Back
Poster Session A
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Session: (0403–0431) Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: AxSpA
0405: Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis by Baseline BMI: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 2 and Phase 3 Trials
Saturday, November 12, 2022
1:00 PM – 3:00 PM Eastern Time
Location: Virtual Poster Hall
- HN
Hillary Norton, MD
Santa Fe Rheumatology
Santa Fe, NM, United States
Abstract Poster Presenter(s)
Hillary Norton1, Paula Sliwinska-Stanczyk2, Tomas Hala3, Bassel Elzorkany4, Lori Stockert5, Harry Shi5, Cunshan Wang6, Jerome Paulissen7 and Christopher Ritchlin8, 1Sante Fe Rheumatology, Santa Fe, NM, 2Reumatika Centrum Reumatologii, Warsaw, Poland, 3Center for Clinical and Basic Research, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 4Department of Rheumatology, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 5Pfizer, Inc, Collegeville, PA, 6Pfizer Inc, Groton, CT, 7Pfizer Inc, New York, NY, 8Allergy, Immunology and Rheumatology Division, University of Rochester Medical School, Canandaigua, NY
Background/Purpose: Higher BMI is associated with reduced response to TNF inhibitors (TNFi) in patients (pts) with AS.1 Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of AS.2 This post hoc analysis assessed the impact of baseline (BL) BMI on tofacitinib efficacy and safety in pts with AS.
Methods: Data were pooled from two placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind studies (16-week Phase [P]2 study: NCT017866683; 48-week P3 study: NCT035026162) in adult pts with active AS receiving ≥ 1 dose of tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily or PBO. Pts were analyzed by BL BMI: < 25 kg/m2, ≥ 25–< 30 kg/m2, or ≥ 30 kg/m2. Efficacy endpoints (full analysis set [FAS]) were assessed at Week (W)12 and included Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) 20%, ASAS40, AS Disease Activity Score(CRP) (ASDAS[CRP]), BASMI, BASDI, and total back pain scores. Safety outcomes (safety analysis set [SAS]) were assessed up to W16, which included adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), discontinuation due to AEs, and changes in laboratory parameters (liver function tests [LFTs] and lipid profile).
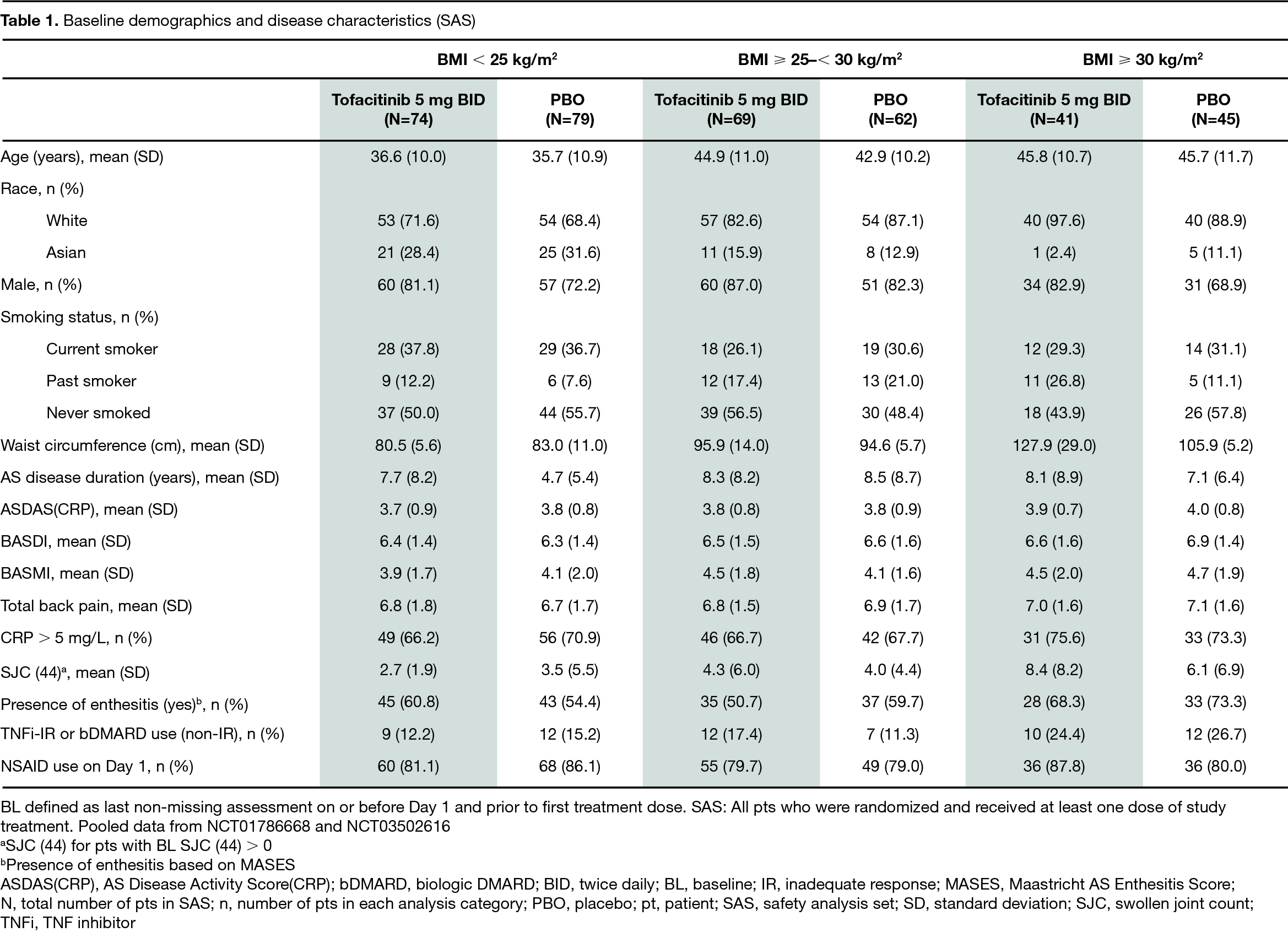
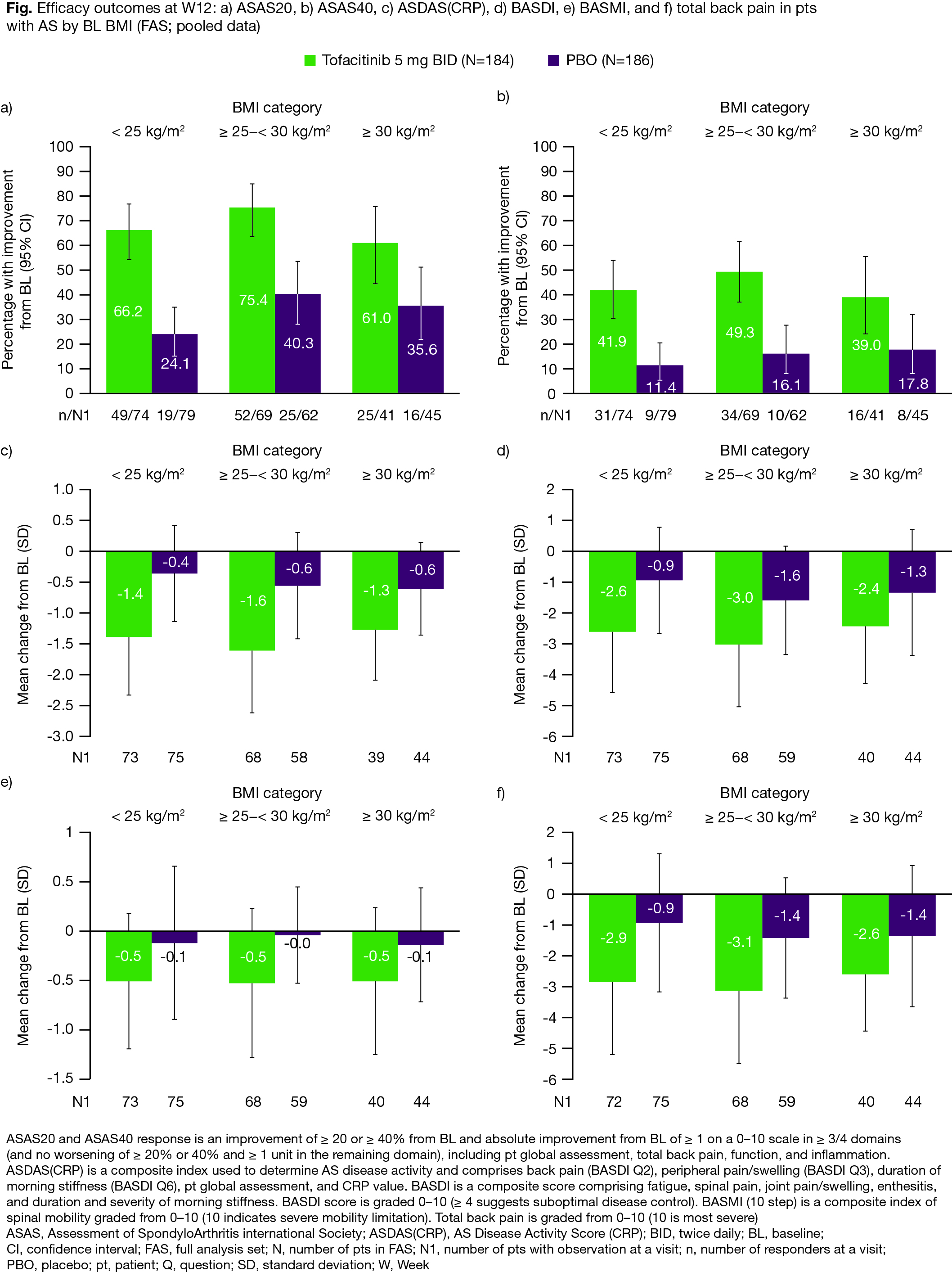
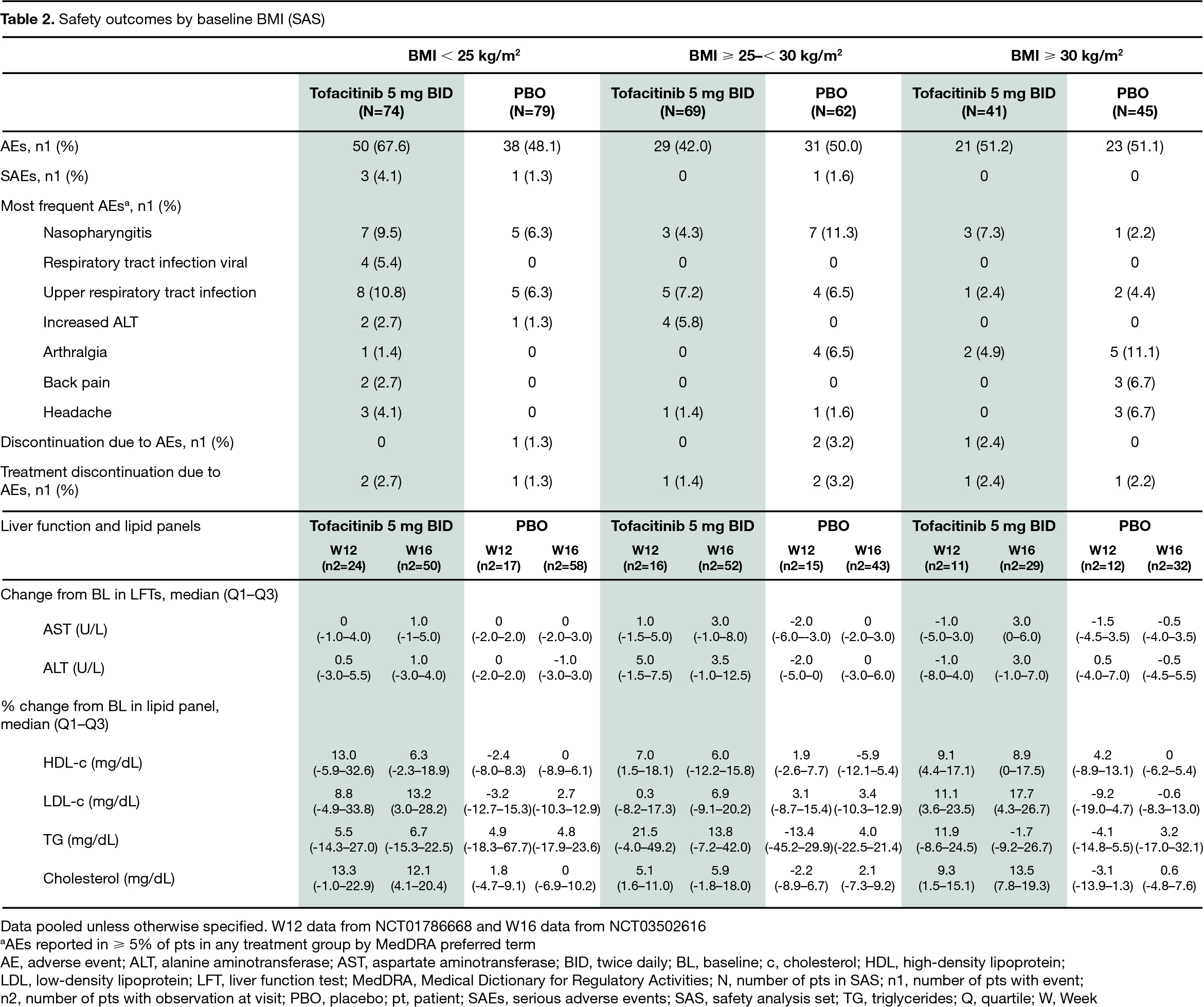
Results: The analysis included 370 pts in both the FAS and SAS. In the tofacitinib/PBO treatment groups, 40% (74/184)/42% (79/186) had BMI < 25 kg/m2, 38% (69/184)/33% (62/186) had BMI ≥ 25–< 30 kg/m2, and 22% (41/184)/24% (45/186) had BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. At BL, pts with a BMI ≥ 25–30 kg/m2 or ≥ 30 kg/m2 were generally older; pts with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 were more likely to have had prior TNFi inadequate response (IR) or biologic DMARD use (non-IR; P3 study only), enthesitis, and higher mean waist circumference and swollen joint count; pts with BMI < 25 kg/m2 were more likely to be current smokers (Table 1). At W12, regardless of BMI, efficacy was greater with tofacitinib compared with PBO; there was no indication of noticeable efficacy differences in pts treated with tofacitinib among the three BMI categories (Fig). AEs and SAEs were reported more frequently in pts with BMI < 25 kg/m2 receiving tofacitinib, compared with other BMI categories. The most frequent AEs (≥ 5% of pts in each treatment group) included nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and arthralgia (Table 2). Generally, change from BL in LFTs was similar, while % change from BL in lipid levels was higher, in tofacitinib vs PBO-treated pts; there were no meaningful differences across BMI categories in pts treated with tofacitinib (Table 2).
Conclusion: Regardless of BL BMI category, tofacitinib showed greater improvements in efficacy outcomes vs PBO in pts with AS; efficacy was comparable across BMI categories in pts treated with tofacitinib. Safety was generally similar across BMI categories in pts receiving tofacitinib; AEs and SAEs occurred more frequently in pts with BMI < 25 kg/m2, more than a third of whom were current smokers. This post hoc analysis was not powered for comparison of BMI categories and was limited by the small sample size within subgroups.
1. Wang et al. JAMA Netw Open 2022; 5: e222312
2. Deodhar et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80: 1004-13
3. van der Heijde et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76: 1340-7
Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by C Zauchenberger, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer Inc.
Disclosures: H. Norton, AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Horizon, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Scipher, UCB; P. Sliwinska-Stanczyk, None; T. Hala, None; B. Elzorkany, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eva, Hekma, Janssen, Eli Lilly, MSD, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Servier; L. Stockert, Pfizer Inc; H. Shi, Pfizer Inc; C. Wang, Pfizer Inc; J. Paulissen, Syneos Health, Pfizer Inc; C. Ritchlin, UCB, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer Inc, Novartis, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Background/Purpose: Higher BMI is associated with reduced response to TNF inhibitors (TNFi) in patients (pts) with AS.1 Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of AS.2 This post hoc analysis assessed the impact of baseline (BL) BMI on tofacitinib efficacy and safety in pts with AS.
Methods: Data were pooled from two placebo (PBO)-controlled, double-blind studies (16-week Phase [P]2 study: NCT017866683; 48-week P3 study: NCT035026162) in adult pts with active AS receiving ≥ 1 dose of tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily or PBO. Pts were analyzed by BL BMI: < 25 kg/m2, ≥ 25–< 30 kg/m2, or ≥ 30 kg/m2. Efficacy endpoints (full analysis set [FAS]) were assessed at Week (W)12 and included Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) 20%, ASAS40, AS Disease Activity Score(CRP) (ASDAS[CRP]), BASMI, BASDI, and total back pain scores. Safety outcomes (safety analysis set [SAS]) were assessed up to W16, which included adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), discontinuation due to AEs, and changes in laboratory parameters (liver function tests [LFTs] and lipid profile).
Results: The analysis included 370 pts in both the FAS and SAS. In the tofacitinib/PBO treatment groups, 40% (74/184)/42% (79/186) had BMI < 25 kg/m2, 38% (69/184)/33% (62/186) had BMI ≥ 25–< 30 kg/m2, and 22% (41/184)/24% (45/186) had BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. At BL, pts with a BMI ≥ 25–30 kg/m2 or ≥ 30 kg/m2 were generally older; pts with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 were more likely to have had prior TNFi inadequate response (IR) or biologic DMARD use (non-IR; P3 study only), enthesitis, and higher mean waist circumference and swollen joint count; pts with BMI < 25 kg/m2 were more likely to be current smokers (Table 1). At W12, regardless of BMI, efficacy was greater with tofacitinib compared with PBO; there was no indication of noticeable efficacy differences in pts treated with tofacitinib among the three BMI categories (Fig). AEs and SAEs were reported more frequently in pts with BMI < 25 kg/m2 receiving tofacitinib, compared with other BMI categories. The most frequent AEs (≥ 5% of pts in each treatment group) included nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and arthralgia (Table 2). Generally, change from BL in LFTs was similar, while % change from BL in lipid levels was higher, in tofacitinib vs PBO-treated pts; there were no meaningful differences across BMI categories in pts treated with tofacitinib (Table 2).
Conclusion: Regardless of BL BMI category, tofacitinib showed greater improvements in efficacy outcomes vs PBO in pts with AS; efficacy was comparable across BMI categories in pts treated with tofacitinib. Safety was generally similar across BMI categories in pts receiving tofacitinib; AEs and SAEs occurred more frequently in pts with BMI < 25 kg/m2, more than a third of whom were current smokers. This post hoc analysis was not powered for comparison of BMI categories and was limited by the small sample size within subgroups.
1. Wang et al. JAMA Netw Open 2022; 5: e222312
2. Deodhar et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2021; 80: 1004-13
3. van der Heijde et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76: 1340-7
Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by C Zauchenberger, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer Inc.



Disclosures: H. Norton, AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Horizon, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Scipher, UCB; P. Sliwinska-Stanczyk, None; T. Hala, None; B. Elzorkany, AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eva, Hekma, Janssen, Eli Lilly, MSD, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Servier; L. Stockert, Pfizer Inc; H. Shi, Pfizer Inc; C. Wang, Pfizer Inc; J. Paulissen, Syneos Health, Pfizer Inc; C. Ritchlin, UCB, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer Inc, Novartis, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb.

