Back
Poster Session B
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Session: (0913–0938) RA – Treatment Poster II
0932: Accelerated Waning of Protective Immunity After SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination in Patients Treated with Biological and Targeted Synthetic Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs
Sunday, November 13, 2022
9:00 AM – 10:30 AM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- ES
Elisabeth Simader, MD
Department of Rheumatology , Medical University of Vienna
Vienna, Austria
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Elisabeth Simader1, Selma Tobudic2, Thomas Deimel3, Peter mandl4, Helmuth Haslacher5, Thomas Perkmann5, Lisa Schneider6, Thomas Nothnagl7, Helga Radner1, Florian Winkler8, Heinz Burgmann8, Karin Stiasny9, Gottfried Novacek10, Walter Reinisch11, Daniel Aletaha12, Stefan Winkler2 and STEPHAN BLUEML1, 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine I, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 3Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 4Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine III, Medical University of Vienna, Wien, Austria, 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 6Department of Internal Medicine I, Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, 7Second Medical Department, Korneuburg-Stockerau Hospital, Lower Austrian Centre for Rheumatology, Stockerau, Austria, 8Department of Internal Medicine I, Division of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 9Center for Virology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 10Department of Internal Medicine III, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 11Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 12Medical University Vienna, Wien, Austria
Background/Purpose: Little is known about the duration of humoral antibody levels after two SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations in patients with immunosuppression. During this ongoing global epidemic, it is of essential interest to gather information about the time of protection after initial immunization in the vulnerable patients receiving either conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) or biological/ targeted drugs (b/tsDMARDs).
In this study we compared the antibody level development after vaccination and after six months in patients with inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and healthy controls. Furthermore, we assessed factors affecting the quality and quantity of the humoral response.
Methods: We enrolled 85 healthy controls (HC), 75 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis and 41 patients suffering from IBD. Patients treated with B-cell depleting therapies were excluded from this study. Binding antibody units were measured after vaccination and 6 or more months. Neutralizing antibodies were measured after 6 months. Multivariate regression analyses analyzing factors associated with low titers after 6 months was performed.
Results: We found that patients with inflammatory arthritis or IBD showed reduced anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers compared to HC. When we stratified for therapies, we found that patients receiving conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic dugs (csDMARDs) had comparable anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers to HC. In contrast, patients receiving biological or targeted synthetic (b/tsDMARDs) showed reduced anti-SARS-CoV-2 Igs as well as neutralizing antibody titers compared with healthy controls (HC) or patients receiving conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs. We further show that anti-SARS-CoV-2 titers declined more rapidly in patients receiving b/tsDMARDs compared to HC, leading to a 50 percent reduction in vaccination-associated protection time in patients receiving b/tsDMARDs when compared to those receiving csDMARDs or even HC. In multivariate regression analyses, we find that in addition to the type of treatment, also age as well as corticosteroid use were associated with reduced anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titer.
Conclusion: Patients under ongoing b/tsDMARDs therapy exposed an accelerated waning of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers and therefore decreased immunity and protection against severe Covid-19 infections over time. These results may lead to more personalized approaches for further vaccination strategies in this group of immunosuppressed patients.
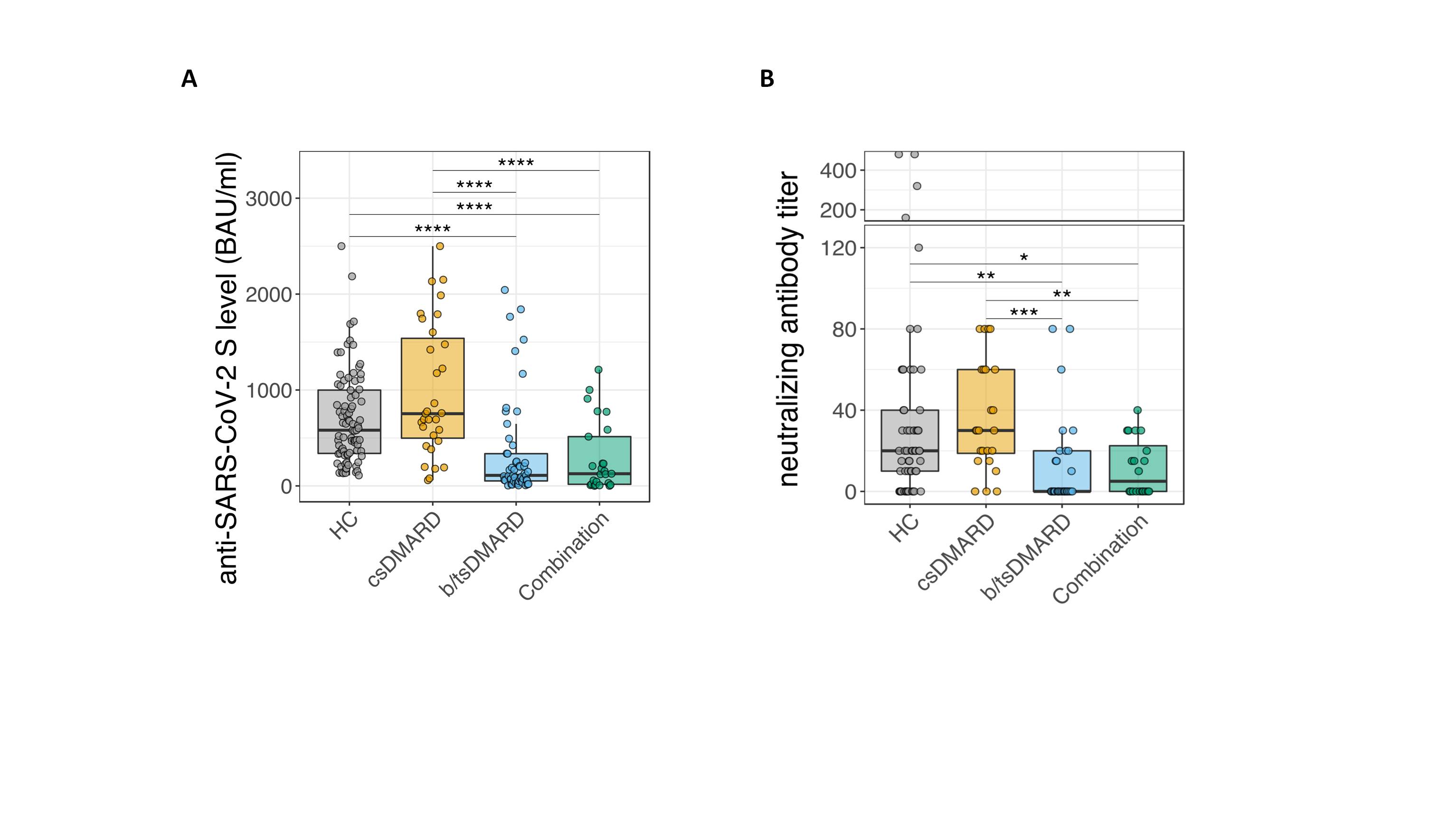 Figure 1: A, Analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers 6 months after the second vaccination in patients with inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and HC (** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.005, **** p ≤ 0.001). B, Quantification of neutralizing antibody activity in inflammatory arthritis patients, according to the given treatments.
Figure 1: A, Analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers 6 months after the second vaccination in patients with inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and HC (** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.005, **** p ≤ 0.001). B, Quantification of neutralizing antibody activity in inflammatory arthritis patients, according to the given treatments.
Disclosures: E. Simader, Boehringer-Ingelheim; S. Tobudic, None; T. Deimel, None; P. mandl, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Merck/MSD, Roche, UCB; H. Haslacher, Glock Health, BlueSky Immunotherapies, Neutrolis; T. Perkmann, None; L. Schneider, None; T. Nothnagl, None; H. Radner, None; F. Winkler, None; H. Burgmann, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Takeda, Gilead, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Shionogi, Valneva, MSD, Gilead; K. Stiasny, Pfizer; G. Novacek, None; W. Reinisch, Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, Aesca, Centocor, Falk Pharma GmbH, Immundiagnostik, Janssen, Sandoz, Takeda, Aptalis, Astellas, Celltrion, Danone Austria, Elan, Ferring, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Otsuka, PDL, Pharmacosmos, PLS Education, Schering-Plough, Shire, Therakos, Vifor, Yakult, Amgen, AM Pharma, AstraZeneca, Biogen IDEC, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Cellerix, Chemocentryx, Celgene, DSM, Galapagos, Genentech, Grünenthal, Inova, Johnson & Johnson, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Lipid Therapeutics, Millenium, Nestlé, Novartis, Ocera, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, Prometheus, Second Genome, Setpointmedical, Tigenix, UCB, Zealand, Zyngenia, 4SC, Algernon, AMT, AOP Orphan, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Avaxia, Roger Berger GmBH, Bioclinica, Covance, Eli Lilly, Ernest & Young, Gatehouse Bio Inc., Gilead, ICON, Index Pharma, Intrinsic Imaging, LivaNova, Mallinckrodt, Medahead, MedImmune, Nash Pharmaceuticals, Nippon Kayaku, OMass, Parexel, Periconsulting, Philip Morris Institute, Protagonist, Provention, Quell Therapeutics, Robarts Clinical Trial, Seres Therapeutics, Sigmoid, Sublimity, Theravance; D. Aletaha, Novartis, SoBi, Sanofi, Amgen, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Janssen, AbbVie; S. Winkler, None; S. BLUEML, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis.
Background/Purpose: Little is known about the duration of humoral antibody levels after two SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations in patients with immunosuppression. During this ongoing global epidemic, it is of essential interest to gather information about the time of protection after initial immunization in the vulnerable patients receiving either conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARD) or biological/ targeted drugs (b/tsDMARDs).
In this study we compared the antibody level development after vaccination and after six months in patients with inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and healthy controls. Furthermore, we assessed factors affecting the quality and quantity of the humoral response.
Methods: We enrolled 85 healthy controls (HC), 75 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis and 41 patients suffering from IBD. Patients treated with B-cell depleting therapies were excluded from this study. Binding antibody units were measured after vaccination and 6 or more months. Neutralizing antibodies were measured after 6 months. Multivariate regression analyses analyzing factors associated with low titers after 6 months was performed.
Results: We found that patients with inflammatory arthritis or IBD showed reduced anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers compared to HC. When we stratified for therapies, we found that patients receiving conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic dugs (csDMARDs) had comparable anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers to HC. In contrast, patients receiving biological or targeted synthetic (b/tsDMARDs) showed reduced anti-SARS-CoV-2 Igs as well as neutralizing antibody titers compared with healthy controls (HC) or patients receiving conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs. We further show that anti-SARS-CoV-2 titers declined more rapidly in patients receiving b/tsDMARDs compared to HC, leading to a 50 percent reduction in vaccination-associated protection time in patients receiving b/tsDMARDs when compared to those receiving csDMARDs or even HC. In multivariate regression analyses, we find that in addition to the type of treatment, also age as well as corticosteroid use were associated with reduced anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titer.
Conclusion: Patients under ongoing b/tsDMARDs therapy exposed an accelerated waning of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers and therefore decreased immunity and protection against severe Covid-19 infections over time. These results may lead to more personalized approaches for further vaccination strategies in this group of immunosuppressed patients.
 Figure 1: A, Analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers 6 months after the second vaccination in patients with inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and HC (** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.005, **** p ≤ 0.001). B, Quantification of neutralizing antibody activity in inflammatory arthritis patients, according to the given treatments.
Figure 1: A, Analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S titers 6 months after the second vaccination in patients with inflammatory arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and HC (** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.005, **** p ≤ 0.001). B, Quantification of neutralizing antibody activity in inflammatory arthritis patients, according to the given treatments.Disclosures: E. Simader, Boehringer-Ingelheim; S. Tobudic, None; T. Deimel, None; P. mandl, AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Merck/MSD, Roche, UCB; H. Haslacher, Glock Health, BlueSky Immunotherapies, Neutrolis; T. Perkmann, None; L. Schneider, None; T. Nothnagl, None; H. Radner, None; F. Winkler, None; H. Burgmann, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Takeda, Gilead, Merck/MSD, Pfizer, Shionogi, Valneva, MSD, Gilead; K. Stiasny, Pfizer; G. Novacek, None; W. Reinisch, Abbott Laboratories, AbbVie, Aesca, Centocor, Falk Pharma GmbH, Immundiagnostik, Janssen, Sandoz, Takeda, Aptalis, Astellas, Celltrion, Danone Austria, Elan, Ferring, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Otsuka, PDL, Pharmacosmos, PLS Education, Schering-Plough, Shire, Therakos, Vifor, Yakult, Amgen, AM Pharma, AstraZeneca, Biogen IDEC, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Cellerix, Chemocentryx, Celgene, DSM, Galapagos, Genentech, Grünenthal, Inova, Johnson & Johnson, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Lipid Therapeutics, Millenium, Nestlé, Novartis, Ocera, Pfizer, Procter & Gamble, Prometheus, Second Genome, Setpointmedical, Tigenix, UCB, Zealand, Zyngenia, 4SC, Algernon, AMT, AOP Orphan, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Avaxia, Roger Berger GmBH, Bioclinica, Covance, Eli Lilly, Ernest & Young, Gatehouse Bio Inc., Gilead, ICON, Index Pharma, Intrinsic Imaging, LivaNova, Mallinckrodt, Medahead, MedImmune, Nash Pharmaceuticals, Nippon Kayaku, OMass, Parexel, Periconsulting, Philip Morris Institute, Protagonist, Provention, Quell Therapeutics, Robarts Clinical Trial, Seres Therapeutics, Sigmoid, Sublimity, Theravance; D. Aletaha, Novartis, SoBi, Sanofi, Amgen, Lilly, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Janssen, AbbVie; S. Winkler, None; S. BLUEML, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis.

