Back
Poster Session C
Imaging
Session: (1228–1266) Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster
1237: Assessment of Common Femoral Vein Intima-Media Thickness by Ultrasound in Behçet’s Disease: Comparative Study of Patients with or Without Vascular Involvement in a National Referral Center
Sunday, November 13, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- BA
Belen Atienza-Mateo, MD, PhD
Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla
Santander, Cantabria, Spain
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Diana Prieto-Peña1, Alfonso del Peral-Fanjul2, Belén Atienza-Mateo1, Veronica Pulito-Cueto1, Miguel Ángel González-Gay3 and Ricardo Blanco4, 1Research Group on Genetic Epidemiology and Atherosclerosis in Systemic Diseases and in Metabolic Bone Diseases of the Musculoskeletal System, IDIVAL; and Department of Rheumatology, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, 2Research Group on Genetic Epidemiology and Atherosclerosis in Systemic Diseases and Metabolic Bone Diseases of the Musculoskeletal System, IDIVAL, Santander, Spain, Spain, 3Department of Medicine and Psychiatry, Universidad de Cantabria; Rheumatology Division, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla; Research group on genetic epidemiology and atherosclerosis in systemic diseases and in metabolic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, IDIVAL, Santander, Spain. Cardiovascular Pathophysiology and Genomics Research Unit, School of Physiology, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 4Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla, IDIVAL, Santander, Spain
Background/Purpose: Clinical vascular involvement is present in up to 40% of patients with Behçet’s disease (BD). Increased venous wall thickness assessed with ultrasound (US) has been reported in BD. However, it remains unclear if US findings correlate with vascular involvement in BD. Our aim was to assess vascular Doppler US findings in patients with BD with and without clinical vascular manifestations.
Methods: Observational study of unselected consecutive patients with BD assessed in a national referral center, from March 2021 to May 2021. All patients fulfilled the 2014 ICBD criteria. They were evaluated sequentially with a scheduled clinic visit after signing an informed consent Demographic and clinical variables were collected. Patients were considered to have vascular involvement if they had history of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary thromboembolism, superficial thrombophlebitis, arterial thrombosis (peripheral arterial thrombosis, stroke, transient ischemic attack), aneurysms, acute myocardial infarction or Raynaud’s disease. Wall thickness of bilateral common femoral vein was measured by assessing the intima-media thickness (IMT) with a high-resolution Doppler US. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS. Student´s t test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables, and Chi-squared test or Fisher´s exact test for categorical variables, as appropriate.
Results: We evaluated 17 BD patients with vascular manifestations and 25 BD patients without vascular manifestations. Main clinical and demographic characteristic are described in Table. The vascular manifestations were deep vein thrombosis (n=4), superficial thrombophlebitis (n=1), arterial aneurysms (n=2), acute myocardial infarction (n=3), arterial thrombosis (n=1) and Raynaud’s disease (n=10). The median [IQR] value of the common femoral vein IMT was significantly higher in patients with vascular manifestations (0.65 [0.45-0.82] vs 0.49 [0.39-0.55]; p= 0.028). A significant increase in vascular manifestations was observed in patients with arterial hypertension (p=0.003). HLA B51 presence was more frequent in patients with no vascular manifestations.
Conclusion: Patients with BD and vascular involvement present higher values of common femoral vein IMT. The assessment of venous wall thickness with Doppler US constitutes a useful technique to evaluate clinical vascular involvement in BD patients.
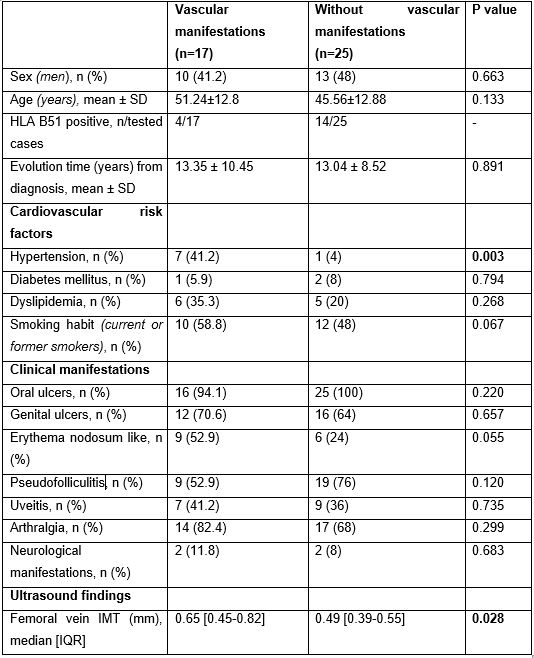 Table. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with Behçet’s disease with or without clinical vascular manifestations.
Table. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with Behçet’s disease with or without clinical vascular manifestations.
Disclosures: D. Prieto-Peña, UCB, Roche, Pfizer, Amgen, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, Eli Lilly; A. del Peral-Fanjul, None; B. Atienza-Mateo, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, Pfizer, Celgene, Novartis, Janssen, UCB, Eli Lilly; V. Pulito-Cueto, None; M. González-Gay, AbbVie/Abbott, Merck/MSD, Janssen, Roche, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Celgene, Sobi, Merck/MSD; R. Blanco, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Janssen, MSD, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Novartis, Sanofi.
Background/Purpose: Clinical vascular involvement is present in up to 40% of patients with Behçet’s disease (BD). Increased venous wall thickness assessed with ultrasound (US) has been reported in BD. However, it remains unclear if US findings correlate with vascular involvement in BD. Our aim was to assess vascular Doppler US findings in patients with BD with and without clinical vascular manifestations.
Methods: Observational study of unselected consecutive patients with BD assessed in a national referral center, from March 2021 to May 2021. All patients fulfilled the 2014 ICBD criteria. They were evaluated sequentially with a scheduled clinic visit after signing an informed consent Demographic and clinical variables were collected. Patients were considered to have vascular involvement if they had history of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary thromboembolism, superficial thrombophlebitis, arterial thrombosis (peripheral arterial thrombosis, stroke, transient ischemic attack), aneurysms, acute myocardial infarction or Raynaud’s disease. Wall thickness of bilateral common femoral vein was measured by assessing the intima-media thickness (IMT) with a high-resolution Doppler US. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS. Student´s t test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables, and Chi-squared test or Fisher´s exact test for categorical variables, as appropriate.
Results: We evaluated 17 BD patients with vascular manifestations and 25 BD patients without vascular manifestations. Main clinical and demographic characteristic are described in Table. The vascular manifestations were deep vein thrombosis (n=4), superficial thrombophlebitis (n=1), arterial aneurysms (n=2), acute myocardial infarction (n=3), arterial thrombosis (n=1) and Raynaud’s disease (n=10). The median [IQR] value of the common femoral vein IMT was significantly higher in patients with vascular manifestations (0.65 [0.45-0.82] vs 0.49 [0.39-0.55]; p= 0.028). A significant increase in vascular manifestations was observed in patients with arterial hypertension (p=0.003). HLA B51 presence was more frequent in patients with no vascular manifestations.
Conclusion: Patients with BD and vascular involvement present higher values of common femoral vein IMT. The assessment of venous wall thickness with Doppler US constitutes a useful technique to evaluate clinical vascular involvement in BD patients.
 Table. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with Behçet’s disease with or without clinical vascular manifestations.
Table. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with Behçet’s disease with or without clinical vascular manifestations.Disclosures: D. Prieto-Peña, UCB, Roche, Pfizer, Amgen, Janssen, AbbVie/Abbott, Novartis, Eli Lilly; A. del Peral-Fanjul, None; B. Atienza-Mateo, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, Pfizer, Celgene, Novartis, Janssen, UCB, Eli Lilly; V. Pulito-Cueto, None; M. González-Gay, AbbVie/Abbott, Merck/MSD, Janssen, Roche, AbbVie/Abbott, Roche, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, Celgene, Sobi, Merck/MSD; R. Blanco, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, Janssen, MSD, AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Novartis, Sanofi.

