Back
Poster Session D
Myopathic rheumatic diseases (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis)
Session: (1856–1887) Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster II
1856: Subclinical Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: A Cross-Sectional Study Evaluation by Computer Tomography Coronary Angiogram
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- TL
Tsz Ho Luk, MBBS
Kwong Wah Hospital
Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Tsz Ho Luk1, Weng Nga Lao1, Steve Pang1, Ho So2, Tak Lung Wong3 and Yan Ki Tang4, 1Kwong Wah Hospital, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 3KWH, Kowloon, Hong Kong, 4Kwong Wah Hospital, Hong Kong, China
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) poses elevated risk of cardiovascular event and mortality, similar to other autoimmune rheumatic diseases. With the use of computer tomography coronary angiogram (CTCA), this study aimed to examine the prevalence and risk factors of subclinical coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with IIM.
Methods: This was a single center, cross-sectional study. CTCA was performed to access the prevalence of CAD in IIM patients without cardiac symptoms, compared with age and sex matched control. Comparisons of traditional cardiovascular risk factors, myositis disease characteristics, medication usage, ejection fraction by echocardiogram between IIM patients with and without obstructive CAD were performed to identify the potential risk factors of obstructive CAD in IIM.
Results: Thirty IIM patients and thirty age, sex matched controls were recruited. The clinical characteristics of IIM patients were shown in Table 1. Prevalences of obstructive CAD and CAD in IIM (13.3%, 66.7% respectively) were significantly higher than control group (0%, 30% respectively, with p< 0.001). There was higher prevalence of mixed plaque in IIM than control (16.7% versus 0%, p=0.02). Diabetes mellitus [adjusted OR 34.5 (95% CI 2.35, 505.75), p=0.01] was found to be independent predictor of obstructive CAD. Age [adjusted coefficient 4.19 (95% CI 1.68, 6.71), p=0.02], maximum level of LDH (IU/L)/100 [adjusted coefficient 14.68 (95% CI 7.22, 22.12) , p< 0.001] and fasting glucose (mmol/L) [adjusted coefficient 48.55 (95% CI 7.61, 89.49), p=0.022] were found to be independently associated with coronary calcification score in IIM with CAD.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated an elevated risk of CAD compared with controls, with diabetes mellitus as a risk factor of developing obstructive CAD. Screening and aggressive treatment of cardiovascular risk factors in high risk IIM patients should be considered.
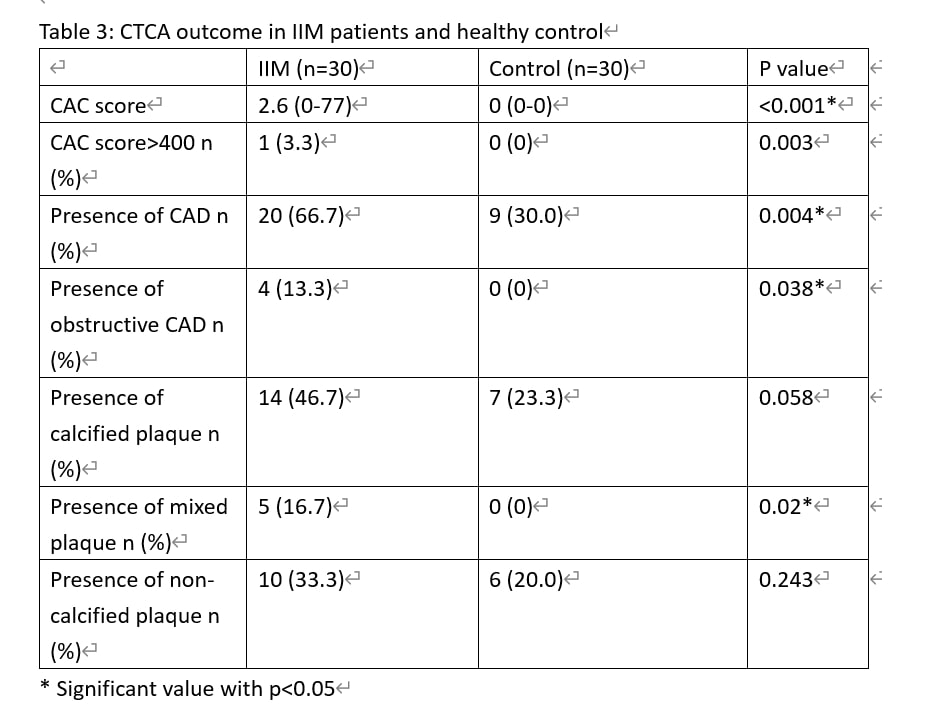 CTCA outcome in IIM and control
CTCA outcome in IIM and control
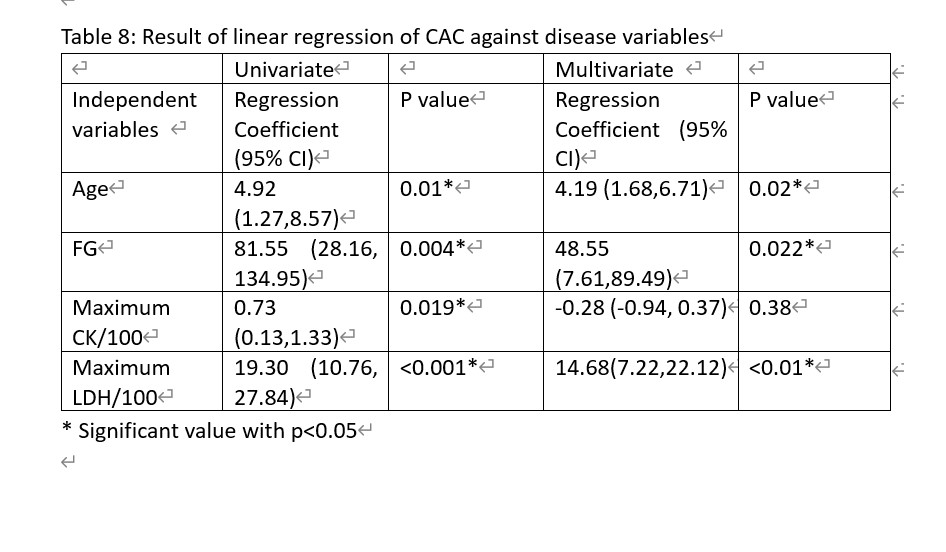 Result of linear regression of CAC against disease variable
Result of linear regression of CAC against disease variable
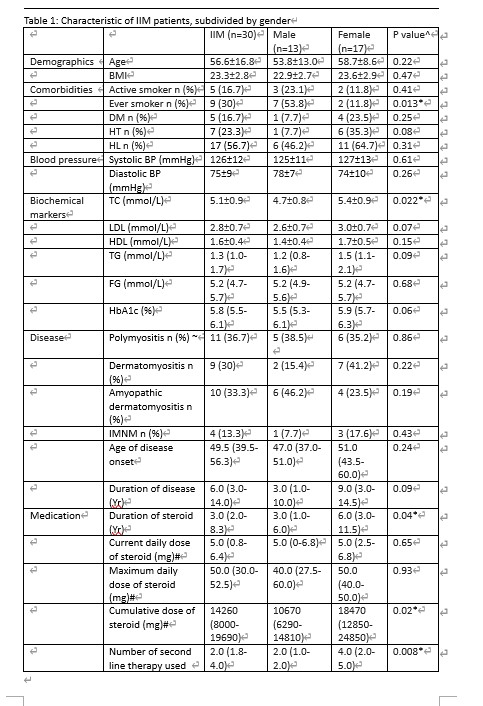 Characteristics of IIM patients
Characteristics of IIM patients
Disclosures: T. Luk, None; W. Lao, None; S. Pang, None; H. So, None; T. Wong, None; Y. Tang, None.
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) poses elevated risk of cardiovascular event and mortality, similar to other autoimmune rheumatic diseases. With the use of computer tomography coronary angiogram (CTCA), this study aimed to examine the prevalence and risk factors of subclinical coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with IIM.
Methods: This was a single center, cross-sectional study. CTCA was performed to access the prevalence of CAD in IIM patients without cardiac symptoms, compared with age and sex matched control. Comparisons of traditional cardiovascular risk factors, myositis disease characteristics, medication usage, ejection fraction by echocardiogram between IIM patients with and without obstructive CAD were performed to identify the potential risk factors of obstructive CAD in IIM.
Results: Thirty IIM patients and thirty age, sex matched controls were recruited. The clinical characteristics of IIM patients were shown in Table 1. Prevalences of obstructive CAD and CAD in IIM (13.3%, 66.7% respectively) were significantly higher than control group (0%, 30% respectively, with p< 0.001). There was higher prevalence of mixed plaque in IIM than control (16.7% versus 0%, p=0.02). Diabetes mellitus [adjusted OR 34.5 (95% CI 2.35, 505.75), p=0.01] was found to be independent predictor of obstructive CAD. Age [adjusted coefficient 4.19 (95% CI 1.68, 6.71), p=0.02], maximum level of LDH (IU/L)/100 [adjusted coefficient 14.68 (95% CI 7.22, 22.12) , p< 0.001] and fasting glucose (mmol/L) [adjusted coefficient 48.55 (95% CI 7.61, 89.49), p=0.022] were found to be independently associated with coronary calcification score in IIM with CAD.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated an elevated risk of CAD compared with controls, with diabetes mellitus as a risk factor of developing obstructive CAD. Screening and aggressive treatment of cardiovascular risk factors in high risk IIM patients should be considered.
 CTCA outcome in IIM and control
CTCA outcome in IIM and control Result of linear regression of CAC against disease variable
Result of linear regression of CAC against disease variable Characteristics of IIM patients
Characteristics of IIM patientsDisclosures: T. Luk, None; W. Lao, None; S. Pang, None; H. So, None; T. Wong, None; Y. Tang, None.

