Back
Poster Session D
Epidemiology, health policy and outcomes
Session: (1750–1786) Epidemiology and Public Health Poster III
1776: COVID-19 Cases in Patients Treated with Secukinumab: Analysis from the Global Safety Database
Monday, November 14, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
.png)
Atul Deodhar, MD
Professor of Medicine, Division of Arthritis and Rheumatic Diseases, School of Medicine
Oregon Health & Science University
Portland, OR, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Atul Deodhar1, Andrew Blauvelt2, Philip J Mease3, Effie Pournara4, Piotr Jagiello4, Weibin Bao5 and Abhishek Sharma6, 1Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR, USA, Portland, OR, 2Oregon Medical Research Center, Portland, OR, USA, Portland, OR, 3Swedish Medical Center/Providence St. Joseph Health, Seattle, WA, 4Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland, 5Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, NJ, 6Novartis Healthcare Pvt. Ltd, Hyderabad, India
Background/Purpose: Although patients (pts) with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases who are taking immunosuppressive therapies are not at a significantly greater risk of SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) infection, the reported risk of severe unfavorable outcome or sequalae varies among studies1,2. As specific data in pts treated with secukinumab are lacking, we analyzed the outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in pts with psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), or ankylosing spondylitis (AS) treated with secukinumab by using the Novartis global safety database.
Methods: The Novartis global safety database was searched for cases reporting COVID-19 in pts receiving secukinumab. Cases reported from clinical trials or post-marketing surveillance between December 2019 and February 2022 were included in the analysis. Potential associations between subgroups (e.g., age, sex, treatment indication) and COVID-19 seriousness or outcomes were examined using Chi-squared testing. P-values were nominal for these exploratory analyses.
Results: As few clinical trials with secukinumab were ongoing, only 8 cases of COVID-19 were reported. All of the cases were hospitalized, and none were suspected to be study drug-related; 7 recovered completely and 1 recovered with sequelae. There were 2948 COVID-19 cases reported from post-marketing surveillance (PsO: N=1126; PsA: N=942; AS: N=469); a higher proportion of pts with AS were younger (43% less than 45 years) compared with pts with PsO or PsA (Table 1). The majority (71.7%) of the cases were not serious. Older age and male sex were associated with COVID-19 seriousness (P< 0.0001 and P=0.0001, respectively; Table 2). Furthermore, pts with AS were less likely to have serious COVID-19 than pts with PsO or PsA (PsO [n=363/1126, 32.2%] vs PsA [n=257/942, 27.3%] vs AS [n=107/469, 22.8%]), potentially due to the younger age in the AS group.
Overall, 27.5% of the reported cases had a complete recovery, 1.6% of the cases were fatal, and for 52.3% the outcome was unknown. Older age and male sex were associated with worse COVID-19 outcome (P< 0.0001 and P=0.0183, respectively; Table 3). Fewer pts with AS had a fatal outcome than pts with PsO or PsA (PsO [n=18/1126, 1.6%] vs PsA [n=14/942, 1.5%] vs AS [n=4/469, 0.9%]), but fewer pts with AS made a complete recovery (PsO [n=390/1126, 34.6%] vs PsA [n=258/942, 27.4%] vs AS [n=114/469, 24.3%]).
Conclusion: This exploratory analysis reports COVID-19 cases in the Novartis global safety database for more than 2 years since the onset of the pandemic. Rates of hospitalization and death from COVID-19 in pts receiving secukinumab were generally in line with reports in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases3 and overall population.4 Consistent with published data, older age and male sex had negative impact on both the seriousness and outcome of COVID-19. Potential associations with underlying disease state warrant further investigation.
References
1. Veenstra J, et al. J Am Acad Derm. 2020;83(6):1696‒1703.
2. Mease PJ, et al. EULAR 2022; abstract OP0247.
3. Haberman R, et al. N Eng J Med. 2020;383:85‒88.
4. WHO. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19, 18 May. www.who.int.
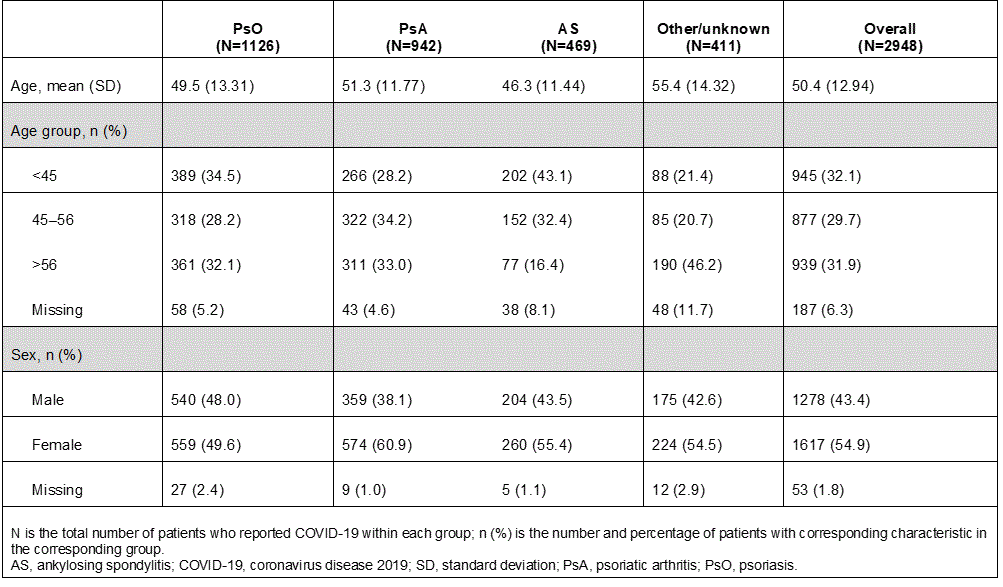 Table 1: Demographics of patients with COVID-19 by treatment indication from post-marketing surveillance of secukinumab
Table 1: Demographics of patients with COVID-19 by treatment indication from post-marketing surveillance of secukinumab
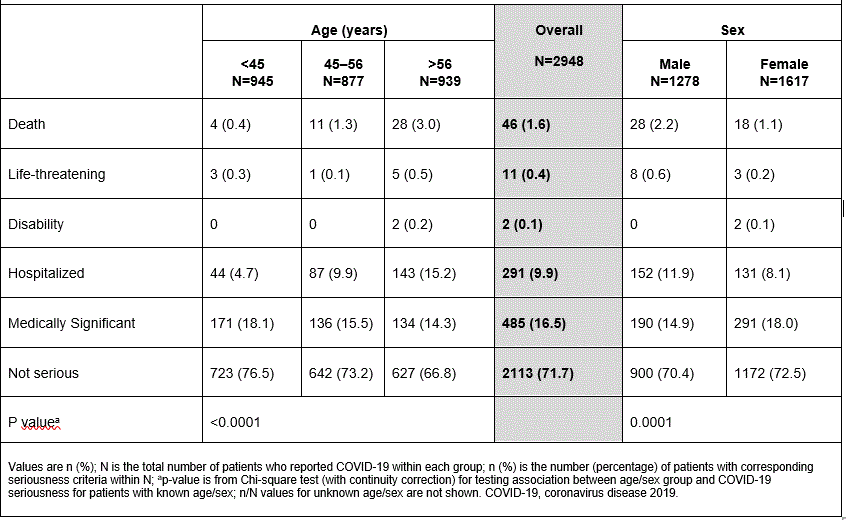 Table 2: Seriousness levels of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)
Table 2: Seriousness levels of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)
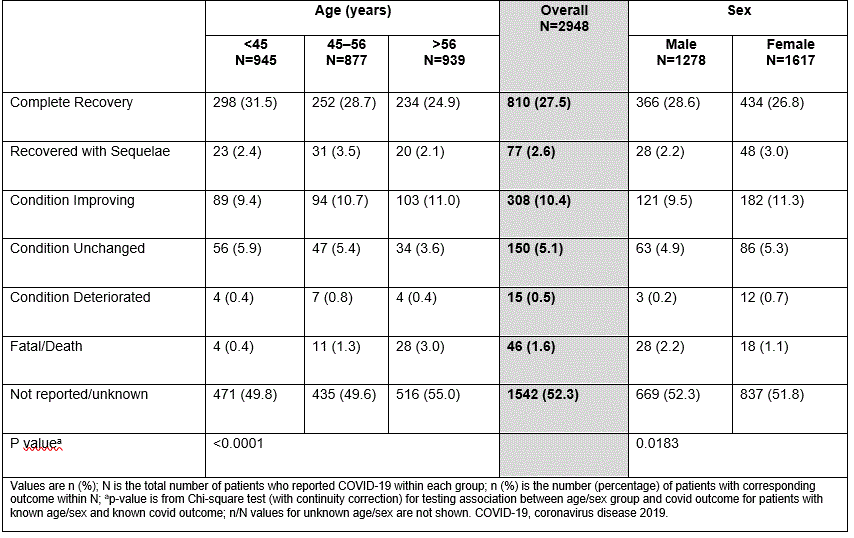 Table 3: Outcomes of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)
Table 3: Outcomes of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)
Disclosures: A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, Aurinia, Moonlake; A. Blauvelt, AbbVie, Abcentra, Aligos, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Arena, Aslan, Athenex, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Evommune, Forte, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Landos, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Rapt, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Sun Pharma, UCB Pharma, EcoR1, Vibliome; P. Mease, AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB, Sun Pharma, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Genentech; E. Pournara, Novartis; P. Jagiello, Novartis; W. Bao, Novartis; A. Sharma, Novartis.
Background/Purpose: Although patients (pts) with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases who are taking immunosuppressive therapies are not at a significantly greater risk of SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) infection, the reported risk of severe unfavorable outcome or sequalae varies among studies1,2. As specific data in pts treated with secukinumab are lacking, we analyzed the outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in pts with psoriasis (PsO), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), or ankylosing spondylitis (AS) treated with secukinumab by using the Novartis global safety database.
Methods: The Novartis global safety database was searched for cases reporting COVID-19 in pts receiving secukinumab. Cases reported from clinical trials or post-marketing surveillance between December 2019 and February 2022 were included in the analysis. Potential associations between subgroups (e.g., age, sex, treatment indication) and COVID-19 seriousness or outcomes were examined using Chi-squared testing. P-values were nominal for these exploratory analyses.
Results: As few clinical trials with secukinumab were ongoing, only 8 cases of COVID-19 were reported. All of the cases were hospitalized, and none were suspected to be study drug-related; 7 recovered completely and 1 recovered with sequelae. There were 2948 COVID-19 cases reported from post-marketing surveillance (PsO: N=1126; PsA: N=942; AS: N=469); a higher proportion of pts with AS were younger (43% less than 45 years) compared with pts with PsO or PsA (Table 1). The majority (71.7%) of the cases were not serious. Older age and male sex were associated with COVID-19 seriousness (P< 0.0001 and P=0.0001, respectively; Table 2). Furthermore, pts with AS were less likely to have serious COVID-19 than pts with PsO or PsA (PsO [n=363/1126, 32.2%] vs PsA [n=257/942, 27.3%] vs AS [n=107/469, 22.8%]), potentially due to the younger age in the AS group.
Overall, 27.5% of the reported cases had a complete recovery, 1.6% of the cases were fatal, and for 52.3% the outcome was unknown. Older age and male sex were associated with worse COVID-19 outcome (P< 0.0001 and P=0.0183, respectively; Table 3). Fewer pts with AS had a fatal outcome than pts with PsO or PsA (PsO [n=18/1126, 1.6%] vs PsA [n=14/942, 1.5%] vs AS [n=4/469, 0.9%]), but fewer pts with AS made a complete recovery (PsO [n=390/1126, 34.6%] vs PsA [n=258/942, 27.4%] vs AS [n=114/469, 24.3%]).
Conclusion: This exploratory analysis reports COVID-19 cases in the Novartis global safety database for more than 2 years since the onset of the pandemic. Rates of hospitalization and death from COVID-19 in pts receiving secukinumab were generally in line with reports in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases3 and overall population.4 Consistent with published data, older age and male sex had negative impact on both the seriousness and outcome of COVID-19. Potential associations with underlying disease state warrant further investigation.
References
1. Veenstra J, et al. J Am Acad Derm. 2020;83(6):1696‒1703.
2. Mease PJ, et al. EULAR 2022; abstract OP0247.
3. Haberman R, et al. N Eng J Med. 2020;383:85‒88.
4. WHO. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19, 18 May. www.who.int.
 Table 1: Demographics of patients with COVID-19 by treatment indication from post-marketing surveillance of secukinumab
Table 1: Demographics of patients with COVID-19 by treatment indication from post-marketing surveillance of secukinumab Table 2: Seriousness levels of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)
Table 2: Seriousness levels of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex) Table 3: Outcomes of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)
Table 3: Outcomes of COVID-19 cases from post-marketing surveillance (overall, by age and sex)Disclosures: A. Deodhar, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB Pharma, Aurinia, Moonlake; A. Blauvelt, AbbVie, Abcentra, Aligos, Almirall, Amgen, Arcutis, Arena, Aslan, Athenex, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dermavant, Eli Lilly, Evommune, Forte, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Landos, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Rapt, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Sun Pharma, UCB Pharma, EcoR1, Vibliome; P. Mease, AbbVie, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, UCB, Sun Pharma, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), Celgene, Genentech; E. Pournara, Novartis; P. Jagiello, Novartis; W. Bao, Novartis; A. Sharma, Novartis.

