Back
Poster Session C
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (1150–1165) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Basic Science Poster
1163: Proteomic Investigation to Identify Urinary Biomarker for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- JL
Jihyun Lee, MS, BS
keimyung university
Dalseo-gu, Daegu, South Korea
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Ji-Hyun Lee1, Jeesoo Kim2, Sang-Hyon kim1, Jong‑Seo kim2 and Chang-Nam son1, 1Keimyung University, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 2seoul national university, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease that affects the spine and peripheral joints, and the exact etiology is still unknown. Diagnosis with urinary sample is a fascinate approach without patient's pain due to its non-invasive nature. In this study, we performed proteomic analysis of AS urinary samples. Our aim is to discover novel diagnostic urinary biomarkers in the AS.
Methods: A total of 50 urine samples from 20 AS and each 10 controls [rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gout, healthy control (HC)] were collected. We collected AS and HC samples only from young males (< 50 years of age). Label-free quantitative proteomics were preformed and the resulting datasets were analyzed by MaxQuant (Ver.1.6.2.3) with Uniprot human database. Differentially expressed proteins were determined based on the fold change and p-value from LFQ(label-free quantitation) intensities log2(fold change >=1.5) and p-value< 0.05.
Results: From all urinary samples analyzed by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), we identified 1,975 proteins. Among them, we first found six proteins were differentially upregulated in AS patient group compared to the control group: cystatin-A(CSTA), collagen alpha-1 chain (COL14A1), alpha-amylase 1A(AMY1A), syndecan-1(SDC1), S100-A6(S100A6) and phosphoinositide-3-kinase-interacting protein 1(PIK3IP1) (Table 1). Interestingly, some of these proteins were previously observed as urinary biomarkers in other disease. For example, alpha-amylase 1A was highly expressed in the urine of prostate cancer, S100-A6 in the urine of upper gastrointestinal cancer, and PIK3IP1 in the urine of exertional rhabdomyolysis.
Conclusion: Diagnosing AS based on non-invasive manner still remains a challenge. We performed quantitative proteomic profiling of the respective urine samples from 4 diseases, i.e., AS, RA, gout and HC, and thereby identified six potential urinary biomarkers for AS. We will conduct molecular biological validation studies.
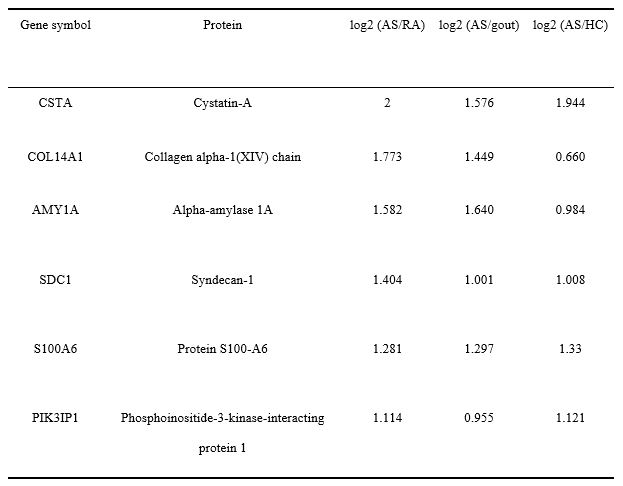 Table 1. List of proteins with increased levels in the Urine of ankylosing spondylitis patients vs other control groups.
Table 1. List of proteins with increased levels in the Urine of ankylosing spondylitis patients vs other control groups.
Disclosures: J. Lee, None; J. Kim, None; S. kim, None; J. kim, None; C. son, None.
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease that affects the spine and peripheral joints, and the exact etiology is still unknown. Diagnosis with urinary sample is a fascinate approach without patient's pain due to its non-invasive nature. In this study, we performed proteomic analysis of AS urinary samples. Our aim is to discover novel diagnostic urinary biomarkers in the AS.
Methods: A total of 50 urine samples from 20 AS and each 10 controls [rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gout, healthy control (HC)] were collected. We collected AS and HC samples only from young males (< 50 years of age). Label-free quantitative proteomics were preformed and the resulting datasets were analyzed by MaxQuant (Ver.1.6.2.3) with Uniprot human database. Differentially expressed proteins were determined based on the fold change and p-value from LFQ(label-free quantitation) intensities log2(fold change >=1.5) and p-value< 0.05.
Results: From all urinary samples analyzed by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), we identified 1,975 proteins. Among them, we first found six proteins were differentially upregulated in AS patient group compared to the control group: cystatin-A(CSTA), collagen alpha-1 chain (COL14A1), alpha-amylase 1A(AMY1A), syndecan-1(SDC1), S100-A6(S100A6) and phosphoinositide-3-kinase-interacting protein 1(PIK3IP1) (Table 1). Interestingly, some of these proteins were previously observed as urinary biomarkers in other disease. For example, alpha-amylase 1A was highly expressed in the urine of prostate cancer, S100-A6 in the urine of upper gastrointestinal cancer, and PIK3IP1 in the urine of exertional rhabdomyolysis.
Conclusion: Diagnosing AS based on non-invasive manner still remains a challenge. We performed quantitative proteomic profiling of the respective urine samples from 4 diseases, i.e., AS, RA, gout and HC, and thereby identified six potential urinary biomarkers for AS. We will conduct molecular biological validation studies.
 Table 1. List of proteins with increased levels in the Urine of ankylosing spondylitis patients vs other control groups.
Table 1. List of proteins with increased levels in the Urine of ankylosing spondylitis patients vs other control groups.Disclosures: J. Lee, None; J. Kim, None; S. kim, None; J. kim, None; C. son, None.

