Back
Poster Session D
Crystal arthropathies
Session: (1787–1829) Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies – Basic and Clinical Science Poster
1825: Vascular Calcifications Adjacent to the Involved Joint of Patients Diagnosed with Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystal Arthritis – a Retrospective Observational Study
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- SB
Shay Brikman, MD
Emek Medical Center
Afula, Israel
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Shay Brikman1, Amir Bieber2 and Reuven Mader1, 1Rheumatic Diseases Unit, Emek Medical Center, Afula, Israel, 2Emek Medical Center, Raanana, Israel
Background/Purpose: Prior studies have shown an association between chondrocalcinosis (CC) and vascular calcifications. In this study, we aimed to assess the presence of vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint seen on plain X-ray radiographs (XR) of patients diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystal arthritis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted assessing joint (knee, wrist) radiographs of patients with CPP crystal arthritis in an academic medical center from 2012 to 2022. All patients included were older than 60 years. Diagnosis of CPP crystal arthritis was considered if the patient had at least one previous acute synovitis with synovial fluid CPP crystals and/or CC and no other rheumatological inflammatory disease. A review of XR for vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint was performed by 2 independent observers. As control served a random sample of patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and no CC, matched for age and gender (1:1). The frequency of the presence of vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint was compared between the CPP and the control groups. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive likelihood ratio (LR) for CPP crystal arthritis based on the detection of XR vascular calcifications were calculated.
Results: 73 patients were included in the CPP crystal arthritis group and 73 patients in the control group. Vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint were seen in 52 patients in the CPP group and only in 13 patients in the control group (71.2% vs 17.8% respectively), which was significantly higher and suggests an association between CPP crystal arthritis and the presence of vascular calcifications on XR (Yates' correction for X2=40.04, P< 0.0001). According to our analysis, the addition of the presence of vascular calcifications on XR to the investigation of inflamed joints in patients between the age of 60-85 with CC seen in the involved joint yielded a high specificity of 0.86 and a positive LR of 4.78.
Conclusion: Vascular calcifications seen on XR adjacent to the involved joint were detected at a significantly higher frequency in patients with CPP crystal arthritis than in patients with OA. Investigation of synovitis and CC in older patients should include the assessment of joint XR for the appearance of vascular calcifications as it may be regarded as an important radiologic sign for CPP crystal arthritis.
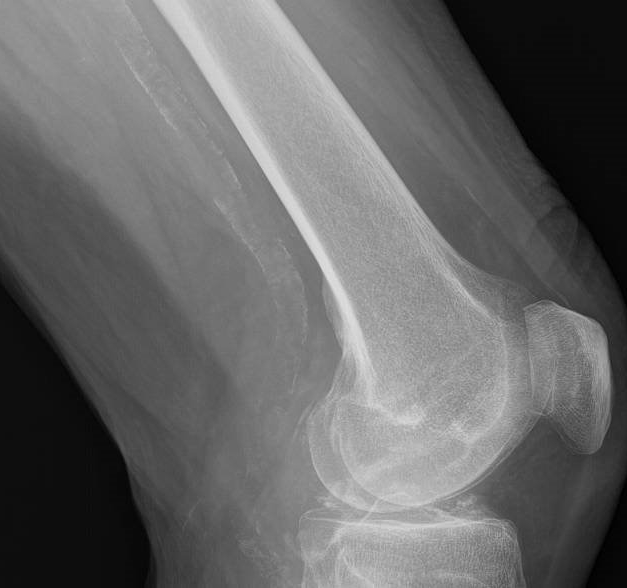 Knee X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications
Knee X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications
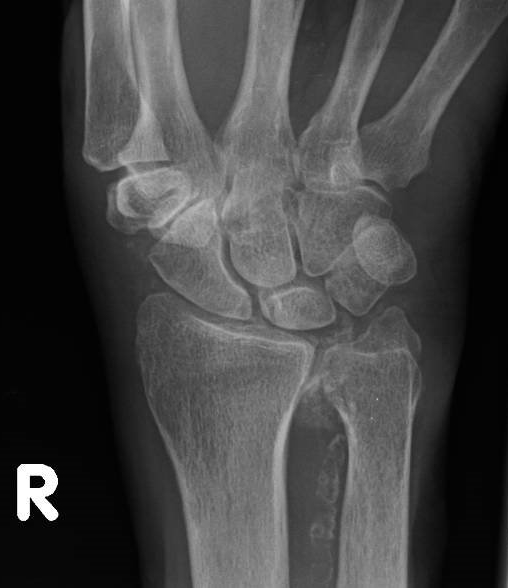 Wrist X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications
Wrist X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications
Disclosures: S. Brikman, None; A. Bieber, None; R. Mader, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Protalix.
Background/Purpose: Prior studies have shown an association between chondrocalcinosis (CC) and vascular calcifications. In this study, we aimed to assess the presence of vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint seen on plain X-ray radiographs (XR) of patients diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystal arthritis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted assessing joint (knee, wrist) radiographs of patients with CPP crystal arthritis in an academic medical center from 2012 to 2022. All patients included were older than 60 years. Diagnosis of CPP crystal arthritis was considered if the patient had at least one previous acute synovitis with synovial fluid CPP crystals and/or CC and no other rheumatological inflammatory disease. A review of XR for vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint was performed by 2 independent observers. As control served a random sample of patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and no CC, matched for age and gender (1:1). The frequency of the presence of vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint was compared between the CPP and the control groups. Sensitivity, specificity, and positive likelihood ratio (LR) for CPP crystal arthritis based on the detection of XR vascular calcifications were calculated.
Results: 73 patients were included in the CPP crystal arthritis group and 73 patients in the control group. Vascular calcifications adjacent to the involved joint were seen in 52 patients in the CPP group and only in 13 patients in the control group (71.2% vs 17.8% respectively), which was significantly higher and suggests an association between CPP crystal arthritis and the presence of vascular calcifications on XR (Yates' correction for X2=40.04, P< 0.0001). According to our analysis, the addition of the presence of vascular calcifications on XR to the investigation of inflamed joints in patients between the age of 60-85 with CC seen in the involved joint yielded a high specificity of 0.86 and a positive LR of 4.78.
Conclusion: Vascular calcifications seen on XR adjacent to the involved joint were detected at a significantly higher frequency in patients with CPP crystal arthritis than in patients with OA. Investigation of synovitis and CC in older patients should include the assessment of joint XR for the appearance of vascular calcifications as it may be regarded as an important radiologic sign for CPP crystal arthritis.
 Knee X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications
Knee X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications Wrist X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcifications
Wrist X-ray radiograph of a patient diagnosed with calcium pyrophosphate crystal arthritis showing vascular calcificationsDisclosures: S. Brikman, None; A. Bieber, None; R. Mader, AbbVie/Abbott, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), Protalix.

