Back
Poster Session A
Myopathic rheumatic diseases (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, inclusion body myositis)
Session: (0150–0180) Muscle Biology, Myositis and Myopathies Poster I
0161: Lenabasum, a Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor Agonist, Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Dermatomyositis in Th1 Cells
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall

DeAnna Diaz, MS
PCOM
Philadelphia, PA, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
DeAnna Diaz1, Thomas Vazquez2, Nilesh Kodali3, Madison Grinnell4, Emily Keyes4, Josh Dan4, Grant Sprow5, Muhammad Bashir6, Meena Sharma7 and Victoria Werth8, 1Philadelphia College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, 2FIU Wertheim College of Medicine, Virginia Beach, VA, 3New Jersey Medical School, Coppell, TX, 4Philadelphia VAMC, Philadelphia, PA, USA and Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, 5Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, 6University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 7Philadelphia VAMC, Philadelphia, PA, USA and Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 8University of Pennsylvania and Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease affecting the skin, muscle, and lungs. Lenabasum, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid type 2 receptor (CB2R) agonist, is currently being investigated as a non-immunosuppressive treatment option for DM. The activation of CB2R has been shown to reduce several key pro-inflammatory cytokines implicated in DM. Our lab has previously demonstrated via immunohistochemistry (IHC) that Lenabasum decreases CD4, IFNβ, IFNγ and IL31 expression in DM skin at 12 weeks (p< 0.05), with no differences in IL4 compared to placebo (p >0.05).
Methods: In this study, we utilized multiplexed flow cytometry on PBMCs and leukocytes eluted from DM skin to analyze the expression of CB2R on 12 cell lineages. When evaluating cell lineages, CD4 T helper (Th) subsets were gated on CD4+ IFNγ+ Th1 and CD4+IL4+ Th2. Using GraphPad prism V8.4.3, comparisons between CD4 T helper (Th) subsets were made with Students t-test and comparison of multiple groups were made by one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test. Twelve cell lineages were evaluated in PBMCs and eluted skin cells using FACS Symphony A3 Lite and analyzed with FlowJo V10.7.1. Imaging mass cytometry was used to confirm the source of key cytokines in lesional DM skin.
Results: There was a significantly higher frequency of parent (FOP) percentage of CB2R in Th1 (61.05%, n=6) versus Th2 cells (25.5%, n=6, p< 0.05) (Figure 1a and b). Among cell lineages, there was greater FOP of CB2R in M2 macrophages (CD68+CD163+), CD14++CD16++ macrophages, and monocyte derived dendritic cells (moDCs; CD11c+CD14+) (Figure 1c).
With 15umol of Lenabasum, there was a trend towards a decrease of: TNFα in M2 macrophages; IFNγ and IFNβ in CD4+ T cells; IFNβ in CD16+ cells; and IL31 in Th1 cells, CD14++CD16+ macrophages, and M2 macrophages. There was a significant decrease in moDCs and Th1 secreting IL31 with Lenabasum (p< 0.01) (Figure 2a, b and c). Imaging mass cytometry of untreated DM skin demonstrated the highest IL31 MPI in moDCs. IL31 was also elevated to a lesser extent in other myeloid cell lineages (Figure 3).
Conclusion: These data suggest there is an increase in CB2R expression on Th1 cells compared to Th2 cells. Lenabasum may exert specific anti-inflammatory effects in DM, particularly on Th1 cells and myeloid cell lineages such as moDCs. Lenabasum also suppressed Th1-derived IL31 and moDC-derived IL31, a cytokine implicated in the pruritus of DM.
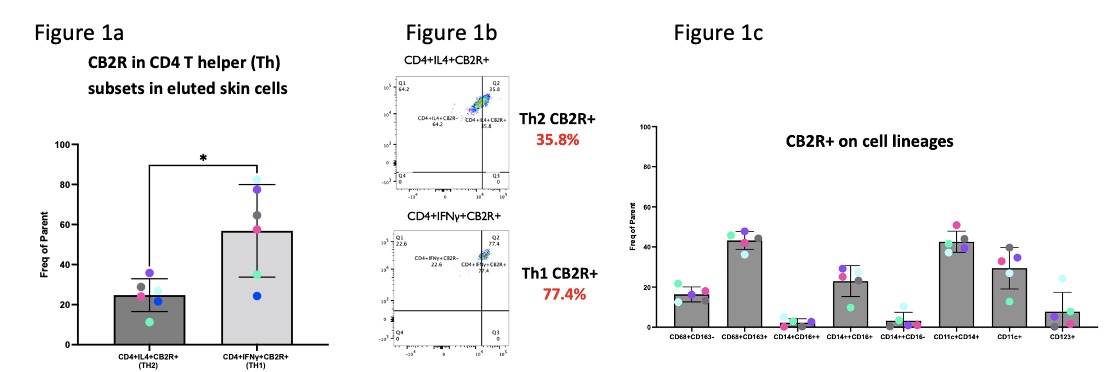 Figure 1. Flow cytometric analysis showing higher numbers of CB2R+ in CD4 T helper (Th) subsets and myeloid lineages in eluted skin cells
Figure 1. Flow cytometric analysis showing higher numbers of CB2R+ in CD4 T helper (Th) subsets and myeloid lineages in eluted skin cells
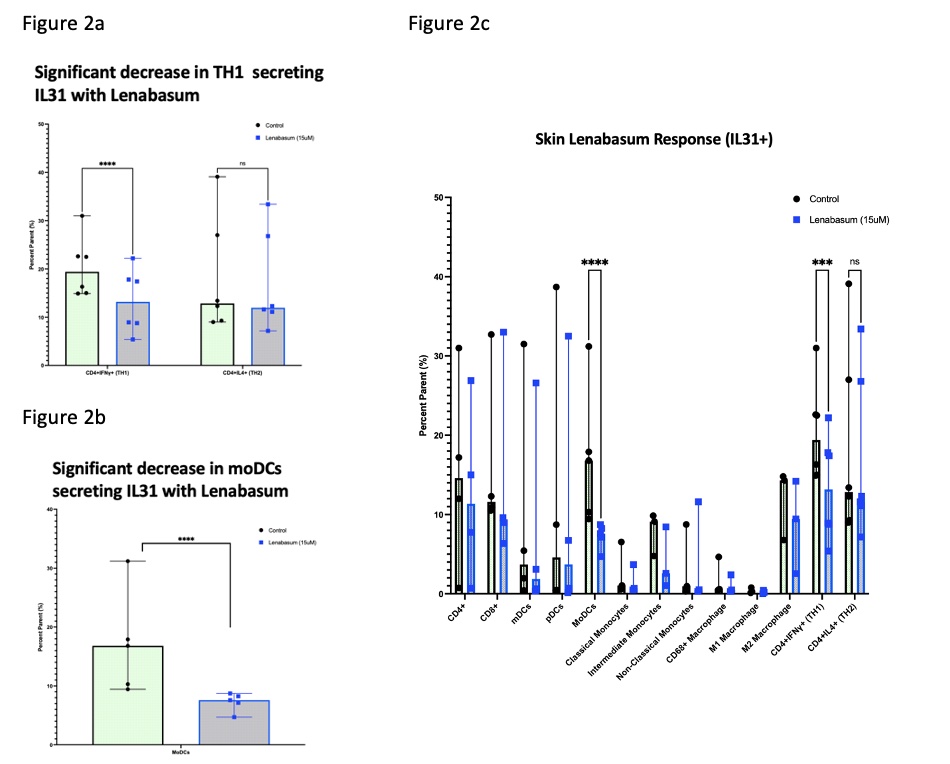 Figure 2. Significant decrease in Th1 and moDCs secreting IL31 with Lenabasum
Figure 2. Significant decrease in Th1 and moDCs secreting IL31 with Lenabasum
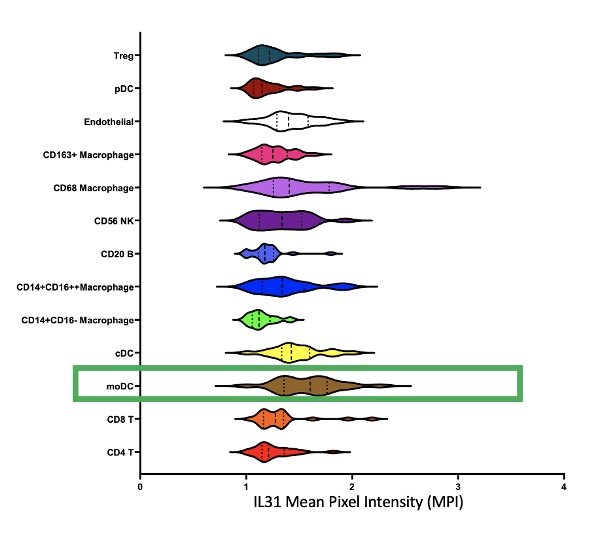 Figure 3. Imaging Mass Cytometry of DM skin
Figure 3. Imaging Mass Cytometry of DM skin
Disclosures: D. Diaz, None; T. Vazquez, None; N. Kodali, None; M. Grinnell, None; E. Keyes, None; J. Dan, None; G. Sprow, None; M. Bashir, None; M. Sharma, None; V. Werth, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Janssen, Merck/MSD, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Rome Pharmaceuticals, Horizon Therapeutics, Regeneron, argenx, CSL Behring, AnaptysBio, Biogen, Corbus, EMD Serono, Galderma, Nektar, Octapharma, Principia, Resolve, Sanofi, Syntimmune, Viela.
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease affecting the skin, muscle, and lungs. Lenabasum, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid type 2 receptor (CB2R) agonist, is currently being investigated as a non-immunosuppressive treatment option for DM. The activation of CB2R has been shown to reduce several key pro-inflammatory cytokines implicated in DM. Our lab has previously demonstrated via immunohistochemistry (IHC) that Lenabasum decreases CD4, IFNβ, IFNγ and IL31 expression in DM skin at 12 weeks (p< 0.05), with no differences in IL4 compared to placebo (p >0.05).
Methods: In this study, we utilized multiplexed flow cytometry on PBMCs and leukocytes eluted from DM skin to analyze the expression of CB2R on 12 cell lineages. When evaluating cell lineages, CD4 T helper (Th) subsets were gated on CD4+ IFNγ+ Th1 and CD4+IL4+ Th2. Using GraphPad prism V8.4.3, comparisons between CD4 T helper (Th) subsets were made with Students t-test and comparison of multiple groups were made by one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test. Twelve cell lineages were evaluated in PBMCs and eluted skin cells using FACS Symphony A3 Lite and analyzed with FlowJo V10.7.1. Imaging mass cytometry was used to confirm the source of key cytokines in lesional DM skin.
Results: There was a significantly higher frequency of parent (FOP) percentage of CB2R in Th1 (61.05%, n=6) versus Th2 cells (25.5%, n=6, p< 0.05) (Figure 1a and b). Among cell lineages, there was greater FOP of CB2R in M2 macrophages (CD68+CD163+), CD14++CD16++ macrophages, and monocyte derived dendritic cells (moDCs; CD11c+CD14+) (Figure 1c).
With 15umol of Lenabasum, there was a trend towards a decrease of: TNFα in M2 macrophages; IFNγ and IFNβ in CD4+ T cells; IFNβ in CD16+ cells; and IL31 in Th1 cells, CD14++CD16+ macrophages, and M2 macrophages. There was a significant decrease in moDCs and Th1 secreting IL31 with Lenabasum (p< 0.01) (Figure 2a, b and c). Imaging mass cytometry of untreated DM skin demonstrated the highest IL31 MPI in moDCs. IL31 was also elevated to a lesser extent in other myeloid cell lineages (Figure 3).
Conclusion: These data suggest there is an increase in CB2R expression on Th1 cells compared to Th2 cells. Lenabasum may exert specific anti-inflammatory effects in DM, particularly on Th1 cells and myeloid cell lineages such as moDCs. Lenabasum also suppressed Th1-derived IL31 and moDC-derived IL31, a cytokine implicated in the pruritus of DM.
 Figure 1. Flow cytometric analysis showing higher numbers of CB2R+ in CD4 T helper (Th) subsets and myeloid lineages in eluted skin cells
Figure 1. Flow cytometric analysis showing higher numbers of CB2R+ in CD4 T helper (Th) subsets and myeloid lineages in eluted skin cells Figure 2. Significant decrease in Th1 and moDCs secreting IL31 with Lenabasum
Figure 2. Significant decrease in Th1 and moDCs secreting IL31 with Lenabasum  Figure 3. Imaging Mass Cytometry of DM skin
Figure 3. Imaging Mass Cytometry of DM skinDisclosures: D. Diaz, None; T. Vazquez, None; N. Kodali, None; M. Grinnell, None; E. Keyes, None; J. Dan, None; G. Sprow, None; M. Bashir, None; M. Sharma, None; V. Werth, AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Janssen, Merck/MSD, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Rome Pharmaceuticals, Horizon Therapeutics, Regeneron, argenx, CSL Behring, AnaptysBio, Biogen, Corbus, EMD Serono, Galderma, Nektar, Octapharma, Principia, Resolve, Sanofi, Syntimmune, Viela.

