 31% [31], African American 5% [5], Asian 4% [4] and Native American 1% [1]. The mean age of diagnosis of T2DM was 16.4±14.0, HgbA1c 7.8±2.04 [4.8-14.7] which represented that 73% [73] were uncontrolled. Smoking habit was seen in 21% [21]. Comorbidities included hypertension 67% [67], hyperlipidemia 79% [79], retinopathy 21% [21] and nephropathy 18% [18].
Capillary visibility was good in 65% [65], poor 33% [33] and none 2% [2]. Architecture was altered in 64%. Decreased density was seen in 58% [58], avascular areas 50% [50], giant capillaries 40% [40], ramified capillaries 31% [31], microhemorrhages 8% [8], scleroderma pattern (SD) 9% [9], tortuous capillaries 79% [79], crosslinked 79% [79] and ectasia 64% [64]. The average of apical capillary diameter was 54.3±2.37 [31.41-70.57].
The uncontrolled group 73% [73] showed more presence of abnormalities in comparison with the controlled group 27% [27]. The architecture was altered in 74% [54], decreased density 66% [48] (p=0.001), avascular areas 58% [42] (p=0.007), ectasias 69% [50] (p=0.052), microhemorrhages 10% [7] (p=0.368), tortuous 87% [63] (p=0.075), crosslinked 81% [59] (p=0.232) and SD pattern 11% [8] (p=0.000). The changes were even more noticeable when compared to the healthy control group (Figure 1).
A control group was selected, it included 50 healthy subjects. Female in 44% [22] and male 56% [28] with a mean age of 45.16±15.5 [23-76]. Race/ethnicity was reported as Hispanic in 82% [41] and white 18% [9].
Capillary architecture was altered in 5% [10] and normal pattern in 90% [10]. Avascular areas were seen in 3% [6], ramified capillaries 16% [8], ectasia 18% [9], tortuous 70% [35], crosslinked 54% [27] and microhemorrhages 2% [1], no giant capillaries and SD pattern was seen. Average of apical diameter was 41.35±8.32 [20.31-59.72].
Conclusion: The overall architecture was altered in 64%, the capillaroscopy diabetes mellitus pattern included reduced density, tortuous, crosslinked and ramified capillaries (Figure 2). The changes were higher in the uncontrolled group. These findings are similar to changes seen in patients with rheumatologic diseases, further studies are needed to compare those two groups in the future.
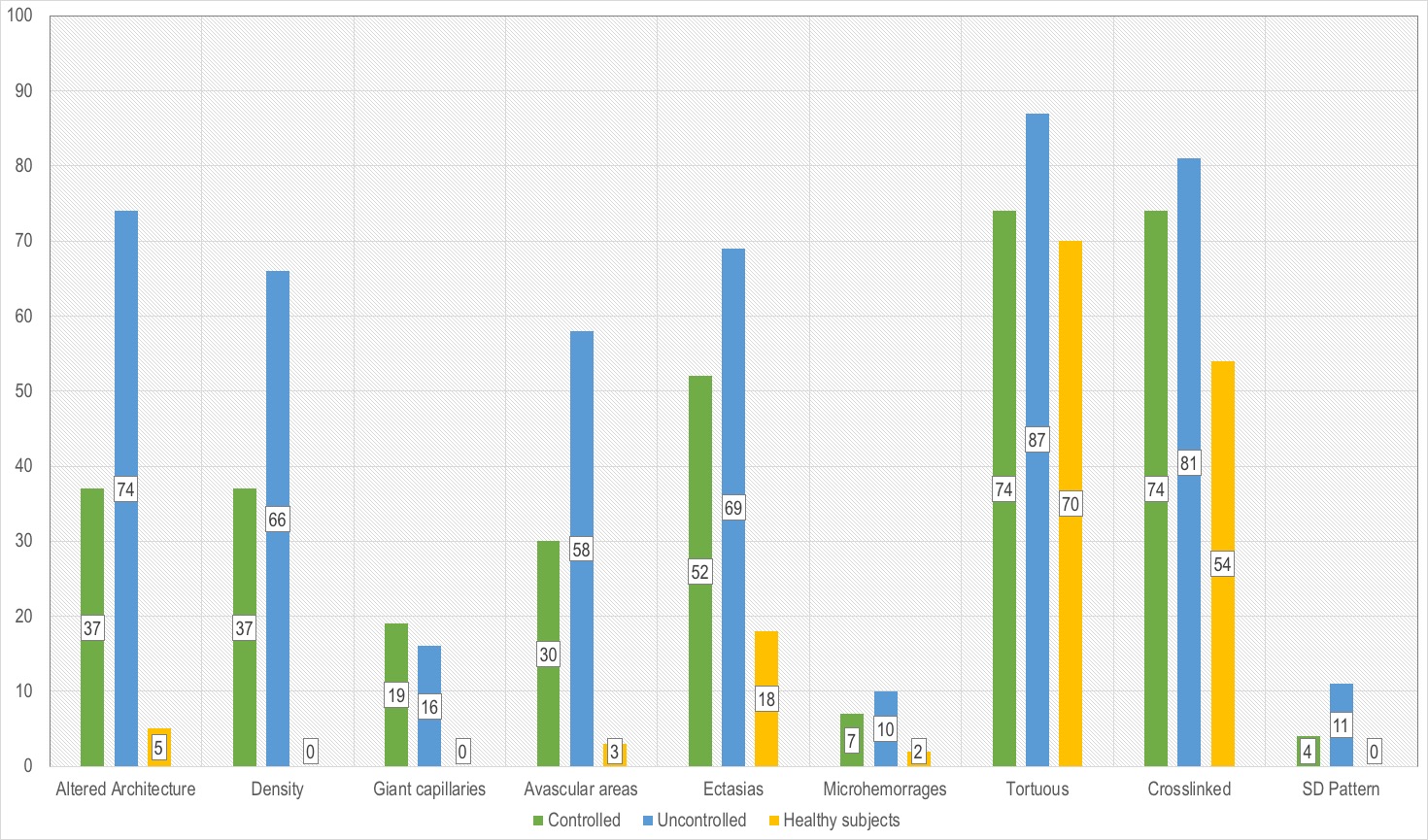 Capillaroscopy abnormalities among groups
Capillaroscopy abnormalities among groups
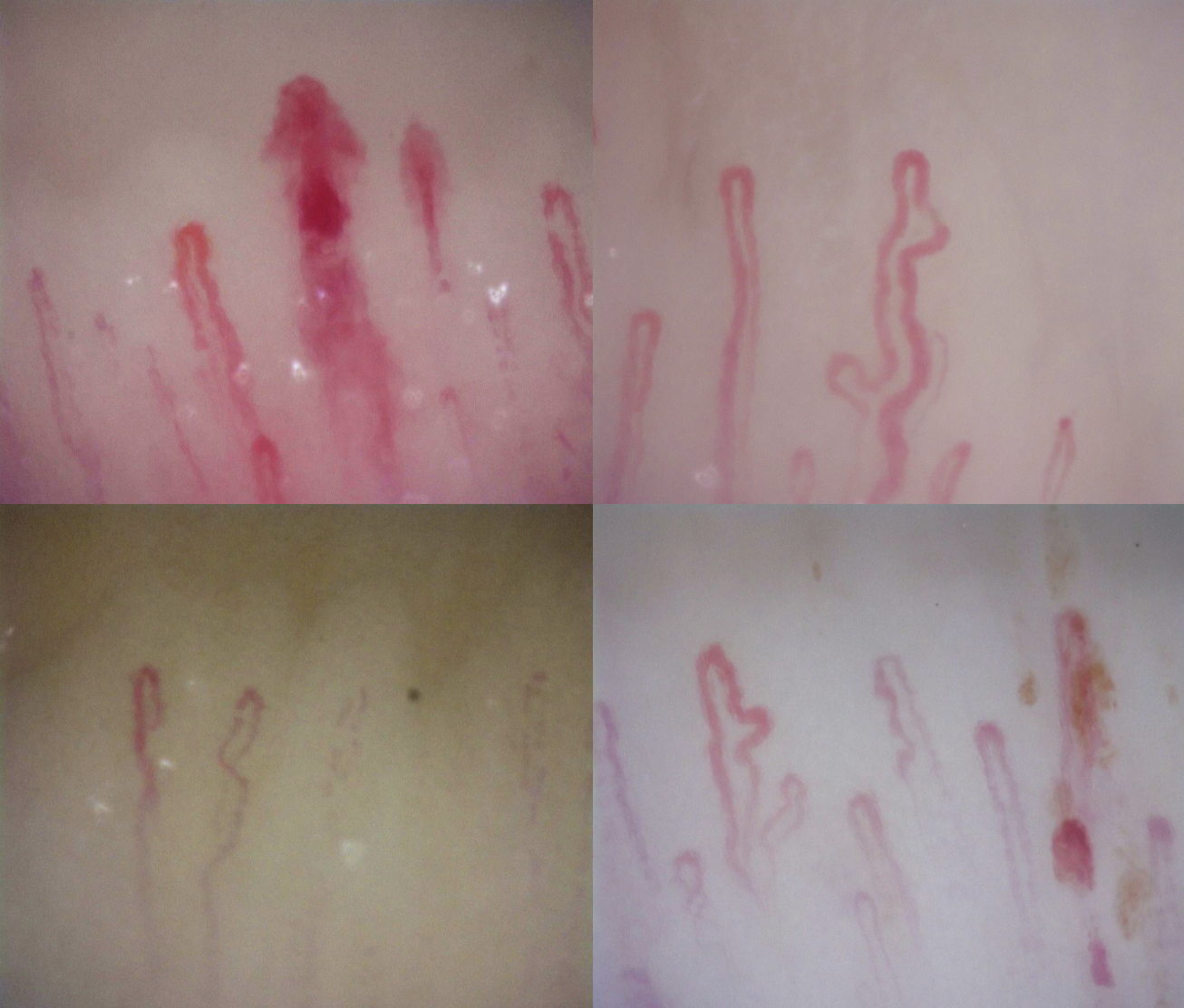 Diabetes Mellitus pattern: decreased density, tortuous capillaries, enlarged capillaries, micro-hemorrhages and avascular areas.
Diabetes Mellitus pattern: decreased density, tortuous capillaries, enlarged capillaries, micro-hemorrhages and avascular areas.
Disclosures: G. Maldonado, None; A. Chacko, None; D. Franco, None; L. Robles, None; D. Navarrete, None; M. Ionescu, None; Z. Aouhab, None.
Background/Purpose: Recent data has shown the presence of nailfold architecture abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), the changes has been associated with uncontrolled disease. The purpose was to identify by nailfold capillaroscopy the microvascular changes in patients with T2DM.
Methods: Observational, descriptive and prospective study which included patients with T2DM. Capillaroscopy was performed with DinoLite capillaroscope in the 4th and 5th digit of the non-dominant hand. Data analysis was performed in SPSS v22.
Results: The study included 100 patients with T2DM. Female in 51% [51] and male 49% [49] with a mean age of 60.13±16.51 [22-92]. Race/ethnicity was reported as Hispanic 59% [59], white 31% [31], African American 5% [5], Asian 4% [4] and Native American 1% [1]. The mean age of diagnosis of T2DM was 16.4±14.0, HgbA1c 7.8±2.04 [4.8-14.7] which represented that 73% [73] were uncontrolled. Smoking habit was seen in 21% [21]. Comorbidities included hypertension 67% [67], hyperlipidemia 79% [79], retinopathy 21% [21] and nephropathy 18% [18].
Capillary visibility was good in 65% [65], poor 33% [33] and none 2% [2]. Architecture was altered in 64%. Decreased density was seen in 58% [58], avascular areas 50% [50], giant capillaries 40% [40], ramified capillaries 31% [31], microhemorrhages 8% [8], scleroderma pattern (SD) 9% [9], tortuous capillaries 79% [79], crosslinked 79% [79] and ectasia 64% [64]. The average of apical capillary diameter was 54.3±2.37 [31.41-70.57].
The uncontrolled group 73% [73] showed more presence of abnormalities in comparison with the controlled group 27% [27]. The architecture was altered in 74% [54], decreased density 66% [48] (p=0.001), avascular areas 58% [42] (p=0.007), ectasias 69% [50] (p=0.052), microhemorrhages 10% [7] (p=0.368), tortuous 87% [63] (p=0.075), crosslinked 81% [59] (p=0.232) and SD pattern 11% [8] (p=0.000). The changes were even more noticeable when compared to the healthy control group (Figure 1).
A control group was selected, it included 50 healthy subjects. Female in 44% [22] and male 56% [28] with a mean age of 45.16±15.5 [23-76]. Race/ethnicity was reported as Hispanic in 82% [41] and white 18% [9].
Capillary architecture was altered in 5% [10] and normal pattern in 90% [10]. Avascular areas were seen in 3% [6], ramified capillaries 16% [8], ectasia 18% [9], tortuous 70% [35], crosslinked 54% [27] and microhemorrhages 2% [1], no giant capillaries and SD pattern was seen. Average of apical diameter was 41.35±8.32 [20.31-59.72].
Conclusion: The overall architecture was altered in 64%, the capillaroscopy diabetes mellitus pattern included reduced density, tortuous, crosslinked and ramified capillaries (Figure 2). The changes were higher in the uncontrolled group. These findings are similar to changes seen in patients with rheumatologic diseases, further studies are needed to compare those two groups in the future.
 Capillaroscopy abnormalities among groups
Capillaroscopy abnormalities among groups Diabetes Mellitus pattern: decreased density, tortuous capillaries, enlarged capillaries, micro-hemorrhages and avascular areas.
Diabetes Mellitus pattern: decreased density, tortuous capillaries, enlarged capillaries, micro-hemorrhages and avascular areas.Disclosures: G. Maldonado, None; A. Chacko, None; D. Franco, None; L. Robles, None; D. Navarrete, None; M. Ionescu, None; Z. Aouhab, None.

