Back
Poster Session A
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Session: (0343–0371) SLE – Treatment Poster I
0358: Long-term Safety and Efficacy of Voclosporin in Hispanic and Latino Patients with Lupus Nephritis
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- VB
Vanessa Birardi, PharmD
Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc
Rockville, MD, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Ellen M. Ginzler1, Amit Saxena2, Victoria Bal3, Vanessa Birardi4 and Henry Leher4, 1SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University, Department of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY, 2NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY, 3Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Victoria, BC, Canada, 4Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc, Rockville, MD
Background/Purpose: The AURORA 1 study demonstrated that addition of voclosporin to MMF and low-dose steroids significantly increased complete renal response rates at 52 weeks, with efficacy maintained for an additional 24 months in patients with lupus nephritis (LN) who continued treatment in the AURORA 2 continuation study.
Due to the differences in treatment response across ethnicities observed with other LN therapies, we performed a post-hoc analysis to investigate the safety and efficacy of voclosporin in Hispanic and Latino patients using 3 years of pooled data from the Phase 3 AURORA 1 and AURORA 2 studies.
Methods: Key inclusion criteria for AURORA 1 included biopsy-proven LN, proteinuria ≥1.5 mg/mg (≥2 mg/mg for Class V) and eGFR >45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients completing AURORA 1 who were eligible to enter AURORA 2 continued on the same blinded therapy (voclosporin or placebo in combination with MMF and low-dose steroids). Voclosporin was compared to control in the overall AURORA 2 study population as well as patients identifying as Hispanic or Latino. Hazard ratios (HR) were calculated for times to UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg and UPCR reduction ≥50% from baseline. Safety outcomes were also assessed.
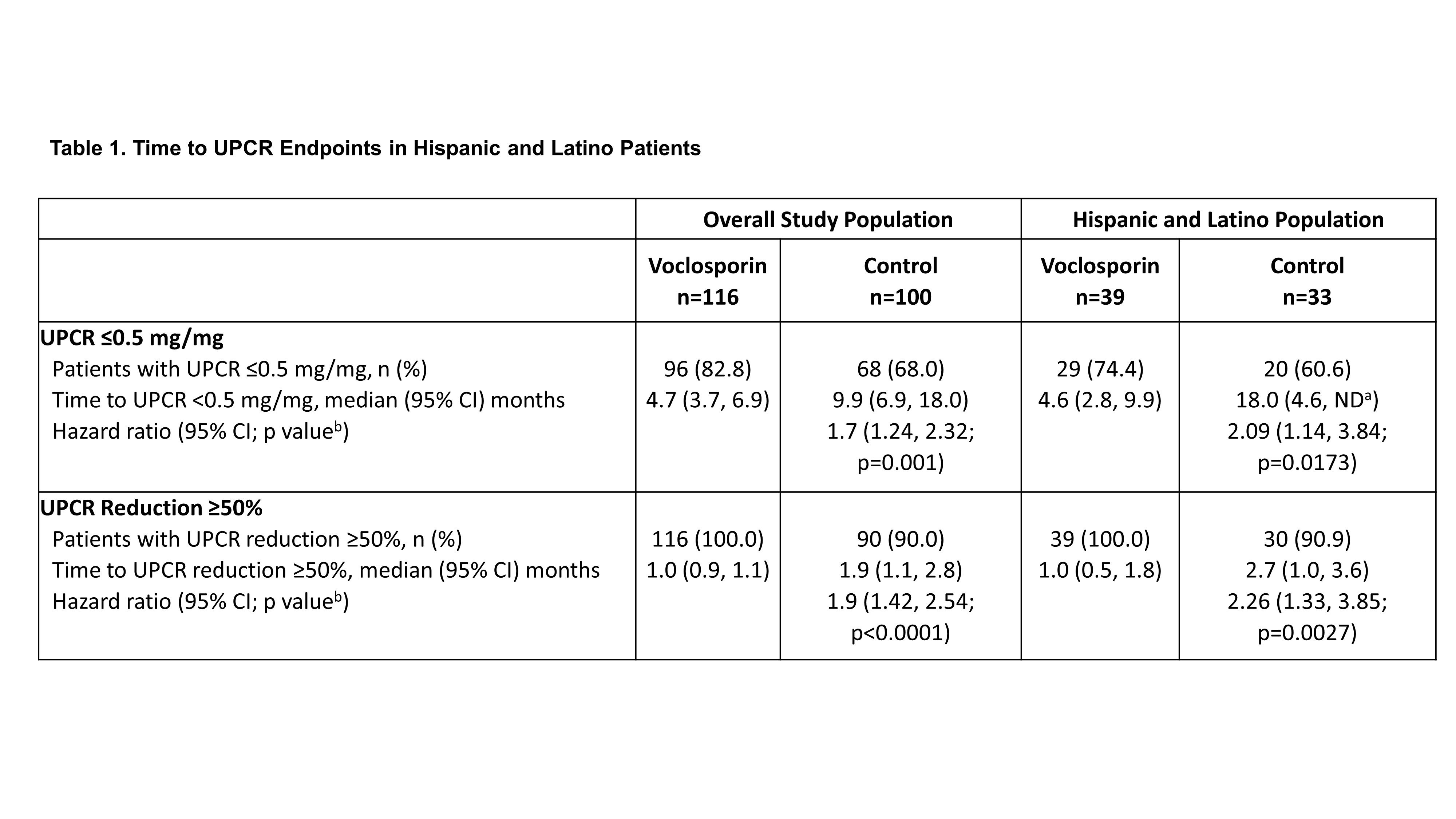
Results: A total of 116 and 100 patients in the voclosporin and control arms, respectively, continued in AURORA 2. Of the 39 and 33 patients in each arm, respectively, who identified as Hispanic or Latino, 29 (74.4%) and 20 (60.6%) achieved a UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg during the 3-year study period (Table 1). As was observed in the overall study population, voclosporin-treated Hispanic and Latino patients achieved this endpoint significantly faster than control-treated patients, with a median time to event of 4.6 and 18.0 months, respectively (HR 2.09, p=0.0173). A ≥50% reduction in UPCR was achieved by all Hispanic and Latino patients treated with voclosporin and 30 (90.9%) control-treated patients; consistent with the overall study population, treatment with voclosporin led to a significantly shorter median time to this endpoint in Hispanic and Latino patients (1.0 vs 2.7 months, HR 2.26, p=0.0027). Differences between treatment arms for both UPCR endpoints were sustained at 3 years. Adverse event rates were comparable between arms (Table 2); mean levels of serum creatinine and eGFR were similar in both arms and stable over the 3-year period (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Patients treated up to 3 years with voclosporin achieved meaningful and sustained reductions in UPCR and achieved those reductions significantly faster than patients treated with MMF and steroids alone. The findings of this analysis of Hispanic and Latino patients are consistent with the long-term safety and efficacy of voclosporin observed in the overall study population.
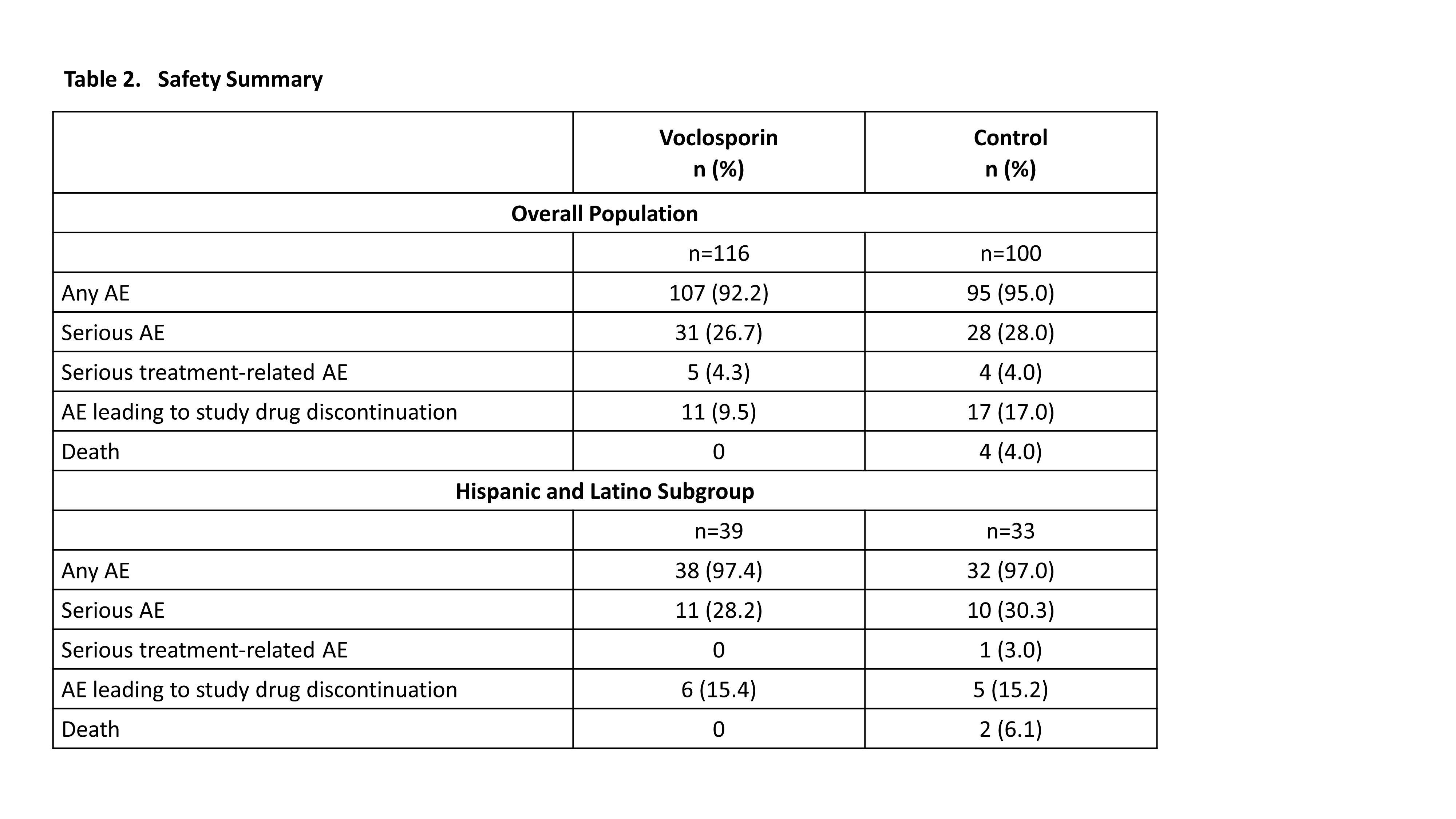 Analysis includes events starting on or after the first dose of study drug in AURORA 1 up to 30 days after the last dose in AURORA 2 and all events of death reported during study follow-up.
Analysis includes events starting on or after the first dose of study drug in AURORA 1 up to 30 days after the last dose in AURORA 2 and all events of death reported during study follow-up.
AE, adverse event.
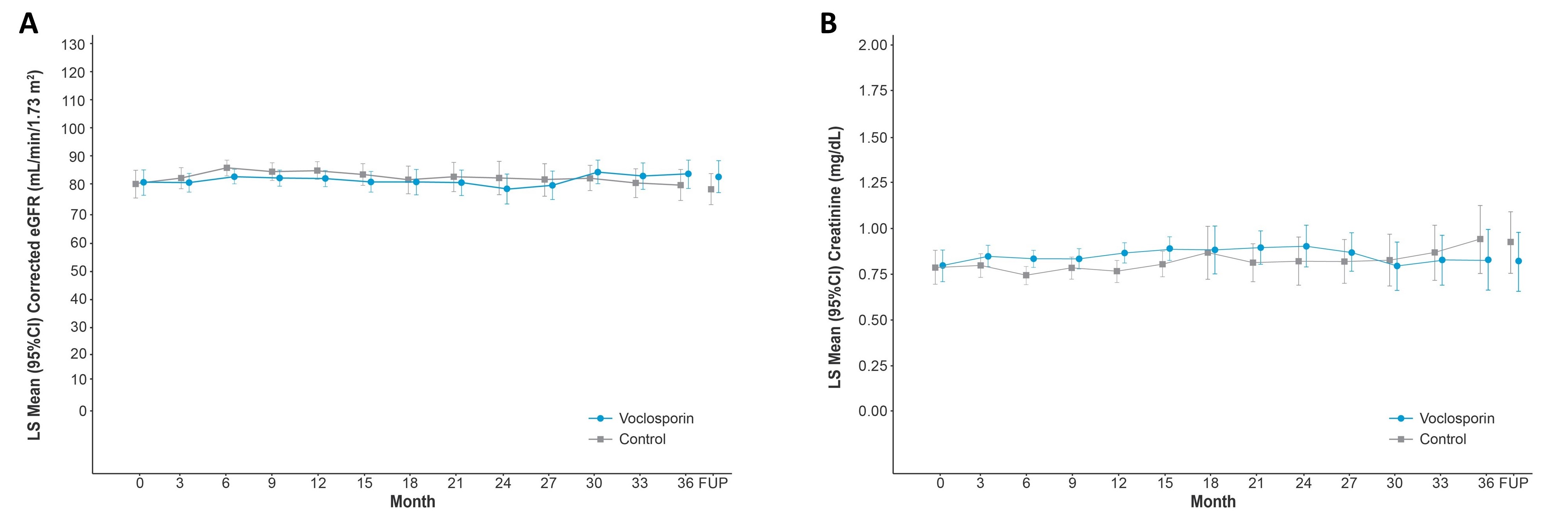 Post-hoc analysis of AURORA 2 patients for mean corrected eGFR and serum creatinine includes pooled data from AURORA 1 and AURORA 2. Renal function was assessed with corrected eGFR (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation) using a prespecified ceiling of 90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Analysis of LS mean corrected eGFR and mean serum creatinine over time includes data from a follow up visit occurring four weeks after study drug discontinuation. CI, confidence interval; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FUP, follow-up; LS, least squares.
Post-hoc analysis of AURORA 2 patients for mean corrected eGFR and serum creatinine includes pooled data from AURORA 1 and AURORA 2. Renal function was assessed with corrected eGFR (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation) using a prespecified ceiling of 90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Analysis of LS mean corrected eGFR and mean serum creatinine over time includes data from a follow up visit occurring four weeks after study drug discontinuation. CI, confidence interval; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FUP, follow-up; LS, least squares.
Disclosures: E. Ginzler, Aurinia Pharma; A. Saxena, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Kezar Life Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS); V. Bal, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc.; V. Birardi, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals; H. Leher, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Background/Purpose: The AURORA 1 study demonstrated that addition of voclosporin to MMF and low-dose steroids significantly increased complete renal response rates at 52 weeks, with efficacy maintained for an additional 24 months in patients with lupus nephritis (LN) who continued treatment in the AURORA 2 continuation study.
Due to the differences in treatment response across ethnicities observed with other LN therapies, we performed a post-hoc analysis to investigate the safety and efficacy of voclosporin in Hispanic and Latino patients using 3 years of pooled data from the Phase 3 AURORA 1 and AURORA 2 studies.
Methods: Key inclusion criteria for AURORA 1 included biopsy-proven LN, proteinuria ≥1.5 mg/mg (≥2 mg/mg for Class V) and eGFR >45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Patients completing AURORA 1 who were eligible to enter AURORA 2 continued on the same blinded therapy (voclosporin or placebo in combination with MMF and low-dose steroids). Voclosporin was compared to control in the overall AURORA 2 study population as well as patients identifying as Hispanic or Latino. Hazard ratios (HR) were calculated for times to UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg and UPCR reduction ≥50% from baseline. Safety outcomes were also assessed.
Results: A total of 116 and 100 patients in the voclosporin and control arms, respectively, continued in AURORA 2. Of the 39 and 33 patients in each arm, respectively, who identified as Hispanic or Latino, 29 (74.4%) and 20 (60.6%) achieved a UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg during the 3-year study period (Table 1). As was observed in the overall study population, voclosporin-treated Hispanic and Latino patients achieved this endpoint significantly faster than control-treated patients, with a median time to event of 4.6 and 18.0 months, respectively (HR 2.09, p=0.0173). A ≥50% reduction in UPCR was achieved by all Hispanic and Latino patients treated with voclosporin and 30 (90.9%) control-treated patients; consistent with the overall study population, treatment with voclosporin led to a significantly shorter median time to this endpoint in Hispanic and Latino patients (1.0 vs 2.7 months, HR 2.26, p=0.0027). Differences between treatment arms for both UPCR endpoints were sustained at 3 years. Adverse event rates were comparable between arms (Table 2); mean levels of serum creatinine and eGFR were similar in both arms and stable over the 3-year period (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Patients treated up to 3 years with voclosporin achieved meaningful and sustained reductions in UPCR and achieved those reductions significantly faster than patients treated with MMF and steroids alone. The findings of this analysis of Hispanic and Latino patients are consistent with the long-term safety and efficacy of voclosporin observed in the overall study population.

Post-hoc analysis of AURORA 2 patients for time to UPCR endpoints includes data from AURORA 1 and AURORA 2. Events that occurred at any point during the three-year study period were included in the analysis. Hazard ratios >1 indicate events occurring earlier in the voclosporin arm compared to control. Median time-to-event (CI) calculated using Kaplan Meier methods.
aValues not determinable due to either the endpoint not being met by 50% of the cohort within the study period or limited additional patients achieving the endpoint after the median timepoint but before the end of the study.
bp-value vs control.
CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; ND, not determinable; UPCR, urine protein creatinine ratio.
aValues not determinable due to either the endpoint not being met by 50% of the cohort within the study period or limited additional patients achieving the endpoint after the median timepoint but before the end of the study.
bp-value vs control.
CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; ND, not determinable; UPCR, urine protein creatinine ratio.
 Analysis includes events starting on or after the first dose of study drug in AURORA 1 up to 30 days after the last dose in AURORA 2 and all events of death reported during study follow-up.
Analysis includes events starting on or after the first dose of study drug in AURORA 1 up to 30 days after the last dose in AURORA 2 and all events of death reported during study follow-up. AE, adverse event.
 Post-hoc analysis of AURORA 2 patients for mean corrected eGFR and serum creatinine includes pooled data from AURORA 1 and AURORA 2. Renal function was assessed with corrected eGFR (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation) using a prespecified ceiling of 90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Analysis of LS mean corrected eGFR and mean serum creatinine over time includes data from a follow up visit occurring four weeks after study drug discontinuation. CI, confidence interval; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FUP, follow-up; LS, least squares.
Post-hoc analysis of AURORA 2 patients for mean corrected eGFR and serum creatinine includes pooled data from AURORA 1 and AURORA 2. Renal function was assessed with corrected eGFR (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation) using a prespecified ceiling of 90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Analysis of LS mean corrected eGFR and mean serum creatinine over time includes data from a follow up visit occurring four weeks after study drug discontinuation. CI, confidence interval; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; FUP, follow-up; LS, least squares.Disclosures: E. Ginzler, Aurinia Pharma; A. Saxena, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Kezar Life Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS); V. Bal, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc.; V. Birardi, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals; H. Leher, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.

