Back
Poster Session C
Genetics, genomics and proteomics
Session: (1118–1149) Genetics, Genomics and Proteomics Poster
1123: Excess of Rare Deleterious Variants Within JAK-STAT Pathway - Related Genes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- PJ
Pierre-Antoine Juge, MD, PhD
Rheumatology department, Bichat Hospital
Paris, France
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Pierre-Antoine Juge1, Steven Gazal2, Raphaël Borie3, Lidwine Wemeau4, Marie-Pierre Debray5, Sebastien Ottaviani6, Sylvain Marchand Adam7, Christophe Richez8, Hilario Nunes9, Pascal Richette10, Caroline Kannengiesser11, Jérome Avouac12, Jean Sibilia13, René-Marc Flipo14, Vincent Cottin15, Thierry Schaeverbeke16, Martin Soubrier17, Nathalie Saidenberg-Kermanac’h18, Dominique Valeyre19, Catherine Boileau11, Bruno Crestani20 and Philippe Dieude21, 1Rheumatology department, Bichat Hospital, Paris, France, 2University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, 3Pulmonology department, Bichat Hospital, Paris, France, 4Pulmonology department, Lille University hospital, Lille, France, 5Radiology department, Hôpital Bichat, Paris, France, 6Hopital Bichat-Claude Bernard, Paris, France, 7Pulmonology department, Tours University Hospital, Tours, France, 8Université de Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France, 9Pulmonology department, Hopital Avicenne, Bobigny, France, 10Department of Rheumatology, Hôpital Lariboisière, Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris, Paris, France, 11Genetic Department, Bichat hospital, Paris, France, 12Rheumatology Department, Cochin hospital, Paris, France, 13University Hospital of Strasbourg, Strasbourg, France, 14Hôpital Roger Salengro, Lille, France, 15Coordinating Reference Center for Rare Pulmonary Diseases, Louis Pradel Hospital, University of Lyon, INRAE, Lyon, France, 16FHU ACRONIM, University Hospital of Bordeaux, University of Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France, 17Gabriel-Montpied Hospital, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 18Rheumatology Department, Avicenne Hospital, Bobigny, France, 19Pulmonology department, Avicenne Hospital, Bobigny, France, 20Hopital Bichat, Paris University, Paris, France, 21Université Paris Cité, Paris, France
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with RA. To date, there are no specific treatments available for patients with RA-ILD. Several arguments suggest a potential role of the JAK-STAT signaling transduction pathway in the RA-ILD physiopathogenesis. Our objective was to test for association JAK-STAT pathway related genes rare coding variants with ILD in patients with RA.
Methods: In this candidate case-control genetic association study, RA-ILD patients were compared to RA-noILD patients. All cases fulfilled the 2010 EULAR-ACR and/or 1987 ACR revised criteria for RA. The ILD status was established by chest HRCT that were centrally reviewed by an experienced reader. Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed, followed by a restricted analysis in JAK-STAT pathway candidate genes extracted from the Gene Ontology database. Two JAK-STAT related genes lists were generated, the first included 110 genes and a second restricted to 9 genes (STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5, TYK2, JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3) for sensitivity analyses. Analyses were restricted to rare variants predicted to be deleterious: 1) variants with a minor allele frequency < 0.1% in non-Finnish Europeans of gnomAD, 2) variants predicted to have a high impact in the protein or to change protein effectiveness, 3) variants with a CADD score ≥ 15. Burden tests were performed using a logistic regression in 163 RA-ILD vs. 232 RA-noILD.
Results: 163 patients with RAILD and 235 with RA-noILD were included in the study. Briefly, RA-ILD patients were more frequently men (81.7% vs. 55.8%), elder at RA onset (64.3 ± 10.9 y/o vs. 44.1 ± 12.7 y/o) and more frequently smokers (60.0% vs. 48.4%). Restricted analysis on the 110 JAK-STAT candidates genes revealed an excess of rare variants in patients with RA-ILD when compared to patients with RA-noILD: 57.06% vs. 46.12%; OR=1.37 95% CI [1.12-1.69], P=2.56x10-3 (Table1, Figure1). The sensitive analyze restricted to STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5, TYK2, JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 found significant excess of rare variants in patients with RA-ILD: OR=1.88 95% CI [1.06-3.57], P=0.04 (Table1, Figure1).
Conclusion: This discovery step study found an excess of rare variants predicted to be deleterious within JAK-STAT pathway related genes in patients with RA-ILD compared to patients with RA-noILD. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT pathway could play a physiopathogenic role in the occurrence of RA-ILD.
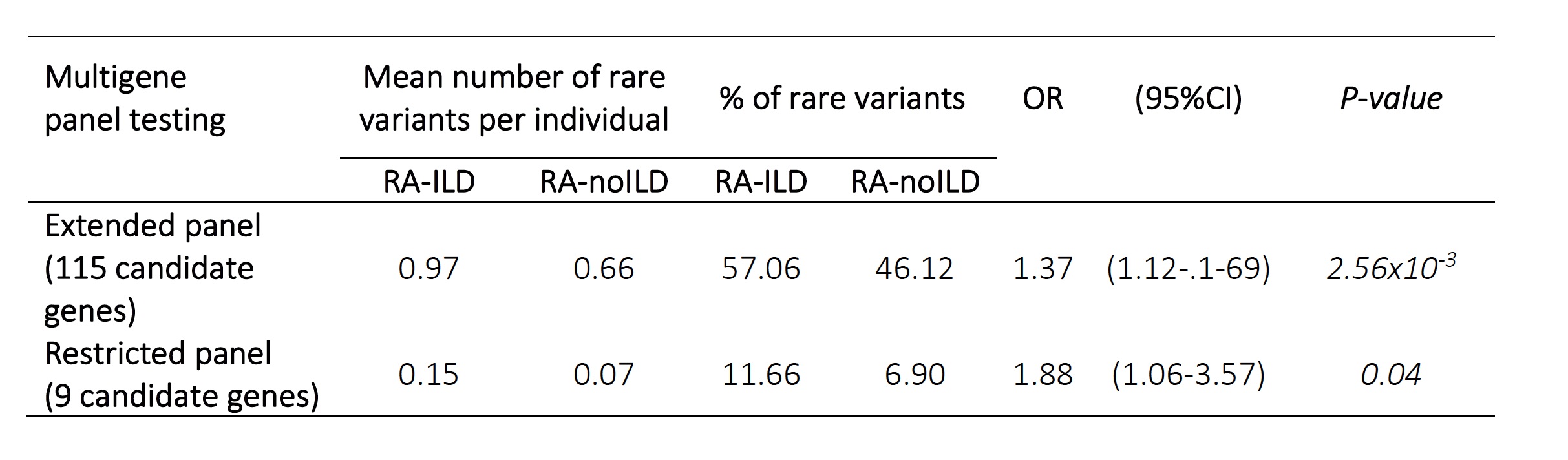 Table 1
Table 1
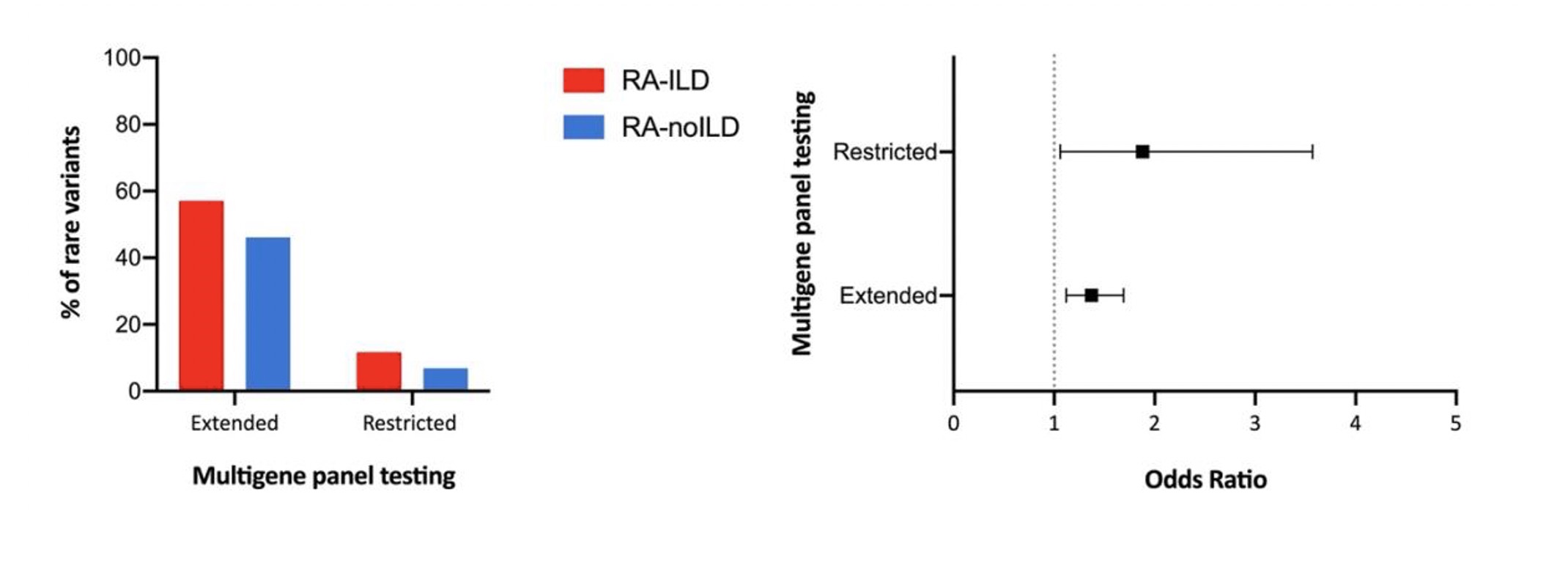 Figure 1
Figure 1
Disclosures: P. Juge, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Novartis, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim; S. Gazal, None; R. Borie, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim; L. Wemeau, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Roche, Sanofi, Pfizer; M. Debray, None; S. Ottaviani, None; S. Marchand Adam, None; C. Richez, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Galapados, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer; H. Nunes, None; P. Richette, AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, UCB; C. Kannengiesser, None; J. Avouac, None; J. Sibilia, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Roche, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, UCB, Novartis; R. Flipo, AbbVie/Abbott, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Mylan, Nordic Pharma France, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche-Chugaï, Sandoz, Sanofi, UCB; V. Cottin, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Shionogi, RedX, PureTech, Celgene/BMS, AstraZeneca, XSL Behring, Sanofi, United Therapeutics, Pliant, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Galapagos, Celgene/BMS, CSL Behring, Galecto, Fibrogen; T. Schaeverbeke, None; M. Soubrier, None; N. Saidenberg-Kermanac’h, None; D. Valeyre, None; C. Boileau, None; B. Crestani, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim; P. Dieude, None.
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with RA. To date, there are no specific treatments available for patients with RA-ILD. Several arguments suggest a potential role of the JAK-STAT signaling transduction pathway in the RA-ILD physiopathogenesis. Our objective was to test for association JAK-STAT pathway related genes rare coding variants with ILD in patients with RA.
Methods: In this candidate case-control genetic association study, RA-ILD patients were compared to RA-noILD patients. All cases fulfilled the 2010 EULAR-ACR and/or 1987 ACR revised criteria for RA. The ILD status was established by chest HRCT that were centrally reviewed by an experienced reader. Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed, followed by a restricted analysis in JAK-STAT pathway candidate genes extracted from the Gene Ontology database. Two JAK-STAT related genes lists were generated, the first included 110 genes and a second restricted to 9 genes (STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5, TYK2, JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3) for sensitivity analyses. Analyses were restricted to rare variants predicted to be deleterious: 1) variants with a minor allele frequency < 0.1% in non-Finnish Europeans of gnomAD, 2) variants predicted to have a high impact in the protein or to change protein effectiveness, 3) variants with a CADD score ≥ 15. Burden tests were performed using a logistic regression in 163 RA-ILD vs. 232 RA-noILD.
Results: 163 patients with RAILD and 235 with RA-noILD were included in the study. Briefly, RA-ILD patients were more frequently men (81.7% vs. 55.8%), elder at RA onset (64.3 ± 10.9 y/o vs. 44.1 ± 12.7 y/o) and more frequently smokers (60.0% vs. 48.4%). Restricted analysis on the 110 JAK-STAT candidates genes revealed an excess of rare variants in patients with RA-ILD when compared to patients with RA-noILD: 57.06% vs. 46.12%; OR=1.37 95% CI [1.12-1.69], P=2.56x10-3 (Table1, Figure1). The sensitive analyze restricted to STAT1, STAT2, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5, TYK2, JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 found significant excess of rare variants in patients with RA-ILD: OR=1.88 95% CI [1.06-3.57], P=0.04 (Table1, Figure1).
Conclusion: This discovery step study found an excess of rare variants predicted to be deleterious within JAK-STAT pathway related genes in patients with RA-ILD compared to patients with RA-noILD. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT pathway could play a physiopathogenic role in the occurrence of RA-ILD.
 Table 1
Table 1 Figure 1
Figure 1Disclosures: P. Juge, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Novartis, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim; S. Gazal, None; R. Borie, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim; L. Wemeau, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Roche, Sanofi, Pfizer; M. Debray, None; S. Ottaviani, None; S. Marchand Adam, None; C. Richez, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Galapados, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer; H. Nunes, None; P. Richette, AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, UCB; C. Kannengiesser, None; J. Avouac, None; J. Sibilia, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Roche, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, UCB, Novartis; R. Flipo, AbbVie/Abbott, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Mylan, Nordic Pharma France, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche-Chugaï, Sandoz, Sanofi, UCB; V. Cottin, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Shionogi, RedX, PureTech, Celgene/BMS, AstraZeneca, XSL Behring, Sanofi, United Therapeutics, Pliant, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Galapagos, Celgene/BMS, CSL Behring, Galecto, Fibrogen; T. Schaeverbeke, None; M. Soubrier, None; N. Saidenberg-Kermanac’h, None; D. Valeyre, None; C. Boileau, None; B. Crestani, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim; P. Dieude, None.

